Lipids (College Board AP® Biology): Study Guide
Structure & function in lipids
Lipids are macromolecules which contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms
They are typically nonpolar, hydrophobic molecules
One type of lipid is fatty acids
Fatty acids contain a methyl group at one end of a hydrocarbon chain (known as the R group) and at the other is a carboxyl group
The shorthand chemical formula for a fatty acid is RCOOH
Saturation
Fatty acids can vary in:
length of the hydrocarbon chain (R group)
saturation of the fatty acid chain (R group), which may be saturated or unsaturated
Differences in saturation determine the structure and function of lipids
Saturated fatty acids contain only single bonds between the carbon atoms
These chains are straight
Being straight means that the fatty acids can pack together tightly, and so these fats are solid at room temperature
E.g. butter
Unsaturated fatty acids contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond
These chains have a bend wherever a double bond is present
The bends in the chain prevent the fatty acids from packing together tightly
The more double bonds in a fatty acid, the more unsaturated the lipid becomes and therefore the more liquid it is at room temperature.
E.g. olive oil


Functions of lipids
Lipids are energy-dense and provide energy storage and support cell function
E.g. Thermal insulation from subcutaneous fat, such as whale blubber
Steroids are a class of lipids; they are hormones that support physiological functions, including growth and development, energy metabolism, and homeostasis
Another lipid is cholesterol which provides essential structural stability to animal cell membranes
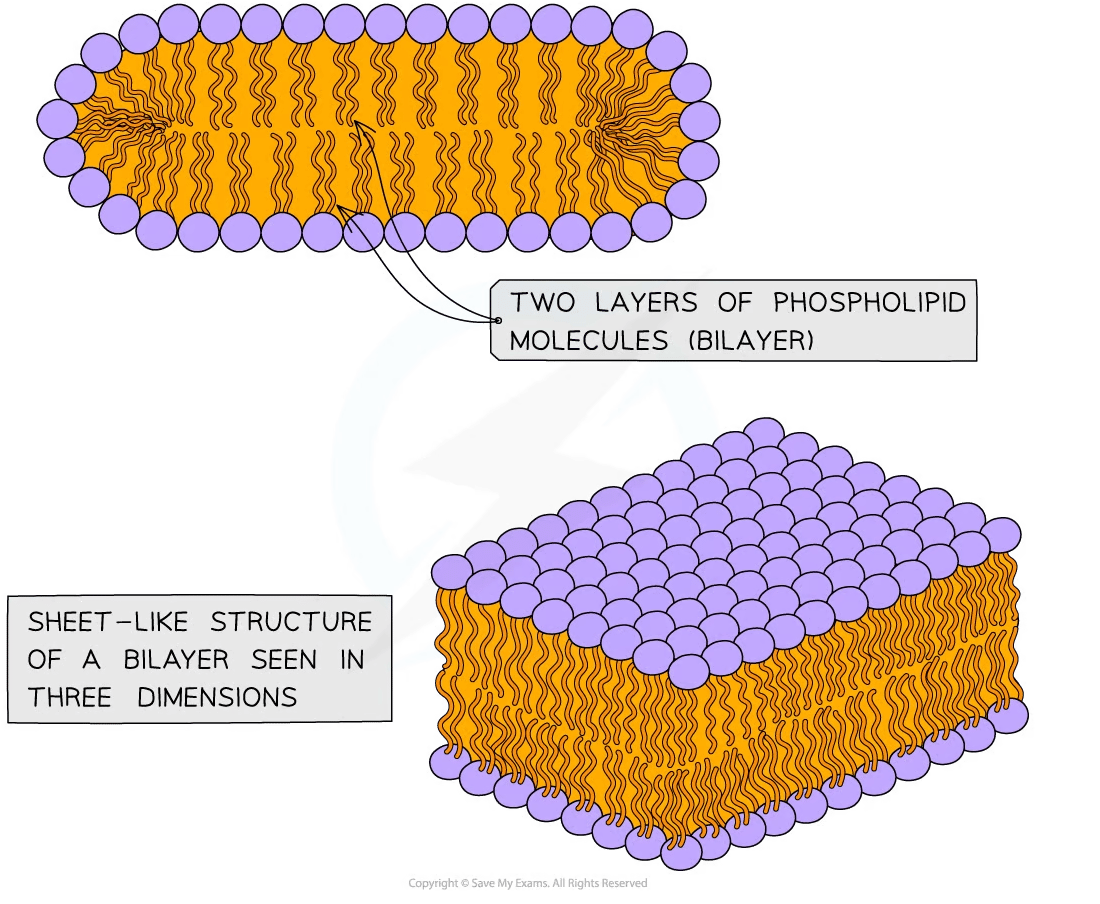
When fatty acids are combined with the monomer glycerol and a phosphate ion, they form phospholipids, which group together to form the lipid bilayers found in plasma and cell membranes
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Ensure that you are familiar with the structure of a triglyceride and that you can recognize whether the fatty acids are saturated or unsaturated. A saturated lipid is saturated with hydrogen atoms; it cannot contain more hydrogen atoms.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
