Subcellular Components (College Board AP® Biology): Study Guide
Cell structure & function
The structure and function of subcellular components and organelles contribute to the function of cells
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are found in all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic
This supports the view that all life forms share common ancestry
Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis; they bind to messenger RNA (mRNA) and synthesize proteins according to mRNA sequences
Within cells ribosomes are either:
free in the cytoplasm (all cells)
bound to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to form rough ER (only eukaryotic cells)
They are non-membrane structures, composed of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA)

Endomembrane system
The endomembrane system consists of a group of membrane-bound organelles and subcellular components
The components of the endomembrane system work together to modify, package, and transport polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins within the cell
The endomembrane system includes:
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Golgi complex
lysosomes
vacuoles
transport vesicles
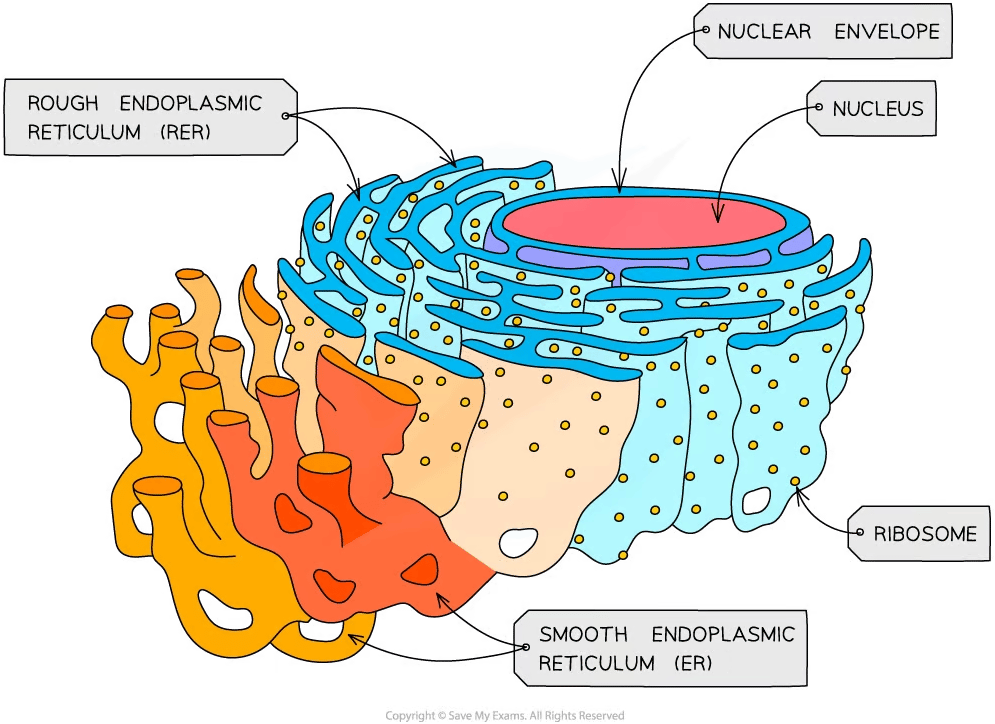
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of interconnected, membrane-bound sacs in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
The ER provides mechanical support by helping cells maintain shape, as well as playing a role in intracellular transport
There are two types of ER:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
The surface is studded with ribosomes
Formed from folds of membrane that are continuous with the nuclear envelope
Helps to compartmentalize the cell and is involved with protein synthesis
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Does not have ribosomes on the surface; its function is distinct from the RER
SER is involved in the detoxification of cells and lipid synthesis
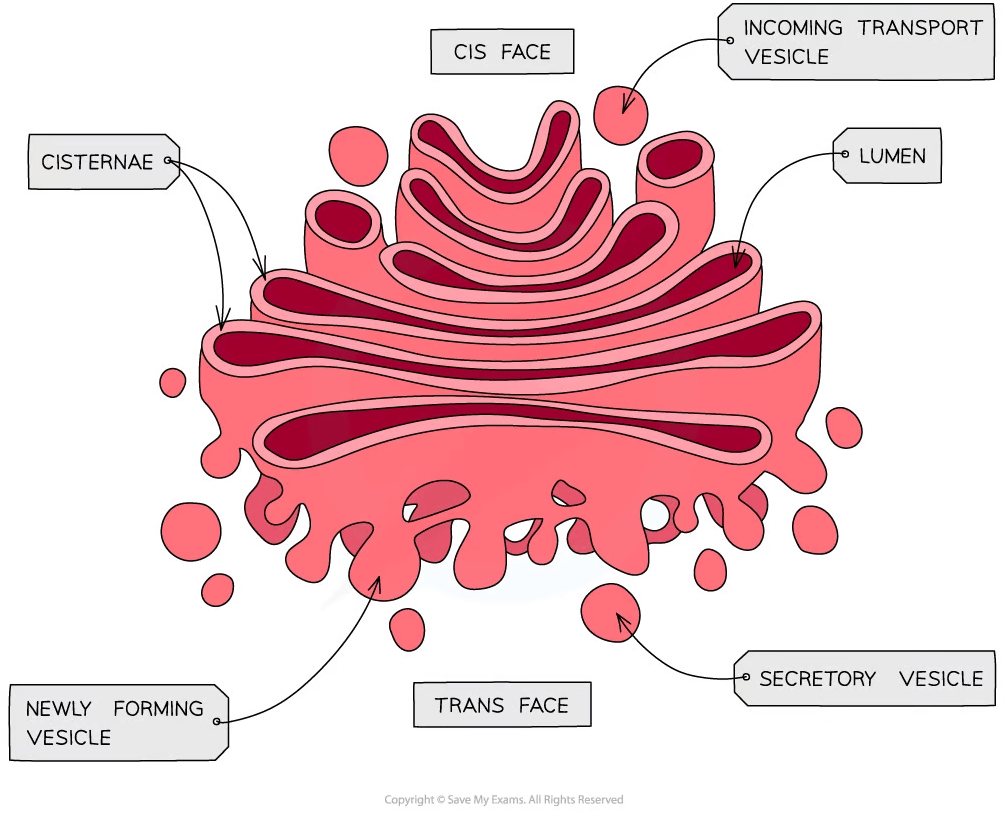
The Golgi complex
The Golgi complex is a membrane-bound structure that consists of a series of flattened membrane sacs called cisternae
Functions of the Golgi include:
correctly folding and chemically modifying newly synthesized cellular products transferred from the ER
packaging proteins for trafficking into vesicles which transport them around the cell
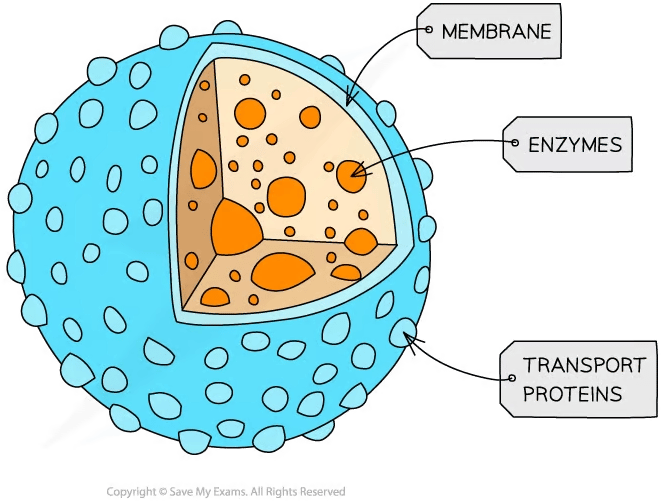
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed sacs which contain hydrolytic enzymes
They have three main roles:
breaking down cellular waste materials, e.g. worn-out organelles
destruction of pathogens
programmed cell death, known as apoptosis
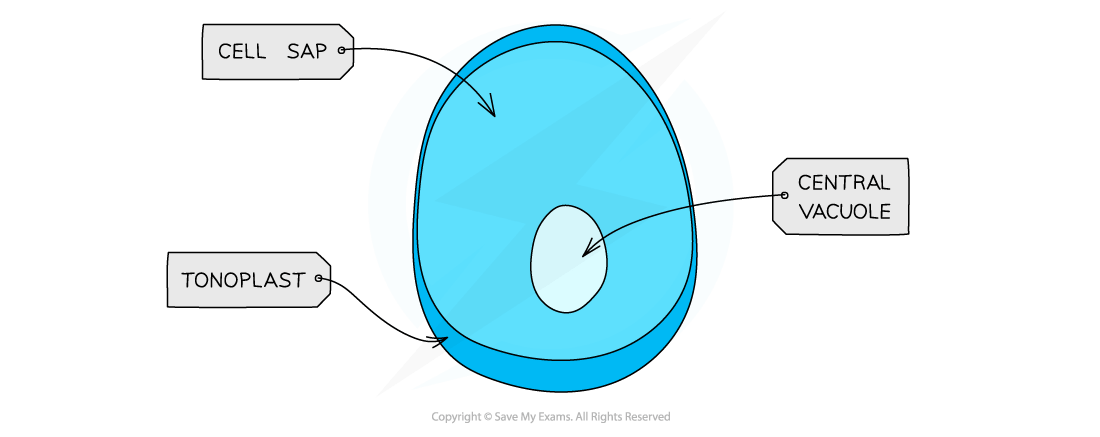
Vacuoles
A vacuole is a membrane-bound sac with contents that are chemically different to those of the cytoplasm
Vacuoles play different roles in different cell types
In plants cells permanent vacuoles store water, helping to maintain water balance and keeping the cell turgid by exerting pressure on the cell wall
In animal cells smaller, temporary vacuoles may store metabolites or transport substances
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is important to note that both lysosomes and vacuoles are bound by membranes that are selectively permeable. This enables cells to compartmentalize their contents effectively.
Mitochondria
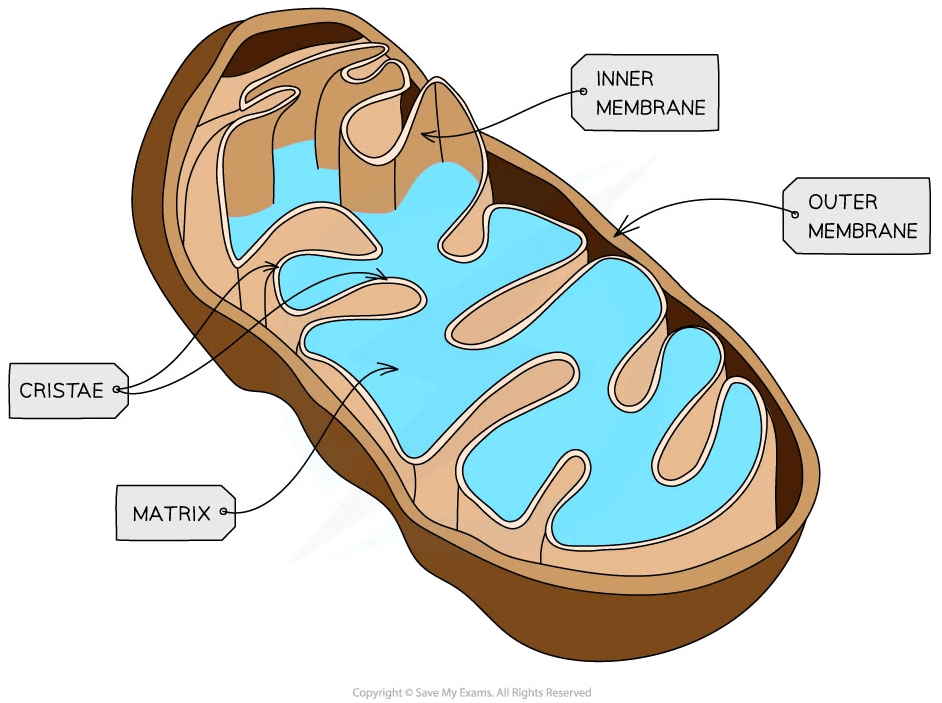
Mitochondria (singular mitochondrion) are membrane-bound organelles that provide compartments for the metabolic reactions of aerobic respiration within eukaryotic cells
A double membrane surrounds each mitochondrion
The outer membrane is smooth
The inner membrane is highly folded to form cristae
The folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane provide a large surface area that enables ATP to be synthesized efficiently during respiration
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are found in green plants and photosynthetic algae
They are also surrounded by a double membrane and are the site of photosynthesis
Membrane-bound compartments called thylakoids stack to form structures called grana
Thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for the reactions of photosynthesis

Examiner Tips and Tricks
The structures of mitochondria and chloroplasts resemble microorganisms in many ways. The topic of endosymbiosis puts forward a theory that these organelles originated from primitive microorganisms and became incorporated into larger, eukaryotic organisms; this theory is explored in more detail in Origins of Compartmentalization

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
