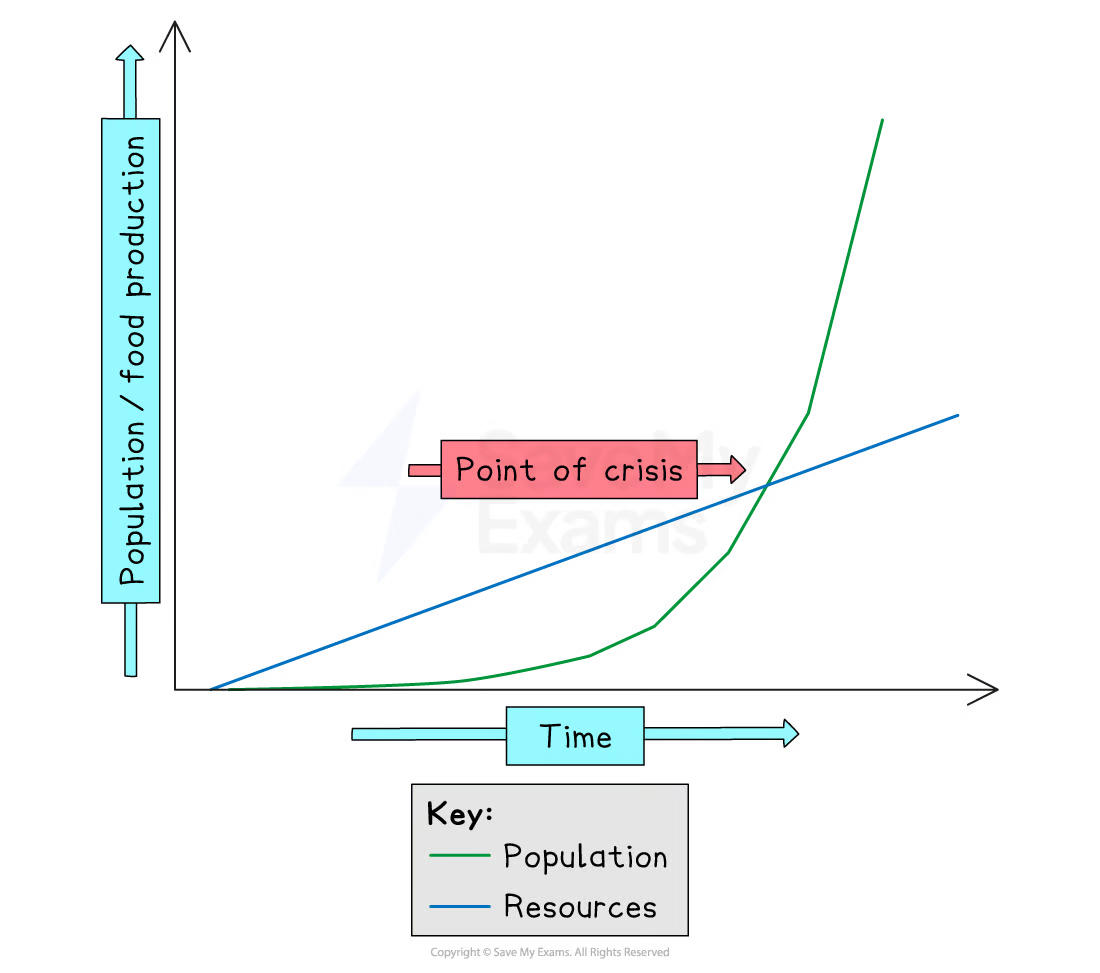
The Total Fertility Rate (TFR) helps Geographers assess annual population growth or decline.
Define the concept of the TFR.
Identify ONE weakness of using TFR as a measure of development.
Explain how education, particularly for women, impacts fertility rates.
Explain ONE economic factor that contributes to a declining fertility rate in developed countries.
Explain ONE social factor that contributes to a high fertility rate in less developed countries.
Identify a consequence of a rapidly declining fertility rate on a country’s population or economy.
Discuss ONE way that government policies can increase or decrease fertility rates. Use an example.
Was this exam question helpful?