The Photoelectric Effect (Edexcel AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 8PH0
The Photoelectric Effect
The photoelectric effect is the phenomena in which electrons are emitted from the surface of a metal upon the absorption of electromagnetic radiation
Electrons removed from a metal in this manner are known as photoelectrons
The photoelectric effect provides important evidence that light is quantised, or carried in discrete packets
This is shown by the fact each electron can absorb only a single photon
This means only the frequencies of light above a threshold frequency will emit a photoelectron
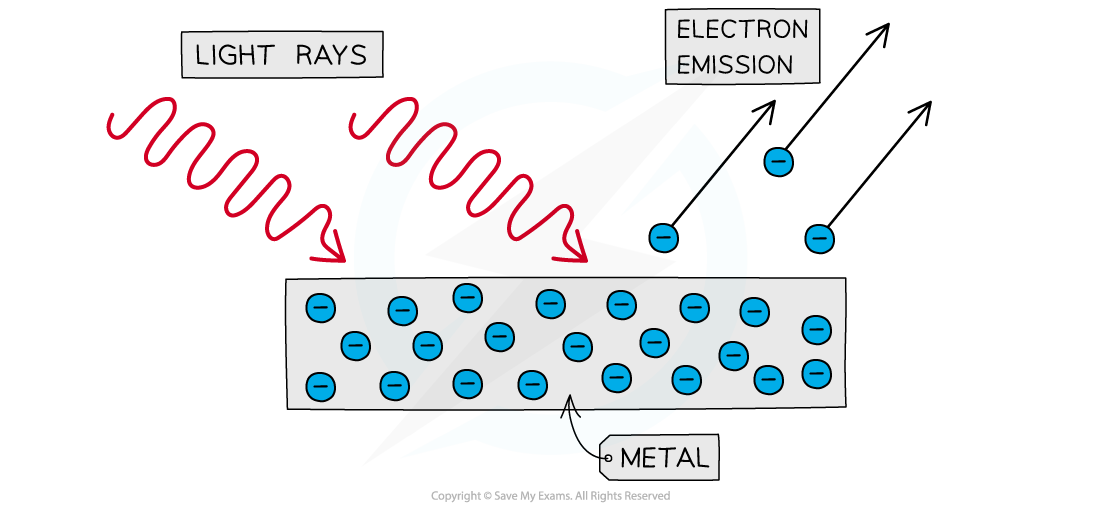
Photoelectrons are emitted from the surface of metal when light shines onto it
The photoelectric effect can be observed on a gold leaf electroscope
A plate of metal, usually zinc, is attached to a gold leaf, which initially has a negative charge, causing it to be repelled by a central negatively charged rod
This causes negative charge, or electrons, to build up on the zinc plate
UV light is shone onto the metal plate, leading to the emission of photoelectrons
This causes the extra electrons on the central rod and gold leaf to be removed, so, the gold leaf begins to fall back towards the central rod
This is because they become less negatively charged, and hence repel less


Typical set-up of the gold leaf electroscope experiment

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
