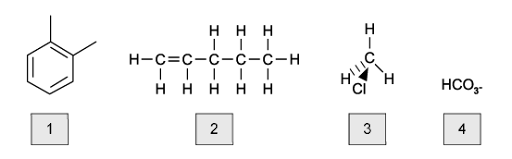
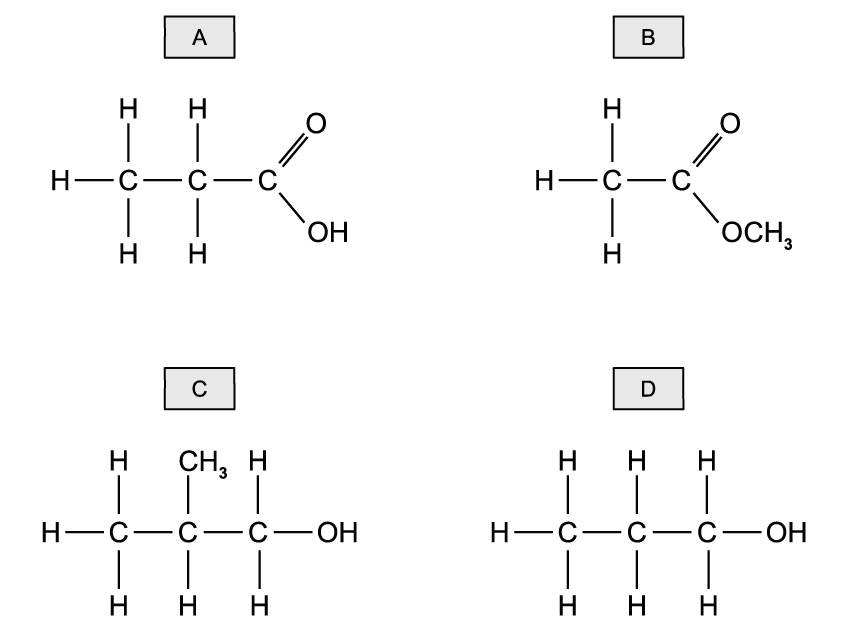
Which of the following shows the correct order of boiling points for pentane, butane and propane?
CH3CH2CH3 > CH3CH2CH2CH3 > CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 > CH3CH2CH2CH3 > CH3CH2CH3
CH3CH2CH2CH3 > CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 > CH3CH2CH3
CH3CH2CH3 > CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 > CH3CH2CH2CH3
Was this exam question helpful?

















![Chemical structure of bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane with two bromine atoms and eight hydrogen atoms attached, forming a bridged cyclic compound.](https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=3840/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2025/07/63796_httpscdn-savemyexams-comuploads2022078488cfbf-6f03-417e-97bc-3d9f4673afcc.jpeg)