Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2025
First exams 2027
Global pattern of development (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Geography): Revision Note
Exam code: 0460 & 0976
Specification link
This page covers section 8.2.2 of the CIE IGCSE specification. (opens in a new tab)
8.2.2 - The current global pattern of low-income countries (LICs), middle-income countries (MICs) and high-income countries (HICs).
Global pattern of development
All countries move through different stages of development; they are not in fixed categories
The UN identifies four main stages of development

Economic development is a constantly shifting process – countries can move up or down
The World Bank regularly revises income classifications based on updated GNI data
For example: China moved from LIC to MIC in under 40 years due to rapid industrialisation and trade integration
Low-income countries (LICs) and developing countries
The countries with the lowest level of development are the low-income countries (LICs) (e.g., Chad, Nepal)
Most people have a poor quality of life with inadequate services and few opportunities
The UN reviews the list of LICs every three years
There are currently 44 LICs (Dec. 2024)
Africa – 31 countries
Asia – 8 countries
Caribbean – 1 country
Small Island Developing States (SIDS) – 4 countries
The criteria for inclusion on the list of LICs are:
Gross National Income (GNI) below US$1,018
Poor health and education levels
Economic and environmental vulnerability
The LICs and developing countries are:
at a disadvantage in world trade
vulnerable to natural hazards
lacking infrastructure
dependent on primary resources
Colonialism has also impacted all 44 of the LICs and many developing countries, leading to:
depletion of resources
environmental degradation
Middle-income countries (MICs)
Middle-income countries (MICs) are also known as newly industrialised countries (NICs)
These countries are experiencing rapid economic growth and development based on industrial development
Incomes are rising and most people enjoy a reasonable standard of living
Countries that have become MICs include:
Singapore
South Korea
Brazil
China
India
High-income countries (HICs)
These countries have modern industries and people enjoy a good standard of living with relatively high levels of income
Good level of services
Countries that have become HICs include:
Norway
Saudi Arabia
Japan
Uruguay
Canada
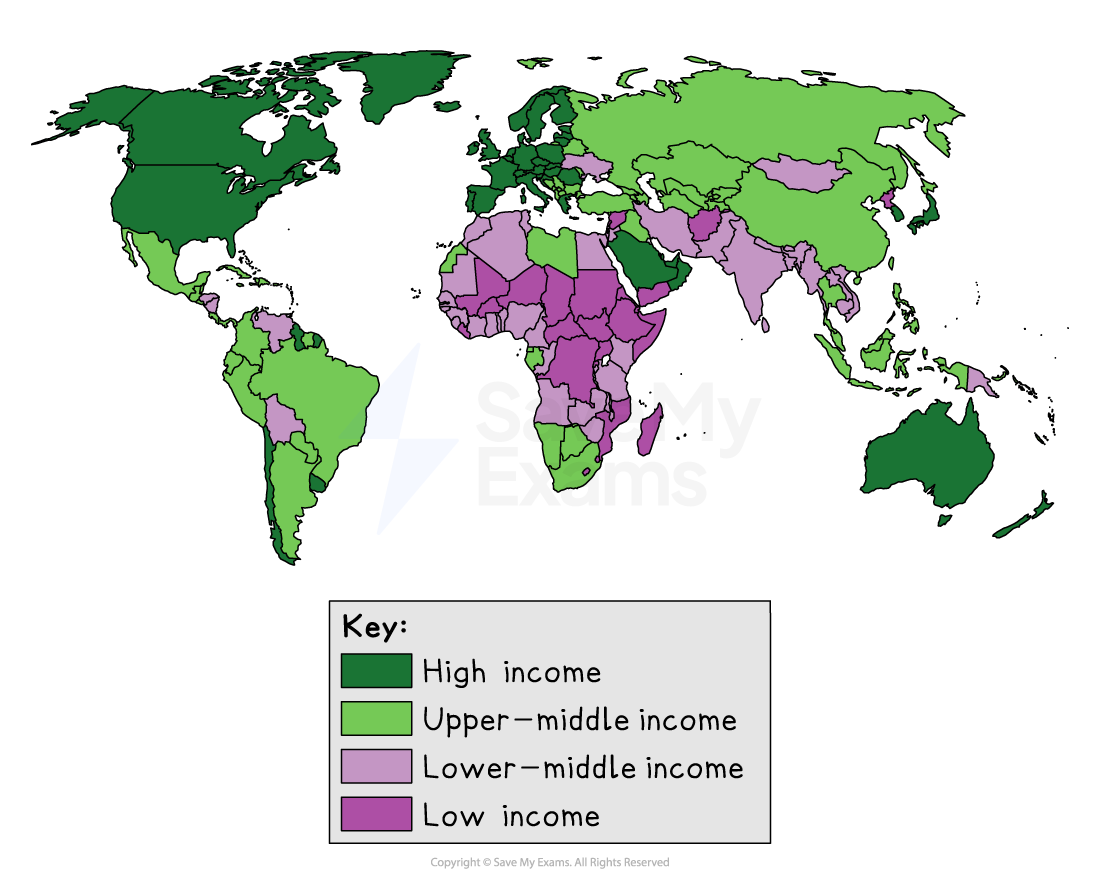
The global pattern of distribution is complicated and changes constantly
However, there are some key features
Asia and Africa have more MICs than LICs
Most HICs and MICs are found in the northern hemisphere
LICs are mostly in the southern hemisphere
Eastern European countries have been classified as MICs
Most South American countries are MICs
Why classifications are contested or dynamic
GNI per capita doesn’t tell the full story – it hides regional inequalities (e.g. urban vs. rural divide)
A country may be wealthy overall but still have large impoverished populations
Data reliability can vary – weak governance or poor census systems affect accuracy
Political sensitivity – calling a country an LIC can change how people see it and affect its chances for aid
Development is multi-dimensional – just because a place is rich doesn’t mean people are happy or the environment is strong
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Classifications can change, but issues like inequality, corruption, and environmental risks might remain.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
