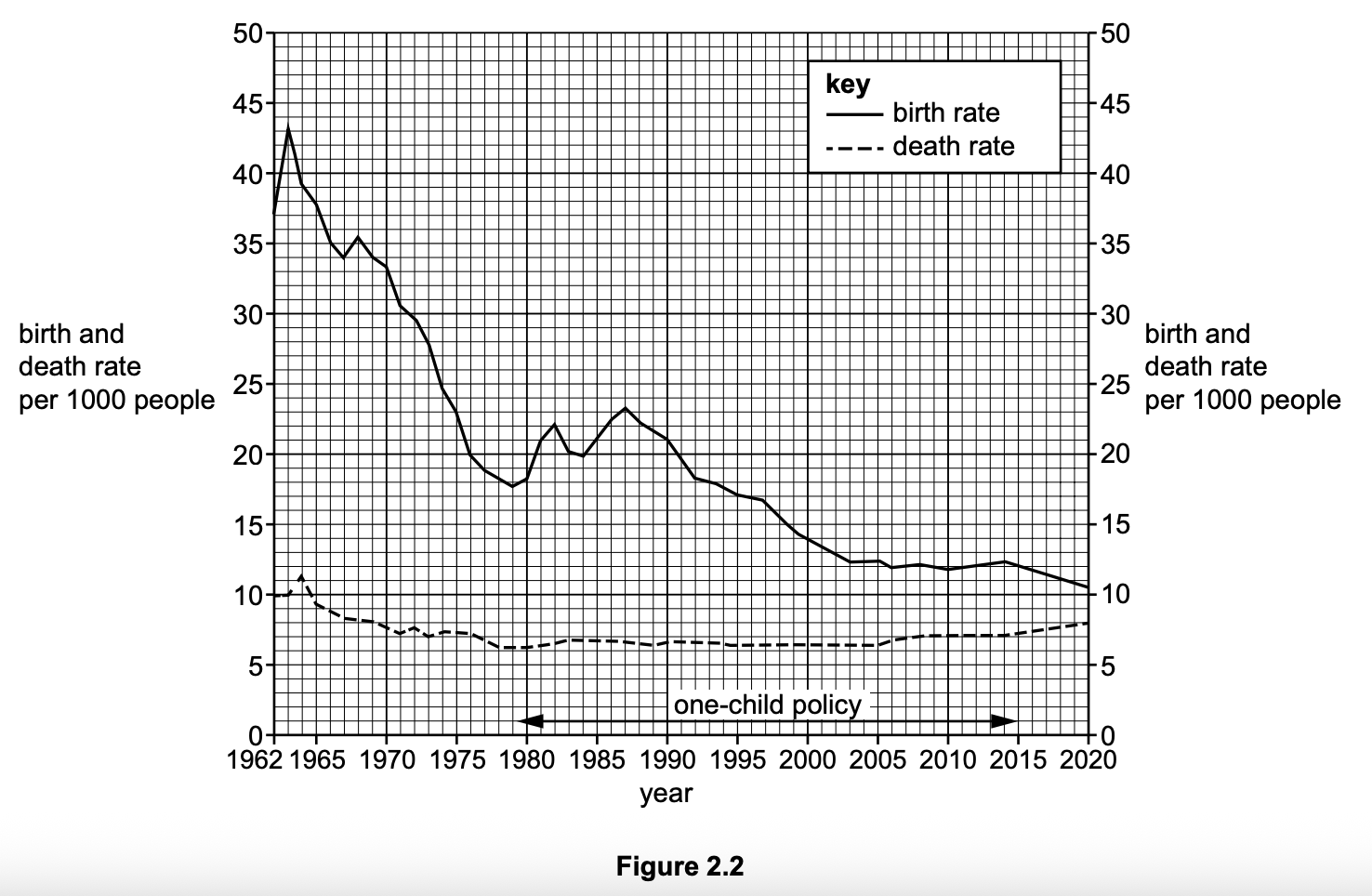
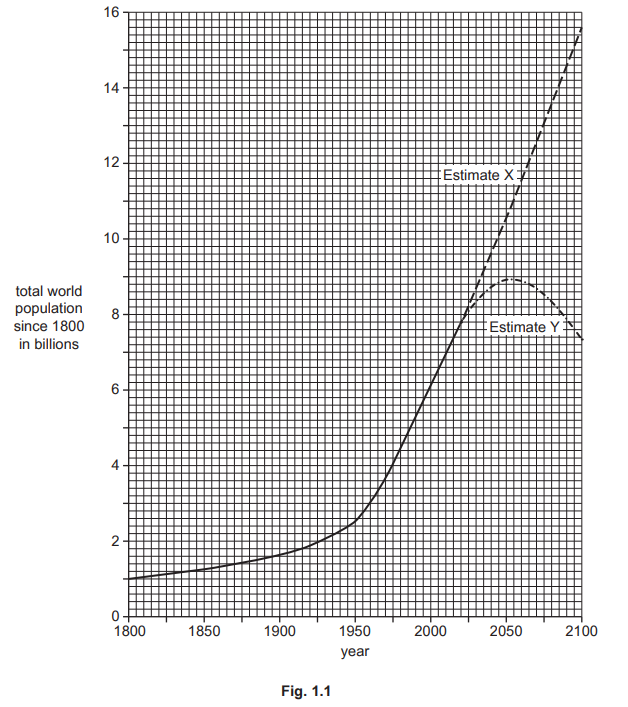
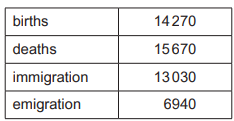
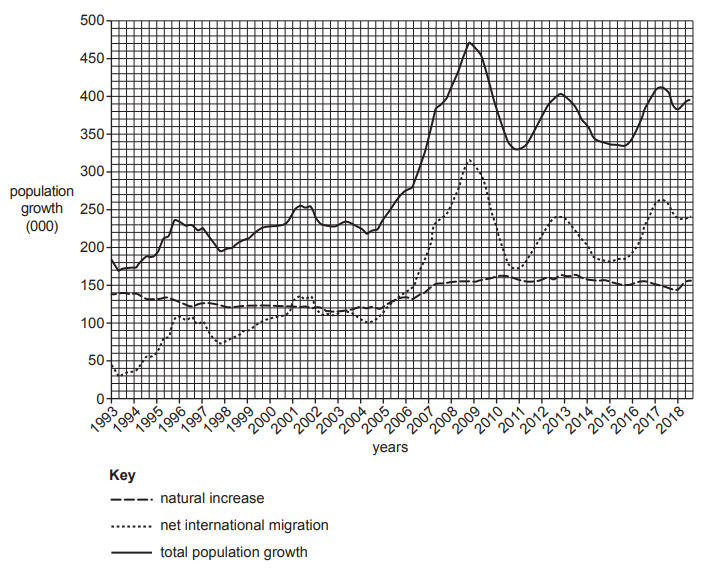
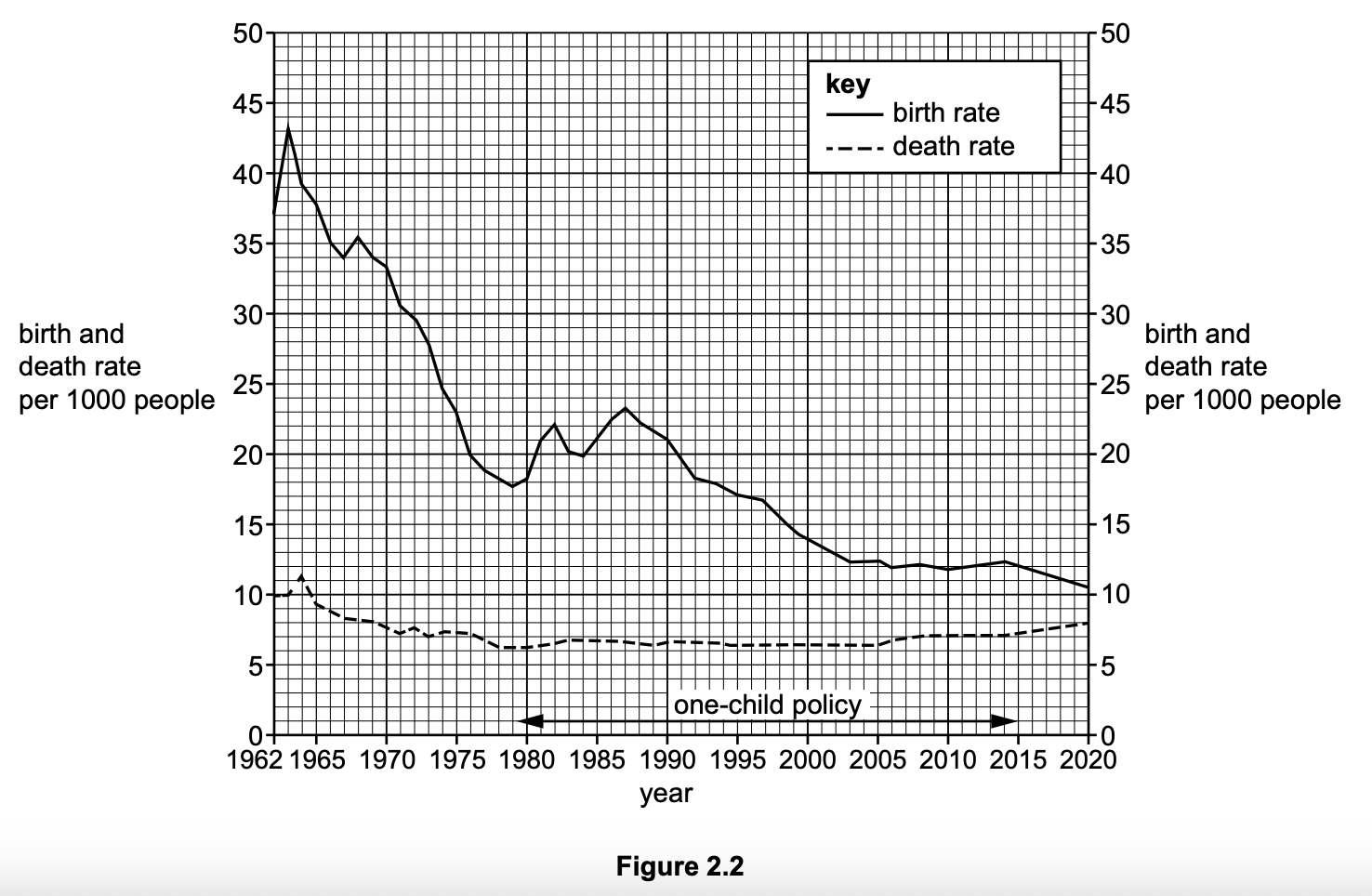
Insert the following words into the equation to show how overall population change is calculated.
death rate
migration
birth rate
..................... - ....................... + or - .................... = overall population change
Use Figure 2.1 to state the average annual rate of population change between 2015 and 2020 of the following countries.
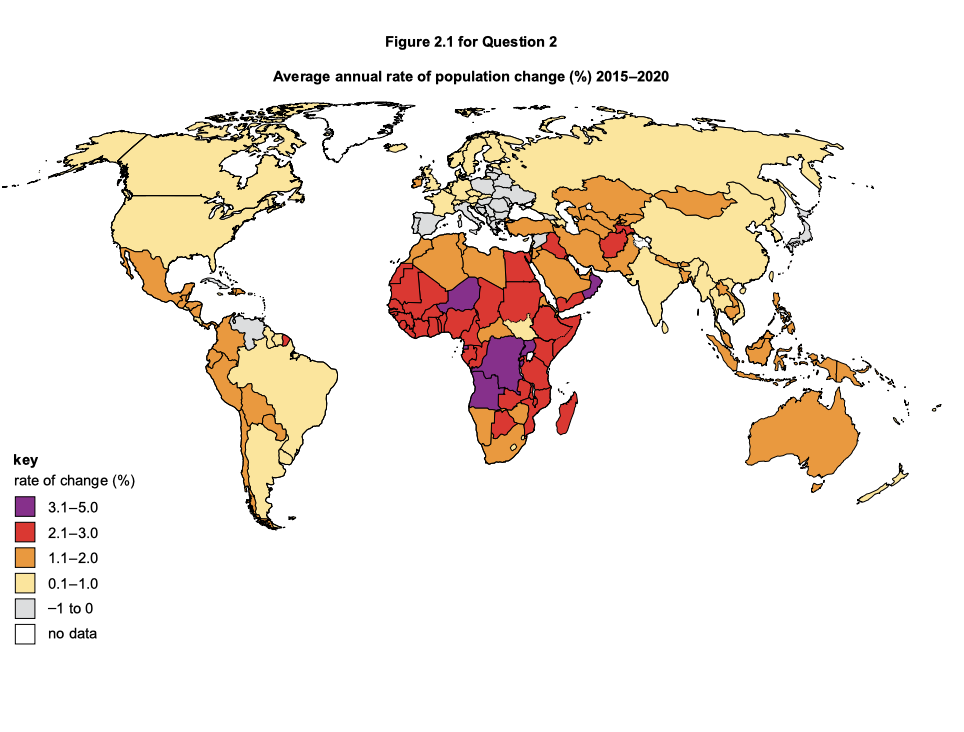
Angola ............................................................%
USA ............................................................%
Use Figure 2.1 to compare the rates of population change in Africa and Europe.
Was this exam question helpful?