Mean Kinetic Energy (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Mean kinetic energy
Heat and temperature are related quantities, but they are not the same
Heat is a measure of the total energy stored in a substance or object
Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold a substance or object is
Heat
The total energy of all the particles within a substance or object
Measured in joules (J)
Depends on the mass, material and temperature of a substance
Temperature
The mean (average) kinetic energy of the particles within a substance or object
Measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or kelvin (K)
Depends only on particle speed
Heating a substance
Heating a substance increases the kinetic energy of its particles
Therefore, the mean kinetic energy of the particles increases, and so the temperature increases
This also means that the total energy stored within the substance increases, so the heat energy increases
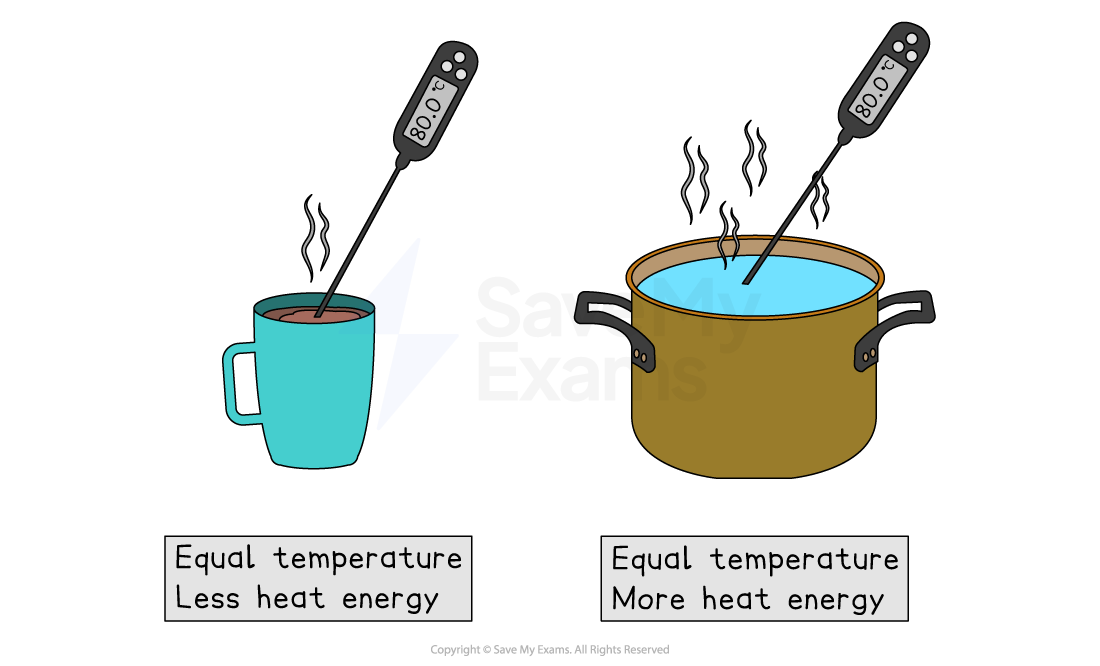
Two substances can have the same temperature but different amounts of heat energy
A mug of coffee at 80 °C has less heat energy than a pan of water at 80 °C
This is because the water in the pan has a greater mass than the coffee in the cup
There are a greater number of particles in the pan than in the mug
Therefore, the total energy of all the particles is greater in the pan than the mug
Even though the speed of particles, and therefore the temperature of the substances, is the same
Worked Example
An ice cube of mass 1 g and an ice cube of mass 3 g have a temperature of 0 °C.
State which ice cube has the least amount of heat energy and explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Both ice cubes have the same temperature
The 1 g ice cube has less mass than the 3 g ice cube
Therefore, the 1 g has the least amount of heat energy
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Even cold substances have heat energy. Remember that the particles in a solid still vibrate due to their kinetic energy. Only particles at absolute zero (0 K) have no kinetic energy.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
