Alpha, Beta & Gamma Radiation (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Alpha, beta & gamma radiation
Radioactive decay is a change in an unstable nucleus that can result in the emission of one of the following types of radiation:
Alpha (α) particles
Beta (β-) particles
Gamma (γ) radiation
Radioactive decay is spontaneous and random
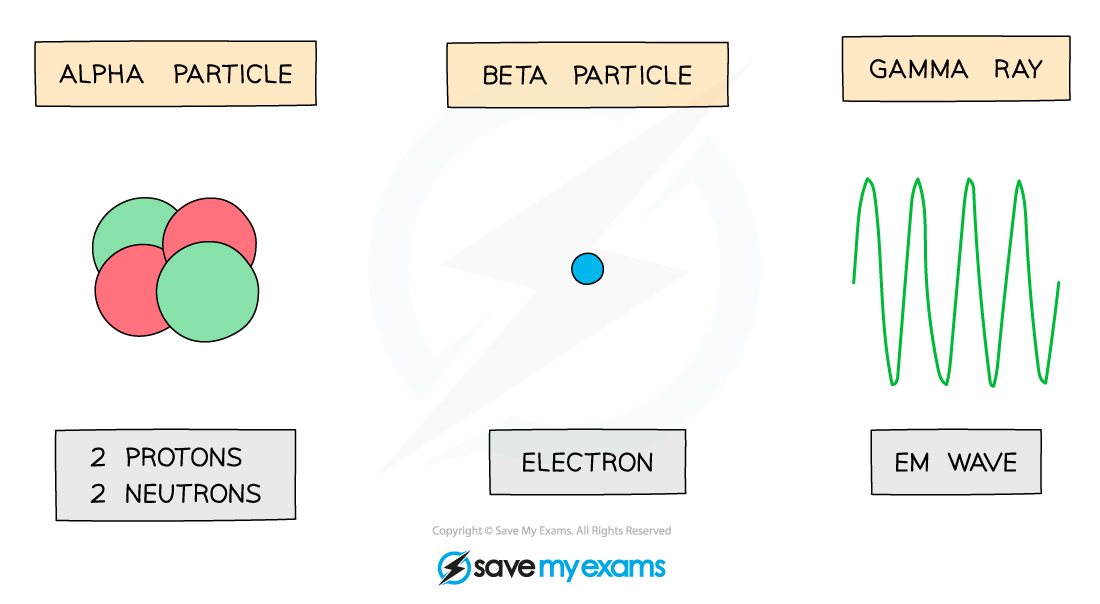
Alpha particles
The radiation symbol for alpha is α
An alpha particle is the same as a helium nucleus
This is because they consist of two neutrons and two protons
Alpha particles have a charge of +2
This is because they consist of two protons that each have a positive charge
Alpha particles can be affected by an electric field due to their charge
Beta particles
The radiation symbol for beta is β-
Beta particles are fast-moving, high-energy electrons
Beta particles have a charge of -1
This is because electrons have a negative charge
Beta particles can be affected by an electric field due to their charge
Gamma rays
The radiation symbol for gamma is γ
Gamma rays are electromagnetic waves
They have the highest energy of the different types of electromagnetic waves
Gamma rays have no charge
Therefore, gamma rays are not affected by an electric field
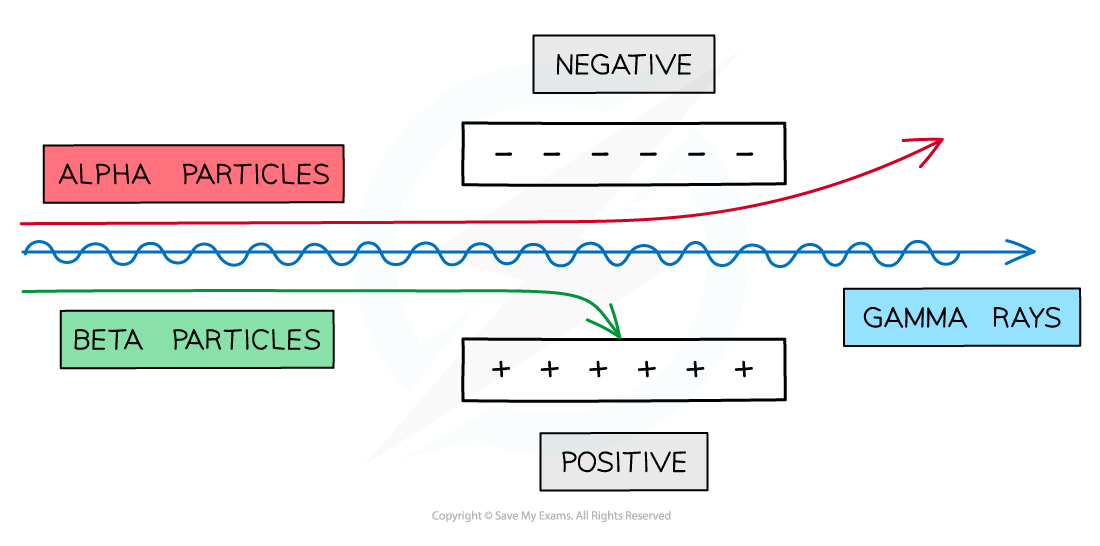
Alpha, beta & gamma radiation in an electric field
Worked Example
An unidentified form of nuclear radiation is passed through an electric field and is deflected toward the positive plate.
Identify the form of radiation and explain your reasoning.
Answer:
The radiation is deflected in an electric field, therefore it must have a charge
The radiation is deflected toward the positive plate, therefore its charge must be negative
The only form of nuclear radiation with a negative charge is beta radiation, because beta particles are high-energy electrons
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Mastering the core properties of alpha, beta and gamma radiation will be crucial for answering both theoretical and application questions in the exam.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
