Fission (SQA National 5 Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: X857 75
Fission
Nuclear fission is defined as:
The splitting of a large, unstable nucleus into two smaller nuclei
There is a lot of energy stored within the nucleus of an atom
This energy can be released in a nuclear reaction such as fission or fusion
Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power stations to generate electricity
This is explored in further detail in Applications of Nuclear Radiation
Nuclear fission reactions
During a fission reaction:
a neutron collides with an unstable nucleus
the nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei (called daughter nuclei)
and two or three neutrons are released
Gamma rays are also emitted
Energy is released
Nuclear fission of uranium-235

The products of fission move away very quickly
Nuclear energy stored in the parent nucleus is transferred to the kinetic energy of the fission products
Energy is also transferred to the surroundings by radiation (gamma rays)
The energy released in a nuclear fission reaction far exceeds that released in a chemical reaction in which a similar mass of material reacts
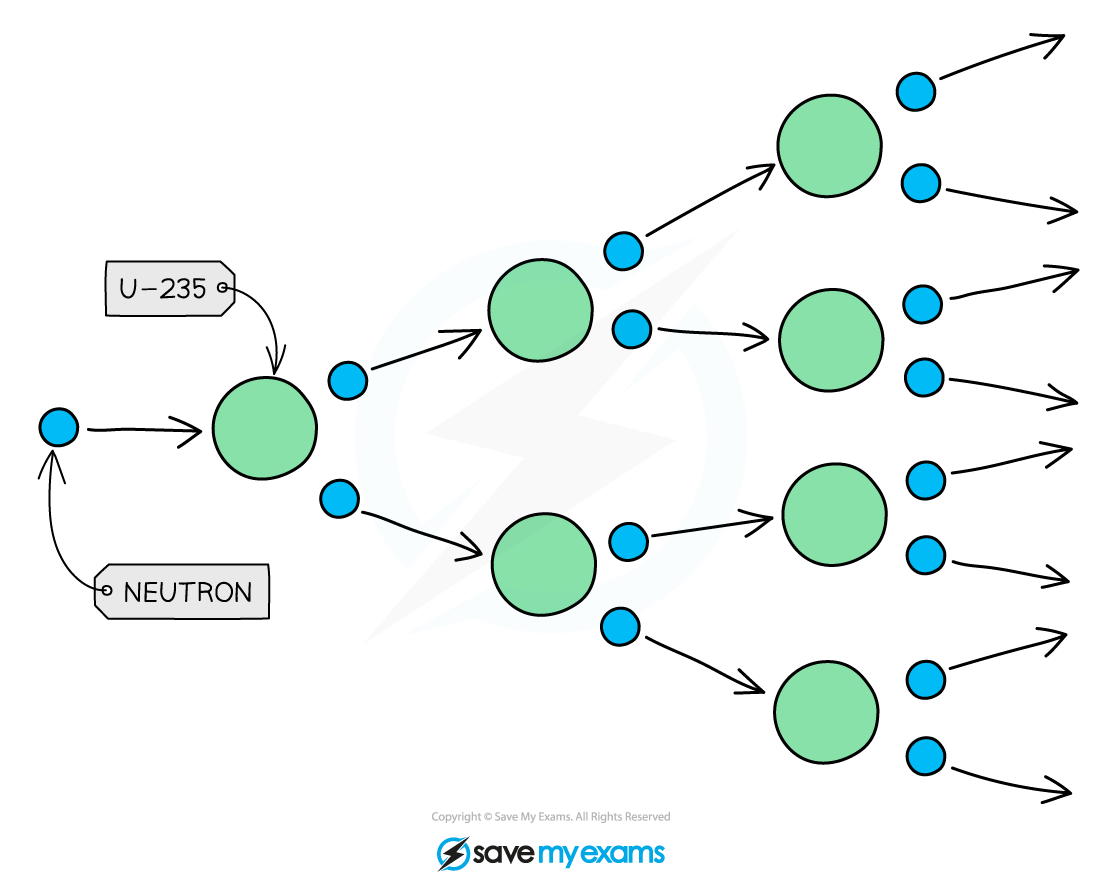
Chain reactions
Only one extra neutron is required to induce fission in a uranium-235 nucleus
During the fission, it produces two or three neutrons which move away at high speed
Each of these new neutrons can start another fission reaction, which again emits further neutrons
This process can start a chain reaction
A chain reaction occurs when a neutron emitted from the splitting of a nucleus causes further nuclei to split
Then the neutrons emitted from these reactions cause further fission reactions, and so on
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Students often lose marks for not showing understanding that the neutrons, released in one fission reaction, go on to initiate another fission reaction in a different nucleus.
Make sure you learn the roles of the neutrons in fission chain reactions.
Worked Example
A nuclear reactor on board a research vessel provides a constant power output of to sustain operations.
Each nuclear fission reaction releases of usable energy.
Determine the minimum number of fission reactions that must occur in the reactor during one day of continuous operation.
Answer:
Step 1: Determine the time in seconds
1 day = 24 h
1 h = 60 min
1 min = 60 s
Step 2: Calculate the total amount of energy produced
Write out the appropriate relationship
Rearrange to make
the subject
Convert power into SI units
mega = 106
Substitute in the known values to calculate
Step 3: Calculate the minimum number of fission reactions required
The number,
, of fission reactions is the total energy divided by the energy released per fission reaction
Energy released by each fission reaction,
Substitute in the known values to calculate
Step 4: Round to an appropriate number of significant figures
The least precise input value was 2 s.f.
Therefore, the answer can only be given to the same precision

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
