Role of the Placenta (Edexcel IGCSE Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 4BI1
Did this video help you?
The Placenta
After fertilisation in the oviduct the zygote divides to form an embryo, and travels to the uterus
Upon reaching the uterus the embryo implants in the uterine lining, where it continues to develop
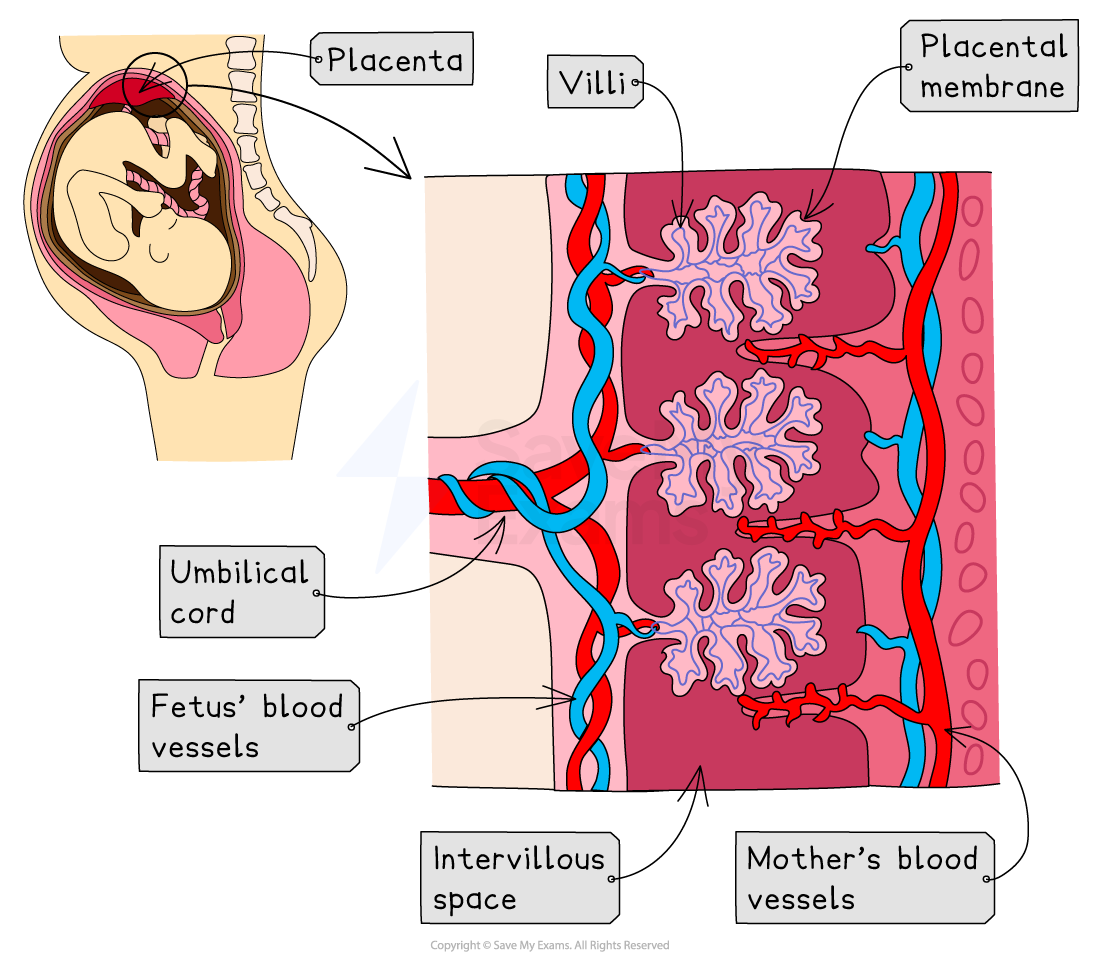
A structure called the placenta forms at the implantation site
The placenta provides the developing embryo with nutrients and oxygen from the mother’s blood, which are essential for growth and development
It also allows waste products from the embryo’s blood to be removed
In the placenta, the mother’s blood comes into very close proximity to the blood of the fetus, but the two blood supplies do not mix
The umbilical cord connects the fetus’ blood supply to the placenta
The role of the placenta is to enable exchange of substances between the mother's blood and that of the fetus
Substances that travel from the mother's blood to the fetus include:
Oxygen
Nutrients, eg. glucose, amino acids, vitamins and mineral (ions)
Substances that travel from the fetus' blood to the mother include:
Carbon dioxide
Urea
The placenta is an efficient exchange surface because it has:
A large surface area
A thin wall for efficient diffusion
The placenta also acts as a barrier to some toxins and pathogens, although not all are stopped from passing through. For example:
Nicotine and alcohol can pass across the placenta
Virus particles can pass across the barrier
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are asked to "describe the role of the placenta in reproduction", be sure to indicate the direction substances are moving.
For example, the placenta provides the fetus with oxygen and nutrients such as glucose and amino acids, as well as antibodies. It removes carbon dioxide and urea.
Other roles of the placenta are that it allows diffusion and it secretes hormones (eg. progesterone).

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
