Gas Exchange in Plants (Edexcel IGCSE Biology (Modular)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4XBI1
Diffusion in Gas Exchange
Particles in a liquid and gas are in constant motion
Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, down a concentration gradient
Diffusion is important in living organisms. Substances that may move into and out of cells by diffusion include the molecules oxygen (O₂) and carbon dioxide (CO₂)
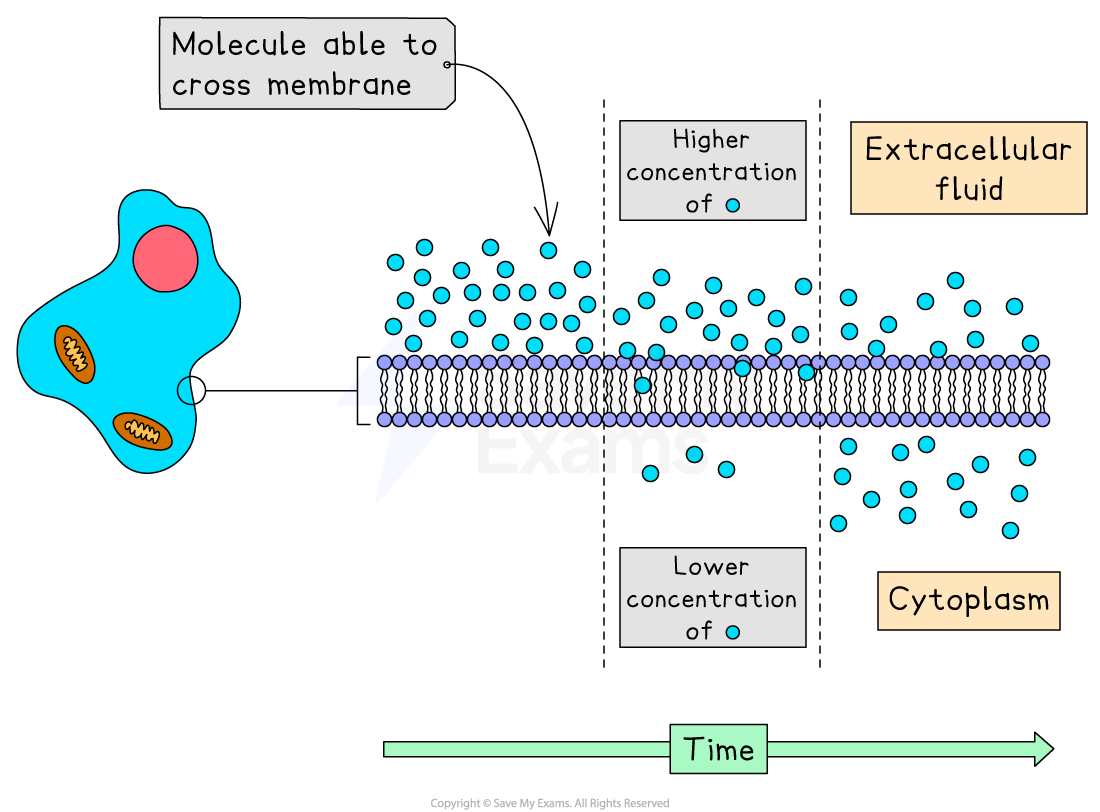
Diffusion in organisms
Gas exchange refers to the exchange of the gases oxygen (O₂) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) between a cell/organism and its environment
Single-celled organisms, such as amoeba, can exchange gases sufficiently by simple diffusion through the cell membrane
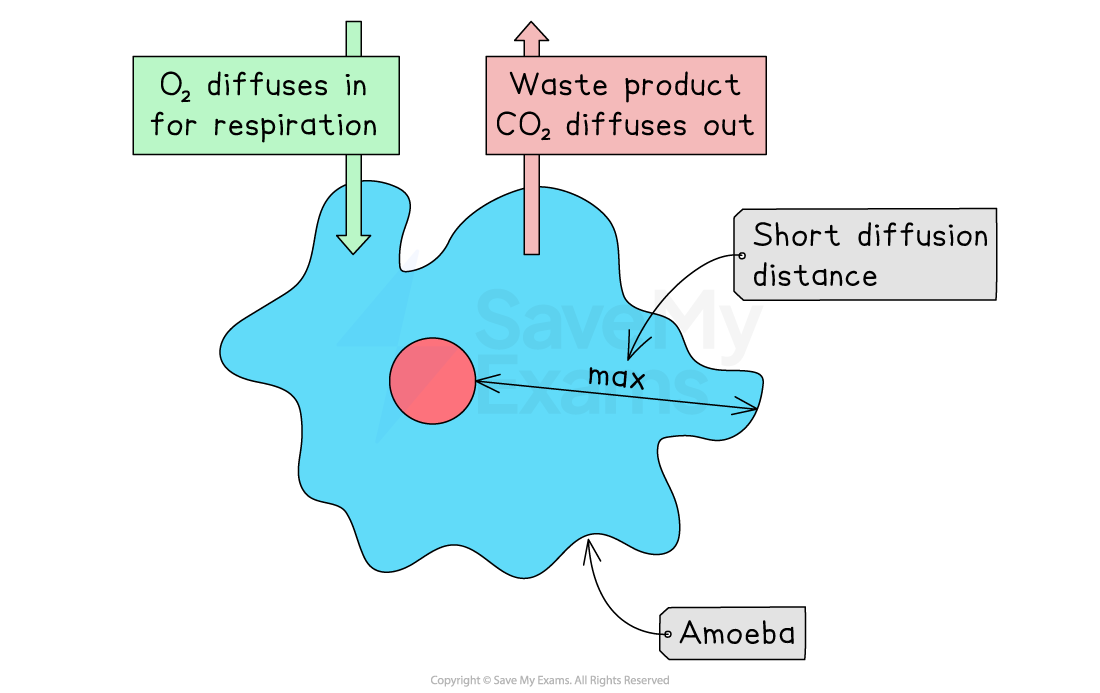
Multicellular organisms (such as plants and animals), however, have exchange surfaces and organ systems that maximise the exchange of materials
Gills are the gas exchange organ in fish, lungs are the gas exchange organ in humans and leaves and roots are the gas exchange organ in plants
These organs increase the efficiency of exchange in several ways by:
Having a large surface area, providing more surface area relative to volume to allow sufficient diffusion
A short diffusion distance for substances to move across. This short distance is created because the barrier that separates two regions is as thin as possible
In addition, animals have gas exchange surfaces that are well-ventilated to maintain steep concentration gradients
Gas Exchange: Photosynthesis & Respiration
The processes of respiration and photosynthesis in cells both rely on the exchange of the gases oxygen and carbon dioxide
Gas exchange during respiration
Plant cells, like all living cells, require energy for cellular processes. Energy is released when respiration occurs. Respiration occurs in plant cells all the time - both during the day and at night
In the daytime, if conditions are sufficient then photosynthesis will also occur in plants cells with chloroplasts
During the night when there is no light no photosynthesis occurs, but respiration will still be occurring
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide
At night, when no photosynthesis is occurring:
Oxygen diffuses down a concentration gradient from a higher concentration outside the leaf to a lower concentration inside the leaf
The cells in the leaf use oxygen in aerobic respiration so the concentration will remain low inside the respiring cells
Carbon dioxide diffuses down a concentration gradient from a higher concentration inside the leaf to a lower concentration outside the leaf

At night, when no photosynthesis is occurring, oxygen diffuses into the leaf and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the leaf. This is an example of gas exchange.
Gas exchange during photosynthesis
Plant cells with chloroplasts can photosynthesise when there is enough sunlight
Photosynthesis requires carbon dioxide and releases oxygen
Carbon dioxide diffuses down a concentration gradient from a region of higher concentration outside the leaf to a region of lower concentration inside the leaf
Cells with chloroplasts use carbon dioxide in photosynthesis so the concentration of carbon dioxide inside the photosynthesising cells is lower than outside
Oxygen diffuses down a concentration gradient from a high concentration (inside the leaf) to a low concentration (outside the leaf)
Note - some of the oxygen released in photosynthesis will be used in respiration!

When photosynthesis occurs, carbon dioxide diffuses into the leaf and oxygen diffuses out of the leaf.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
