Practical: Investigate the Solubility of a Solid in Water at a Specific Temperature (Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 4CH1
Practical: Investigate the solubility of a solid in water at a specific temperature
Aim
To find the solubility of a solid in water at a given temperature by preparing a saturated solution, evaporating the solvent, and measuring the mass of the solid obtained
Method
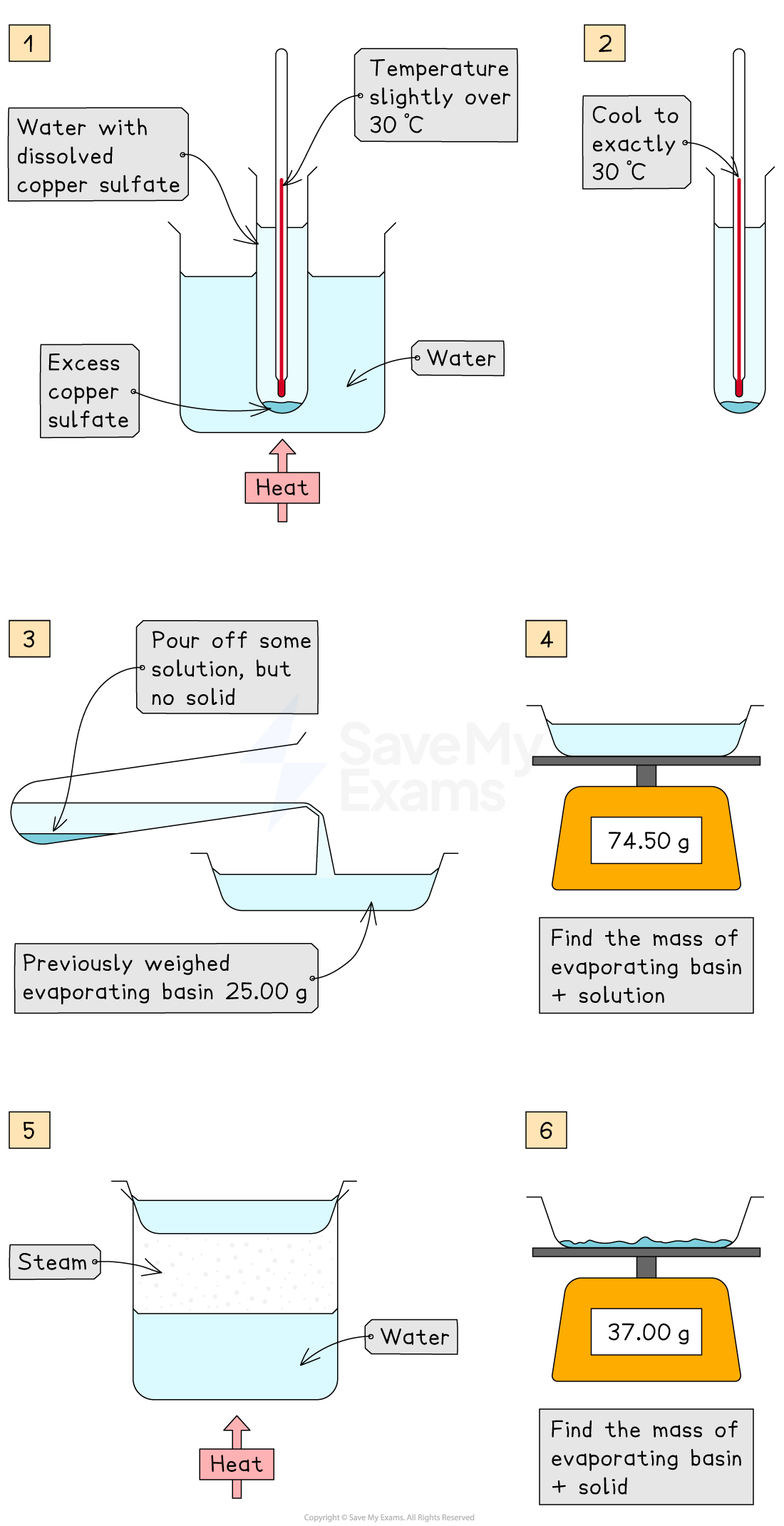
Weigh an empty evaporating basin using a balance and record its mass
Warm a boiling tube of water to just above 30°C using a water bath or beaker of hot water
Add copper(II) sulfate crystals to the water in the boiling tube and stir thoroughly until no more will dissolve and some undissolved solid remains at the bottom.
This ensures that the solution is saturatedAllow the saturated solution to cool to exactly 30°C
Pour a portion of the clear solution (without any solid) into the pre-weighed evaporating basin
It is important that no undissolved copper(II) sulfate is transferred
Weigh the evaporating basin and the solution together and record the total mass
Gently heat the evaporating basin to evaporate all the water, taking care to avoid spitting or loss of solid
When the water appears to have evaporated completely, allow the basin to cool slightly and then weigh it again
Reheat, cool, and reweigh the basin once more
Repeat this process until the mass remains constant
This is called heating to constant mass and confirms that all water has been removed
Calculate the solubility of copper(II) sulfate in water at 30°C using the masses recorded
Results
Mass of empty evaporating basin, mb = 25.00 g
Mass of basin + saturated solution, mb+ soln = 74.50 g
Mass of basin + dry copper(II) sulfate (after heating to constant mass), mb + solid = 37.00 g
Calculation
Step 1: Find the masses you need
Mass of solution
m(soln) = mb + soln − mb = 74.50 − 25.00 = 49.50 g
Mass of dissolved solute (CuSO4.5H2O)
m(solute) = mb + solid − mb = 37.00 − 25.00 = 12.00 g
Mass of water
m(water) = m(soln) − m(solute) = 49.50 − 12.00 = 37.50 g
Step 2: Calculate solubility (g solute per 100 g water)
Solubility at 30 °C = x 100
x 100 = 32.0 g per 100 g
Step 3: Express as mass percentage of the solution
% solute in solution = x 100 = 24.2%
Examiner Tips and Tricks
“Heating to constant mass” means:
Reheating
Cooling
Reweighing until two consecutive masses are the same
This confirms all water has been removed.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
