Work out the size of one interior angle of a regular 16-sided polygon.
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 0580 & 0980
Work out the size of one interior angle of a regular 16-sided polygon.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Work out the size of one interior angle of a regular 9-sided polygon.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
i) Write down the mathematical name for an 8-sided polygon.
[1]
ii) Work out the size of an interior angle of a regular 24-sided polygon.
[2]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Find the size of one interior angle of a regular octagon.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

The diagram shows two parallel lines and a straight line crossing them.
Write down, using letters from to
,
the angle that is alternate to angle ,
How did you do?
the angle that is corresponding to angle .
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Find the size of one interior angle of a regular 10-sided polygon.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Work out the size of one interior angle of a regular polygon with 20 sides.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

The diagram shows a triangle drawn between a pair of parallel lines.
Find the value of and the value of
.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A regular polygon has an exterior angle of 20°.
Work out the number of sides of this polygon.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

The diagram shows two parallel lines and two straight lines.
i) Find the value of .
Give a reason for your answer.
a = ................ because ..................................................................................................... [2]
ii) Find the value of .
Give a reason for your answer.
b = ................ because ......................................................................................................[2]
iii) Find the value of .
= ................................................. [2]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

In the diagram, is parallel to
.
Find the value of.
Give a geometrical reason for your answer.
= ......................... because ....................................
How did you do?
Work out the value of .
Give a geometrical reason for your answer.
.................because ......................
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

Work out the value of
i)
=..........................[1]
ii)
...........................[1]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The diagram shows a triangle between two parallel lines, and
.

Find the value of
i)
=............................. [1]
ii)
............................. [1]
iii) .
= ............................. [1]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

Complete the statements.
............................ because ............................
........................... because ............................
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

is a rectangle.
is parallel to
.
Find the value of and the value of
.
= ......................................................
= ................................................. .....
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

Two regular octagons and a square meet at point .
Show, by calculation, that the three interior angles at add up to 360°.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

The diagram shows two pairs of parallel lines.
Find the value of , the value of
and the value of
.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
The diagram shows part of a different regular polygon.

is an exterior angle.
is an interior angle.
The ratio .
i) Work out angle .
[3]
ii) Work out the number of sides of this regular polygon.
[1]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

is a pentagon.
Explain why the diagram shows that the sum of the interior angles of a pentagon is 540°. Do not measure any angles.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

In the diagram and
are straight lines.
Lines and
are parallel.
Find angle and give a reason for your answer.
Angle = ................................. because ...................................
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

The diagram shows two regular pentagons.
Pentagon is an enlargement of pentagon
, centre
.
Find angle .
Angle = ..............................
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?

In the diagram, is a straight line.
is parallel to
, angle
= 34° and
i) Complete the statements.
a) ................ because ................................
[2]
b) ................ because .................................
[2]
ii) Work out the value of and the value of
.
....................
.................... [2]
iii) Find the value of t and give a reason for your answer.
................ because ........................
[2]
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Each interior angle of a regular polygon is 162°.
Calculate the number of sides of the polygon.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
A model of a hall in the shape of a trapezium is made by joining together three equilateral triangles.

The perimeter of one of the triangles is 72 cm.
Work out the perimeter of the trapezium.
How did you do?
The trapezium model from part (a) is duplicated, with the copy being rotated and attached along the bottom of the original trapezium, making a regular polygon.
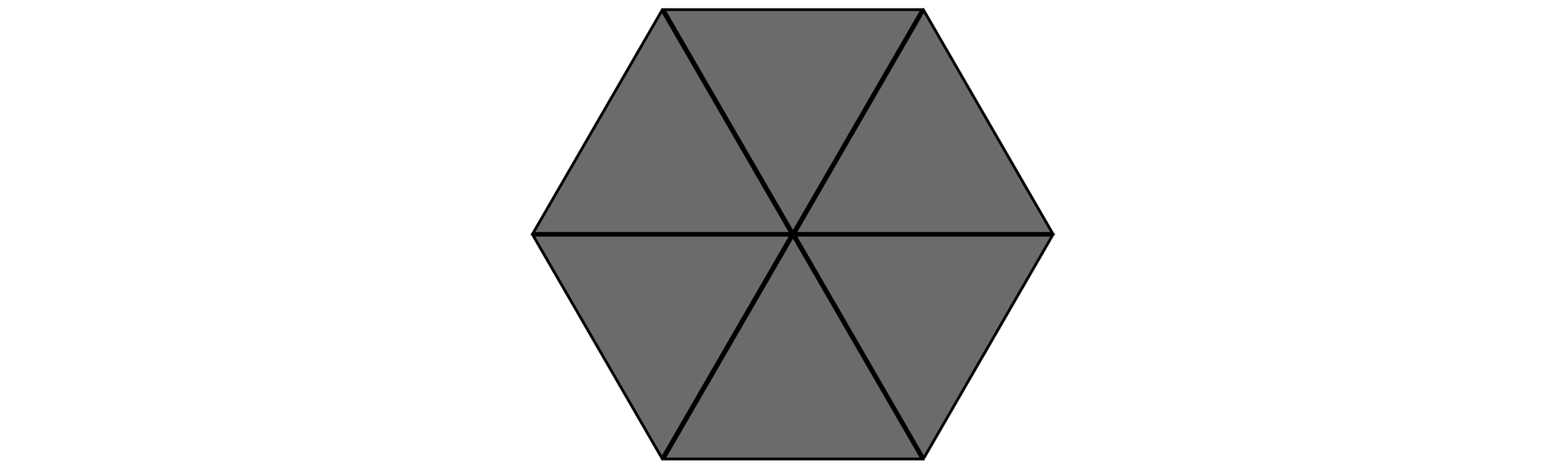
Give the name of this regular polygon.
How did you do?
Calculate the exterior angle, , of the polygon in part (b).
How did you do?
Work out the interior angle, ,of the polygon in part (b).
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
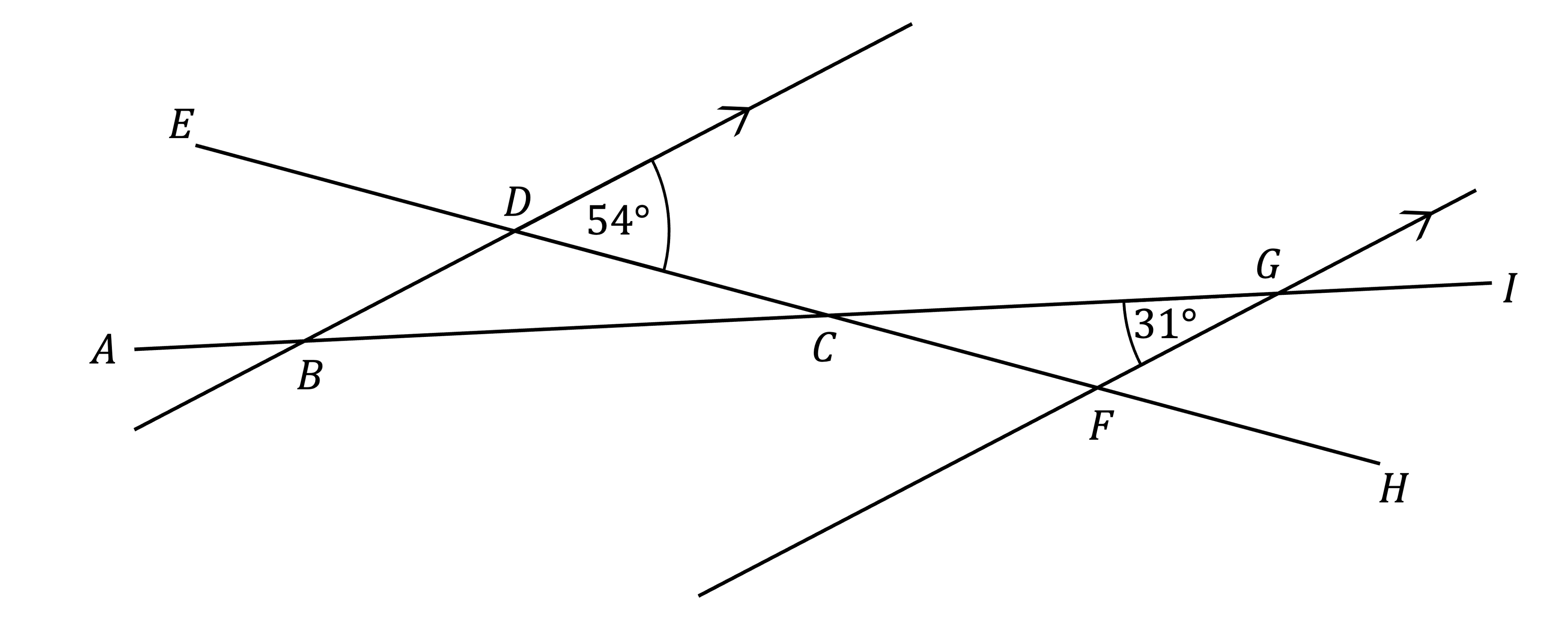
In the diagram, and
are straight lines.
Lines and
are parallel.
Find the angle .
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Show that the sum of the interior angles in a hexagon is .
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?