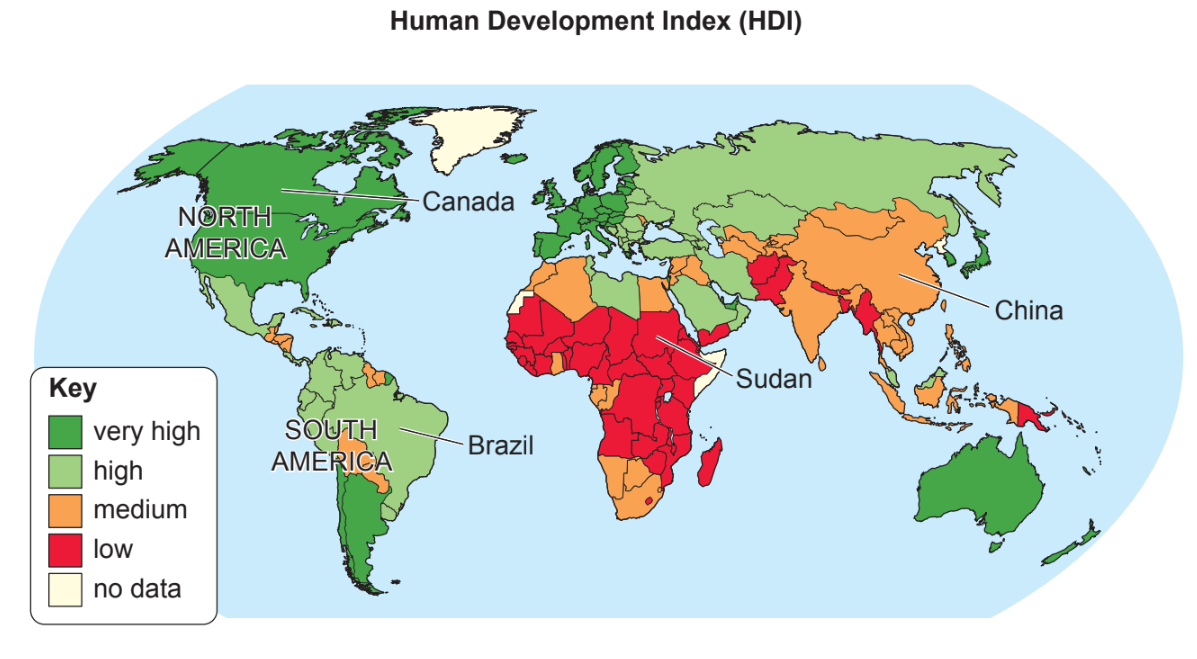
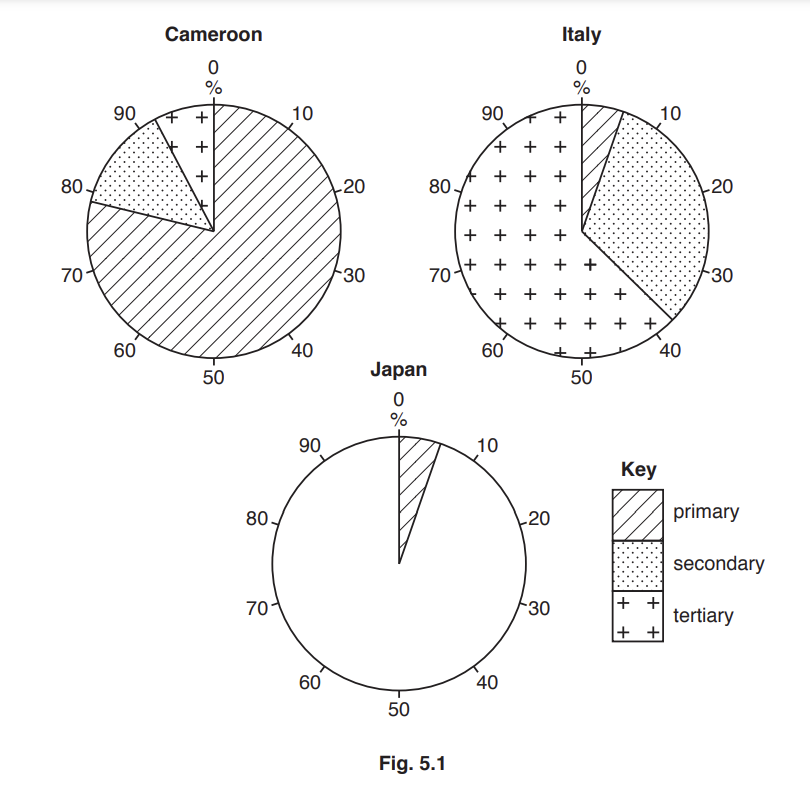
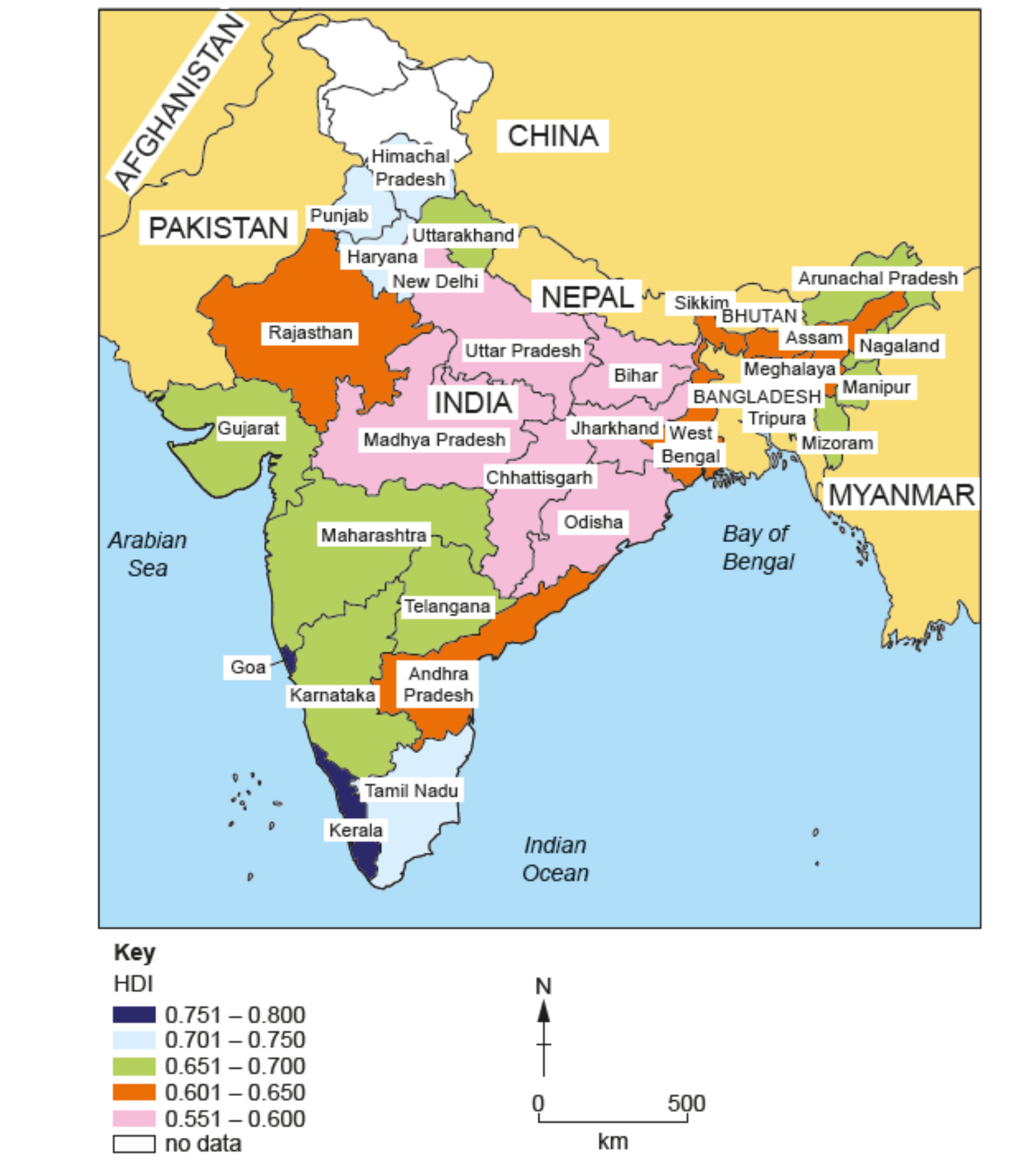
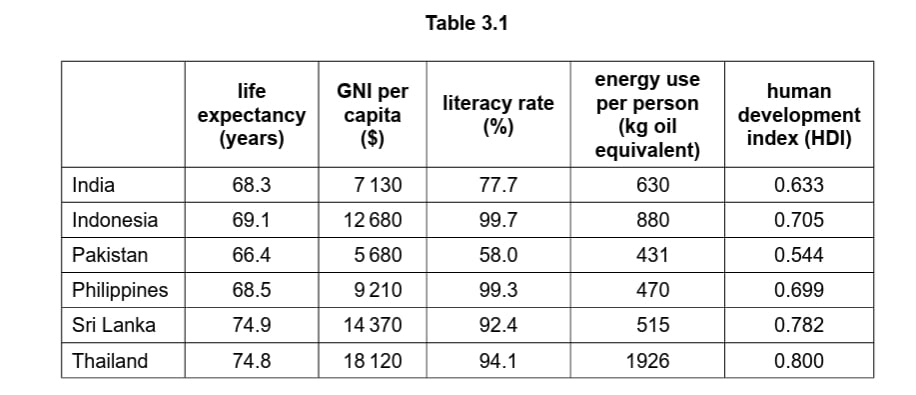
Study Table 3.1, which shows indicators of development for six countries in Asia.
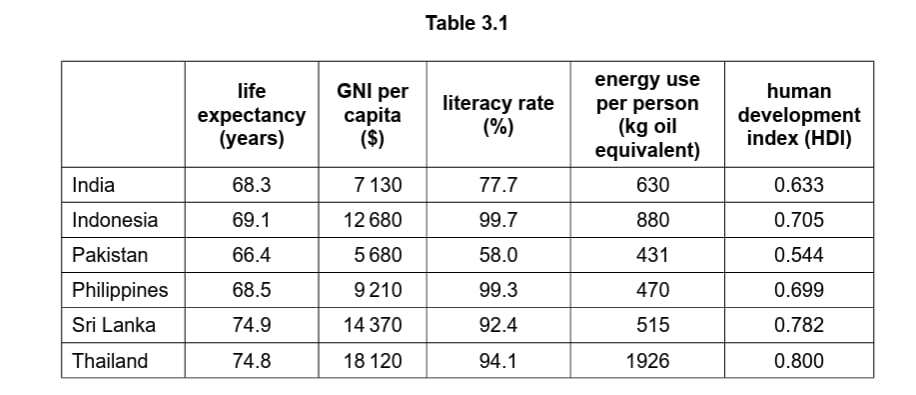
Identify one country listed in Table 3.1 with a life expectancy greater than 70 years.
Define the following terms:
GNI per capita
Literacy rate
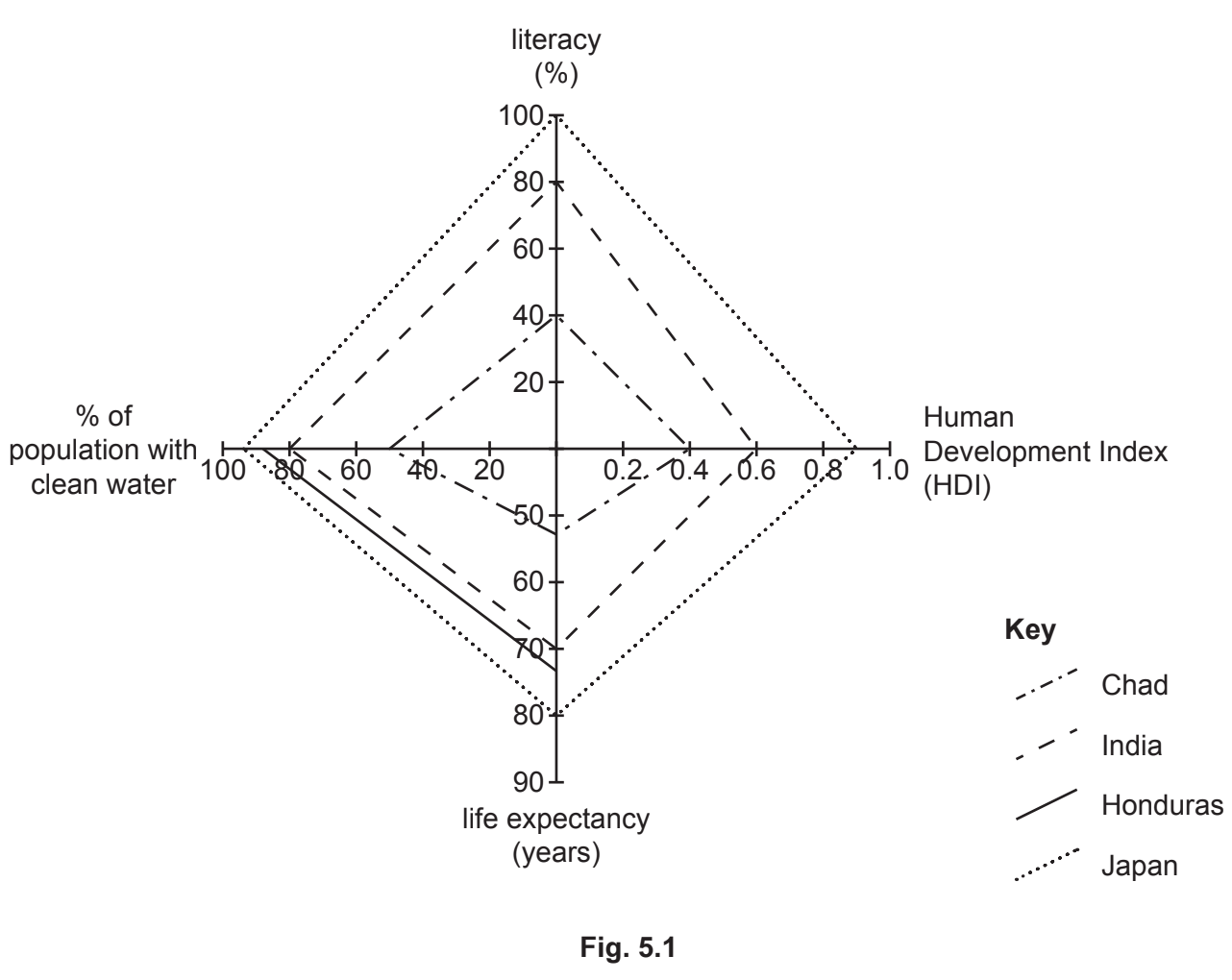
Study Figure 3.1, a scatter graph showing information about the human development index (HDI) and energy use per person in the six countries listed in Table 3.1.
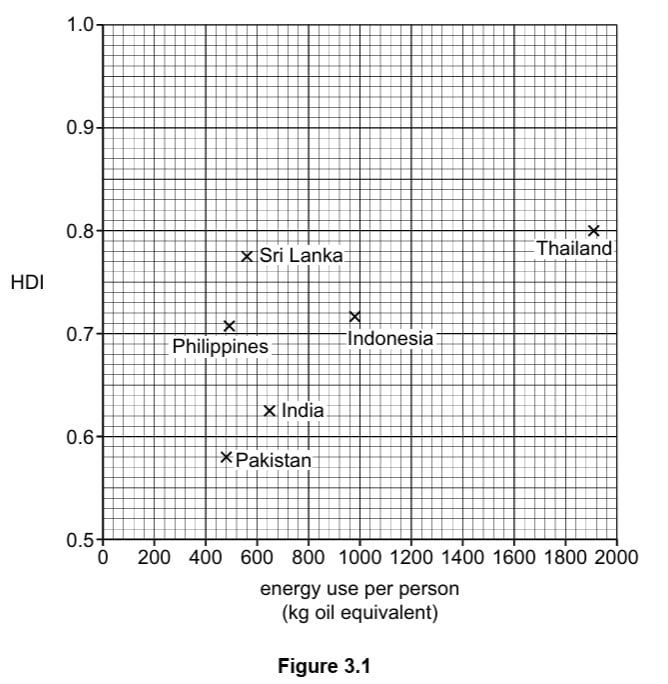
Describe the relationship between HDI and energy use per person. Use data to support your answer.
Did this page help you?