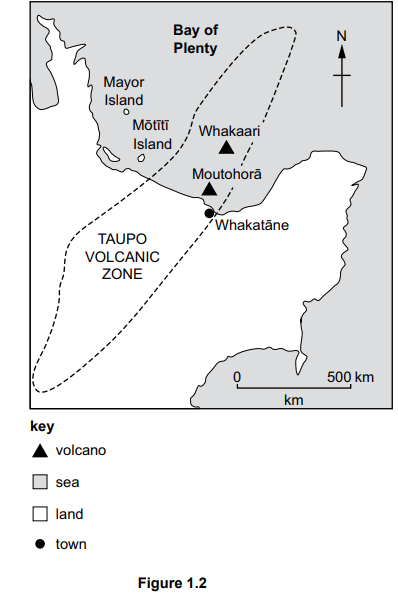
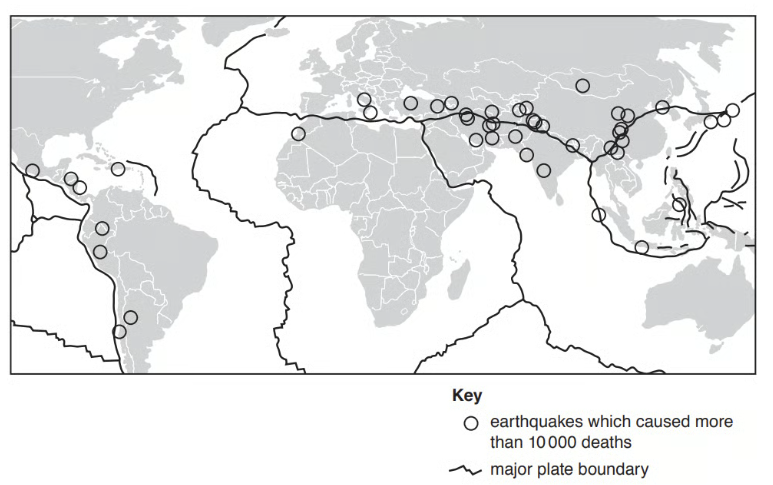
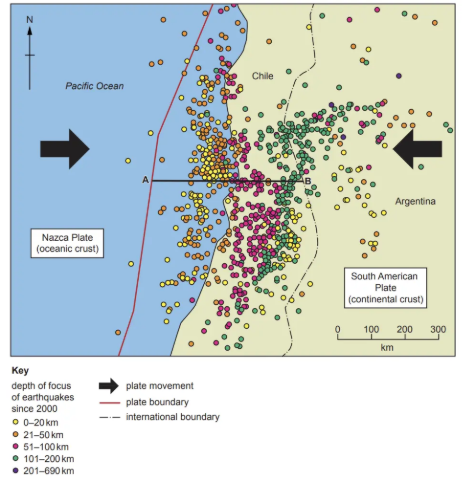
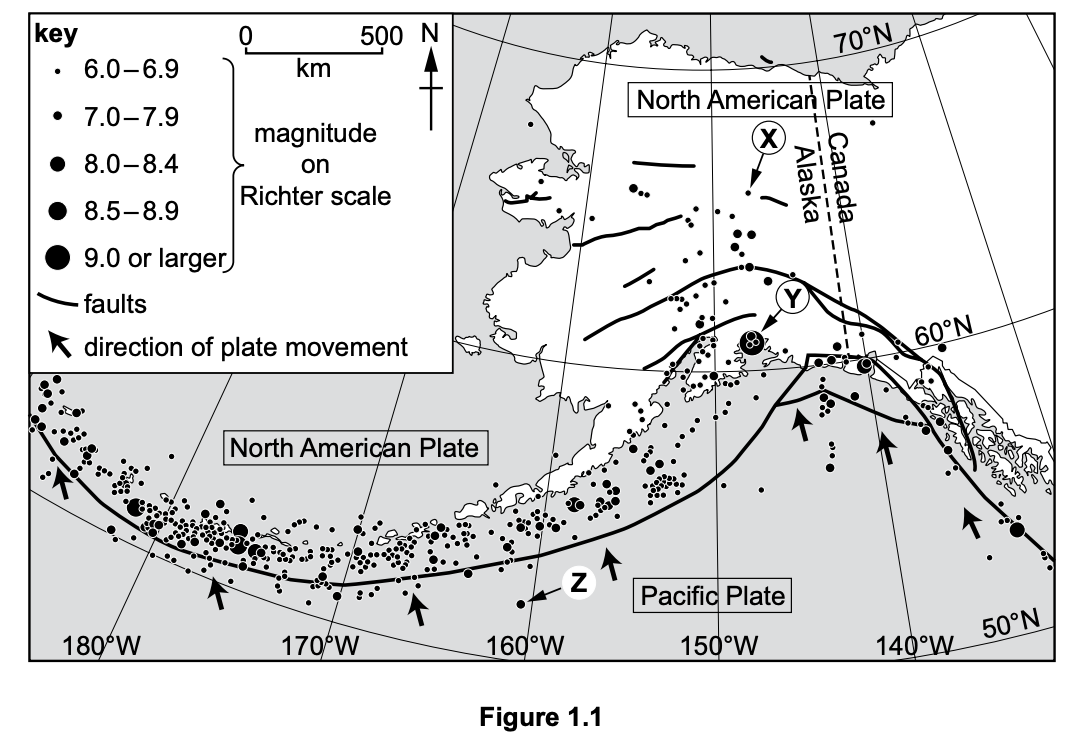
Study Figure 1.1, a map showing the location and magnitude of earthquakes in Alaska, USA.
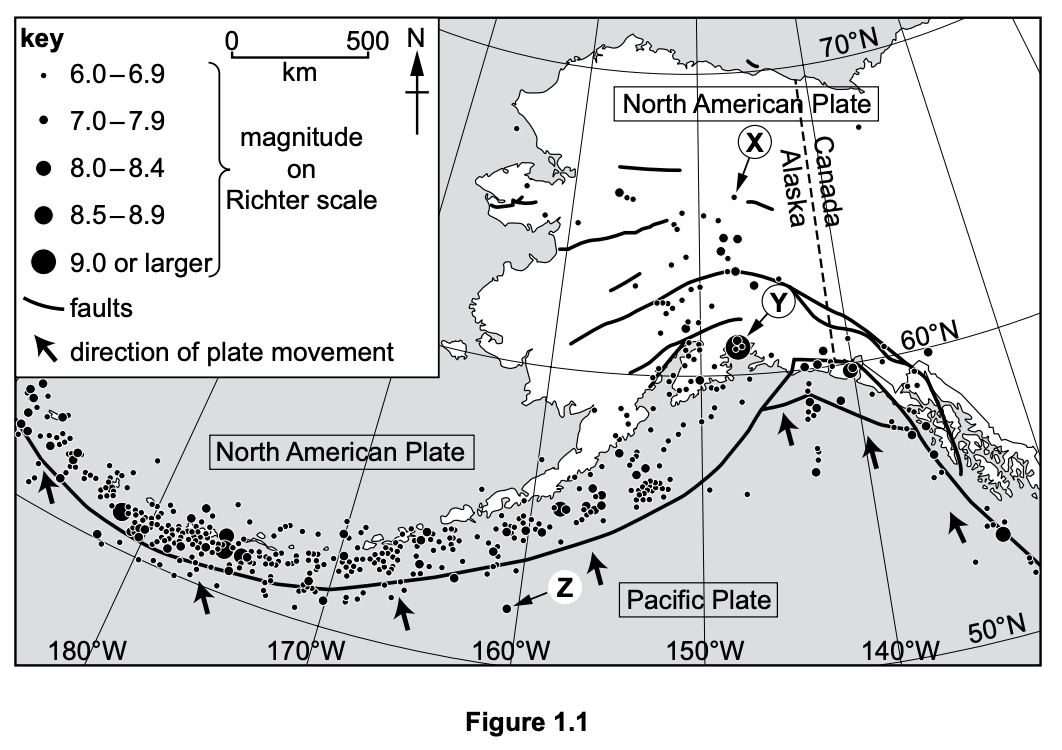
In which direction is the Pacific Plate moving?
north (N)
north-north-west (NNW)
north-west (NW)
south-east (SE)
south-south-east (SSE)
State the latitude and longitude of the earthquake labelled X in Figure 1.1
Was this exam question helpful?