Linear Simultaneous Equations using Elimination (Edexcel International AS Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: XMA01
Did this video help you?
Linear simultaneous equations using elimination
What are linear simultaneous equations?
When you have more than one equation in more than one unknown, then you are dealing with simultaneous equations
An equation is linear if none of the unknowns in it is raised to a power other than one
Solving a pair of simultaneous equations means finding pairs of values that make both equations true at the same time
A linear equation in two unknowns will produce a straight line if you graph it... linear = line
A pair of simultaneous equations will produce lines that will cross each other (if there is a solution!)
How do I use elimination to solve linear simultaneous equations?
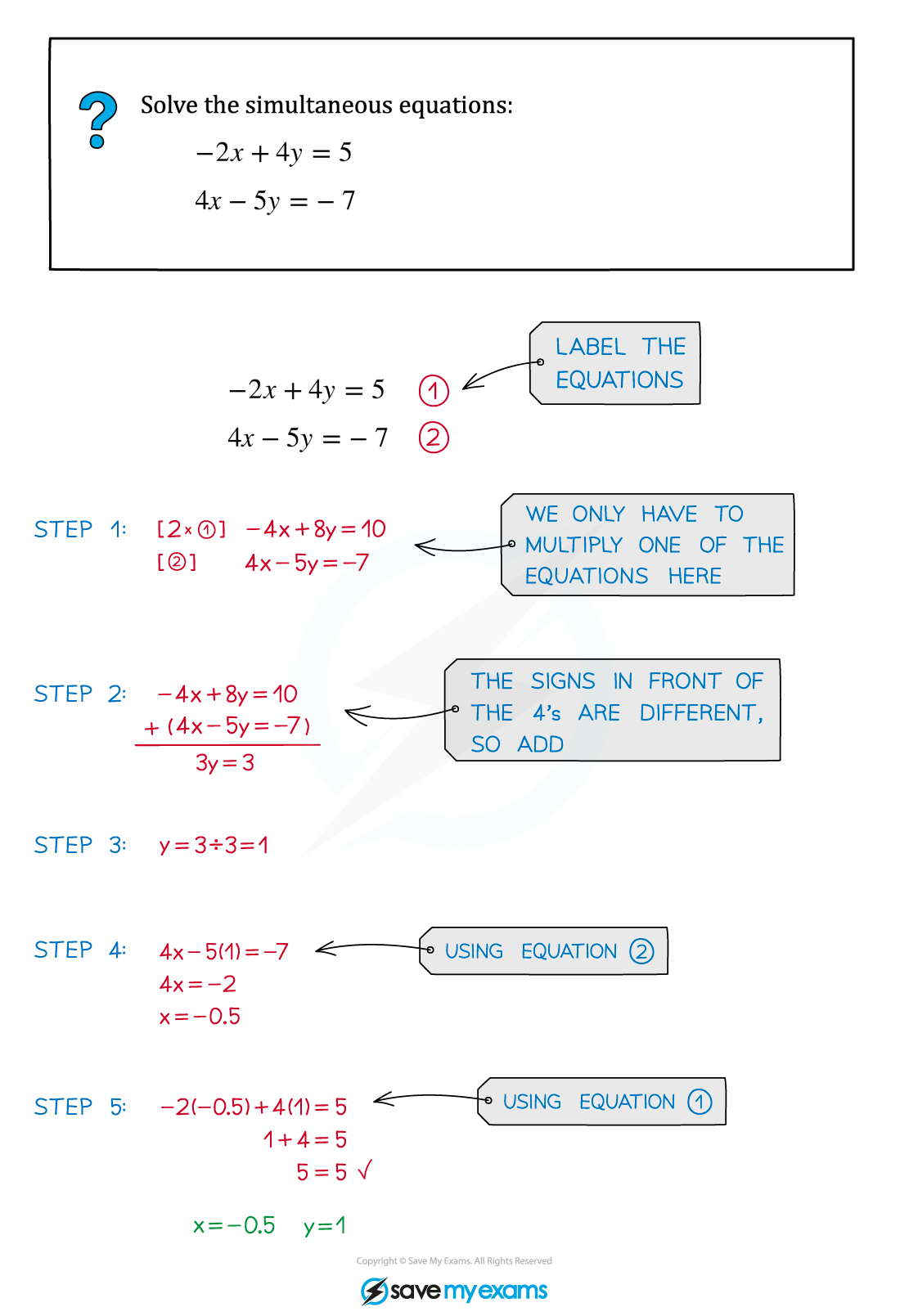
Step 1: Multiply one (or both) of the equations by a constant (or constants) to get the numbers in front of one of the unknowns to match
Step 2: If the matching numbers have the same sign, then subtract one equation from the other. If the matching numbers have different signs then add the equations together
Step 3: Solve the new equation from Step 2 to find the value of one of the unknowns
Step 4: Substitute the value from Step 3 into one of the original equations, and solve to find the value of the other unknown
Step 5: Check your solution by substituting the values for the two unknowns into the original equation you didn't use in Step 4
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don't skip the checking step (it only takes a few seconds) – there are many places to go wrong when solving simultaneous equations!
Mishandling minus signs is probably the single biggest cause of student error in simultaneous equations questions
Worked Example

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
