Language of Functions (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9709
Written by: Paul
Updated on
Did this video help you?
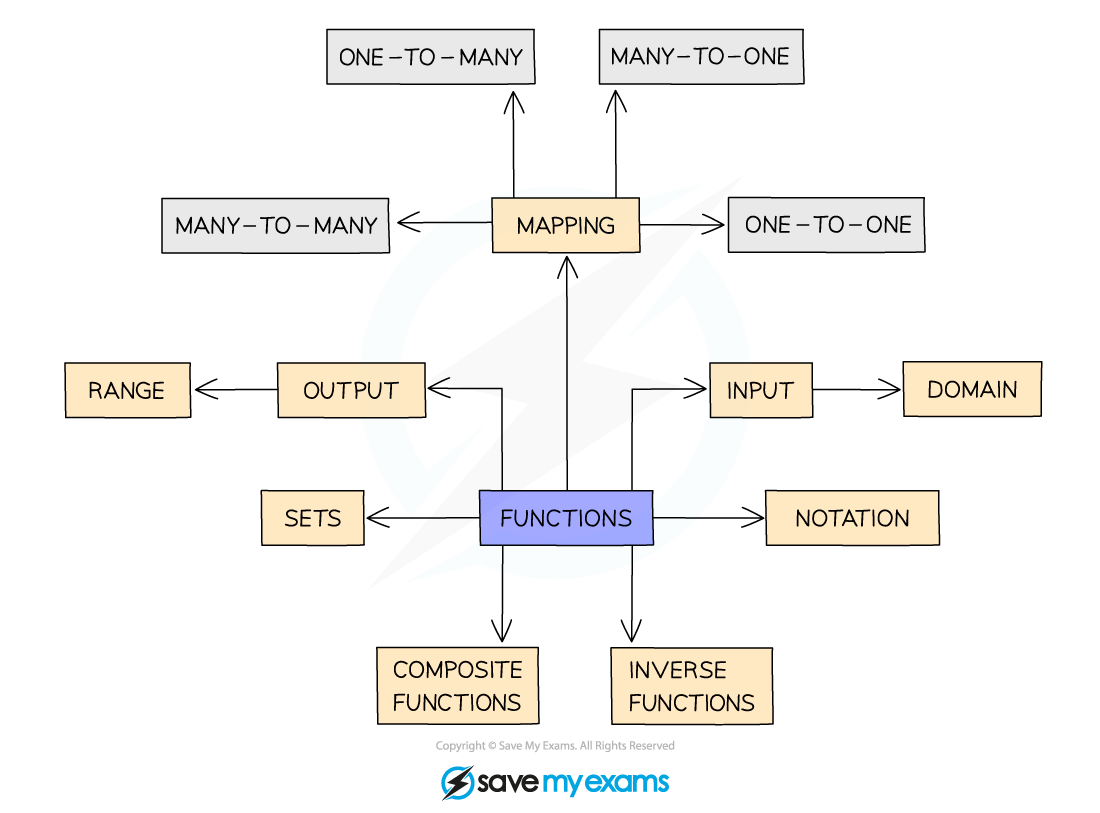
Language of functions
What language is used with functions?
The language of functions has many keywords associated with it that need to be understood
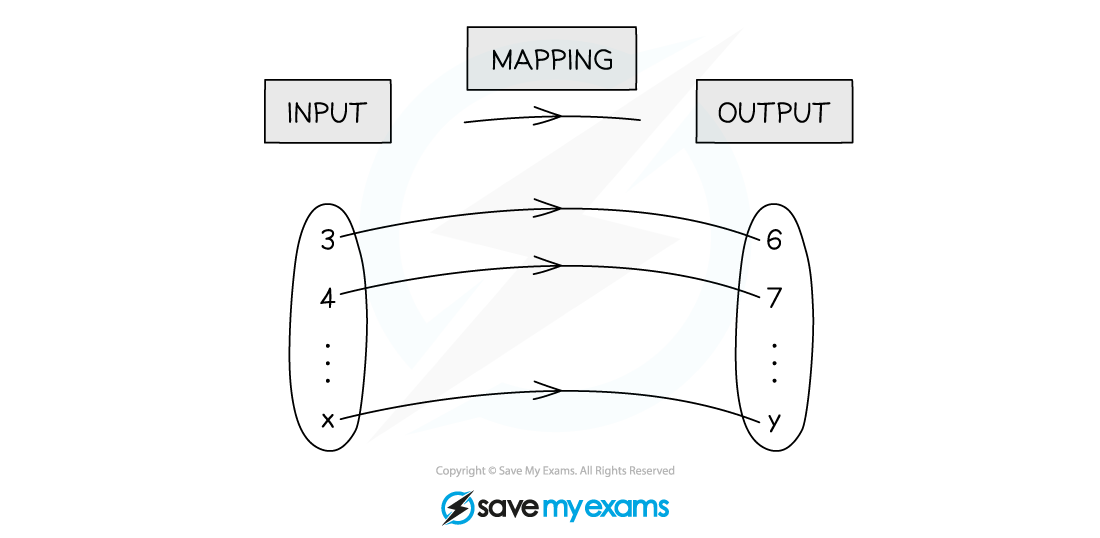
What are mappings?
A mapping takes an ‘input’ from one set of values to an ‘output’ in another
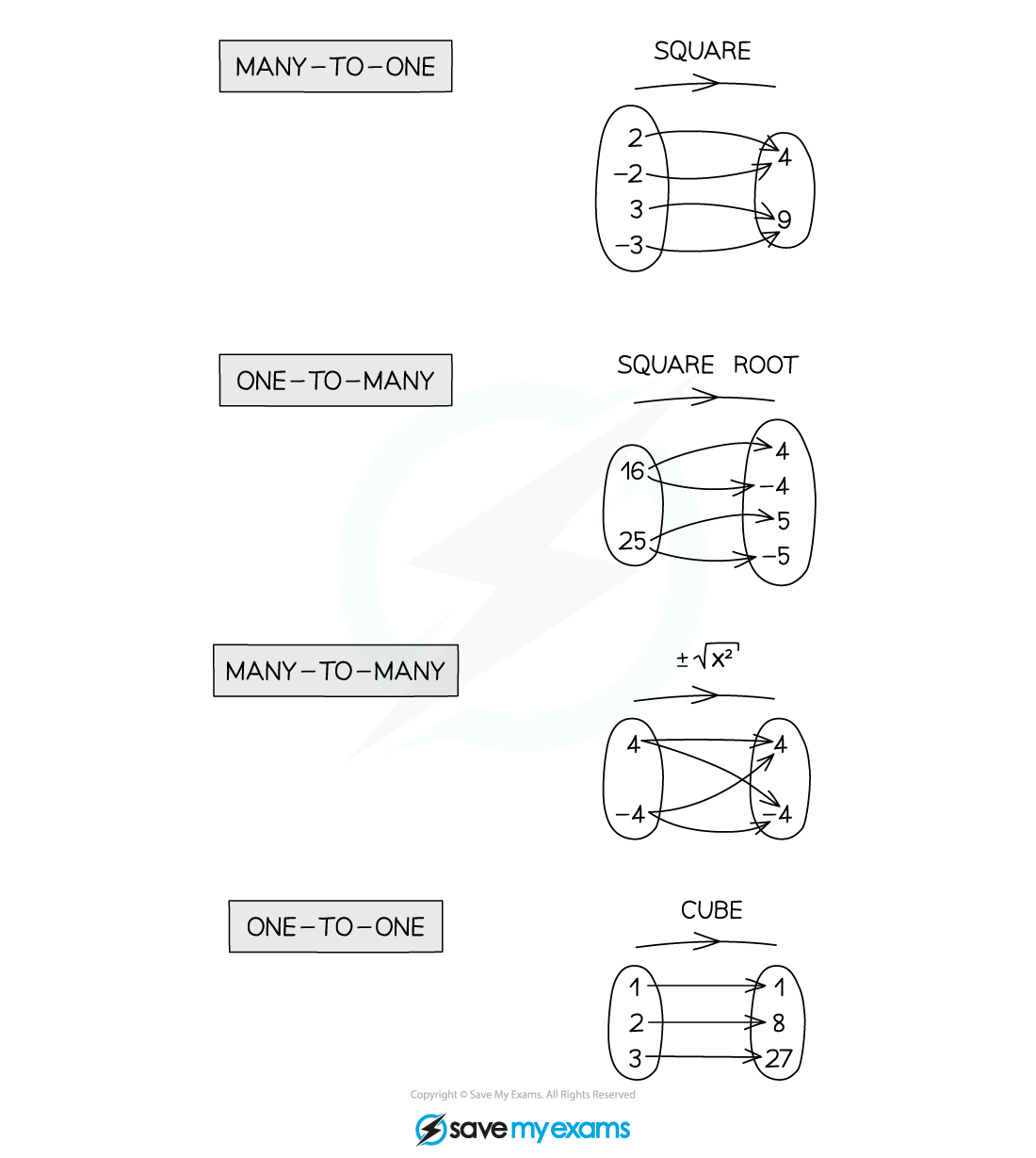
Mappings can be
‘many-to-one’ (many ‘input’ values go to one ‘output’ value)
‘one-to-many’
‘many-to-many’
‘one-to-one’
What is the difference between a mapping and a function?
A function is a mapping where every ‘input’ value maps to a single ‘output’
Many-to-one and one-to-one mappings are functions
Mappings which have many possible outputs are not functions

What is function notation?
Functions are denoted by the notation f(x), g(x), etc
eg. f(x) = x2 - 3x + 2
Or the alternative notation
eg. f : x ↦ x2 – 3x + 2
What sets of numbers do I need to know?
Functions often involve domains and ranges for specific sets of numbers
All numbers can be organised into different sets ℕ, ℤ, ℚ, ℝ
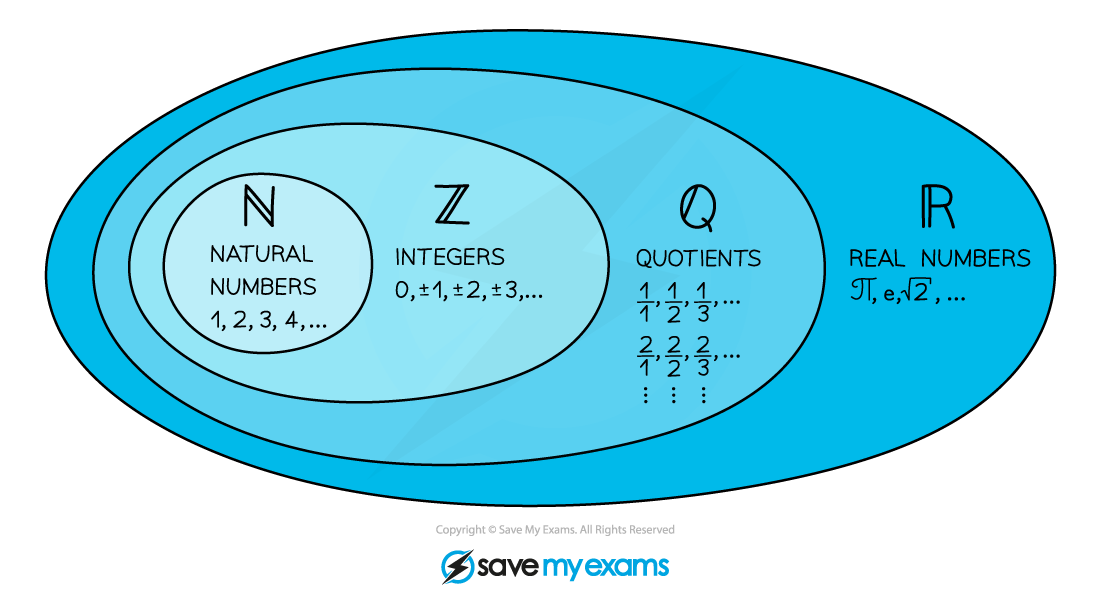
So ℕ is a subset of ℤ etc
ℤ- would be the set of negative integers only
What is the domain of a function?
The domain of a function is the set of values that are allowed to be the ‘input’

A function is only fully defined once its domain has been stated
Restrictions on a domain can turn many-to-one functions into one-to-one functions
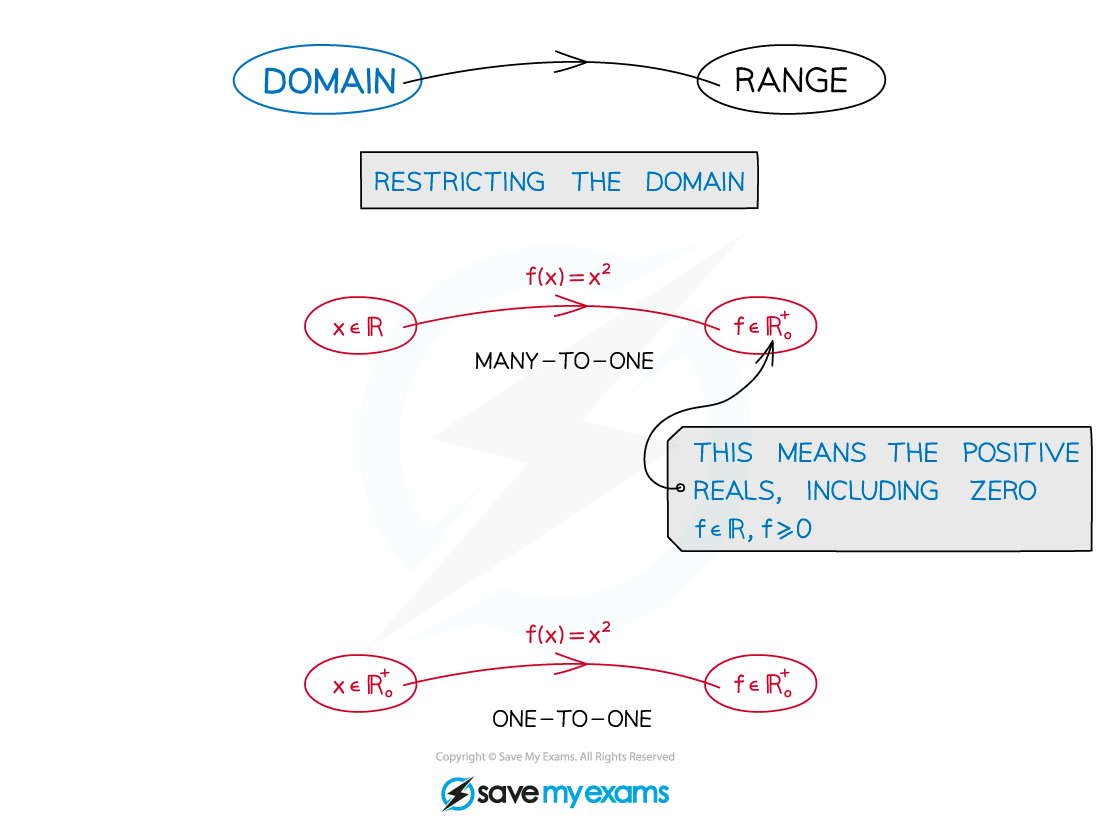
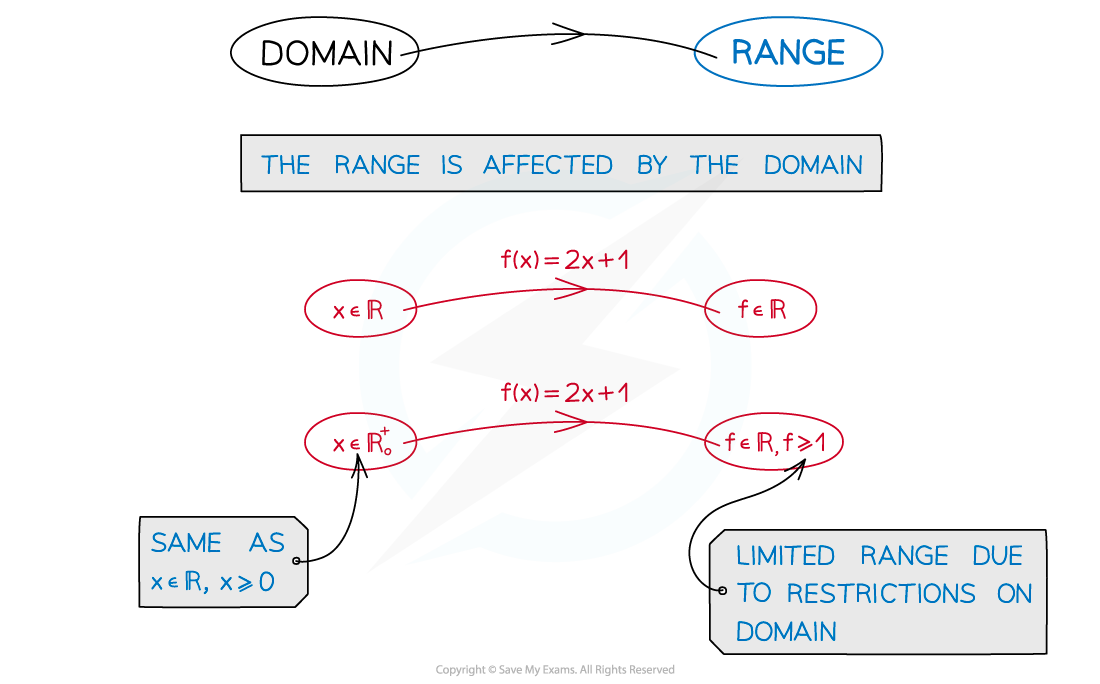
What is the range of a function?
The range of a function is the set of values of all possible ‘outputs’

The type of values in the range depend on the domain
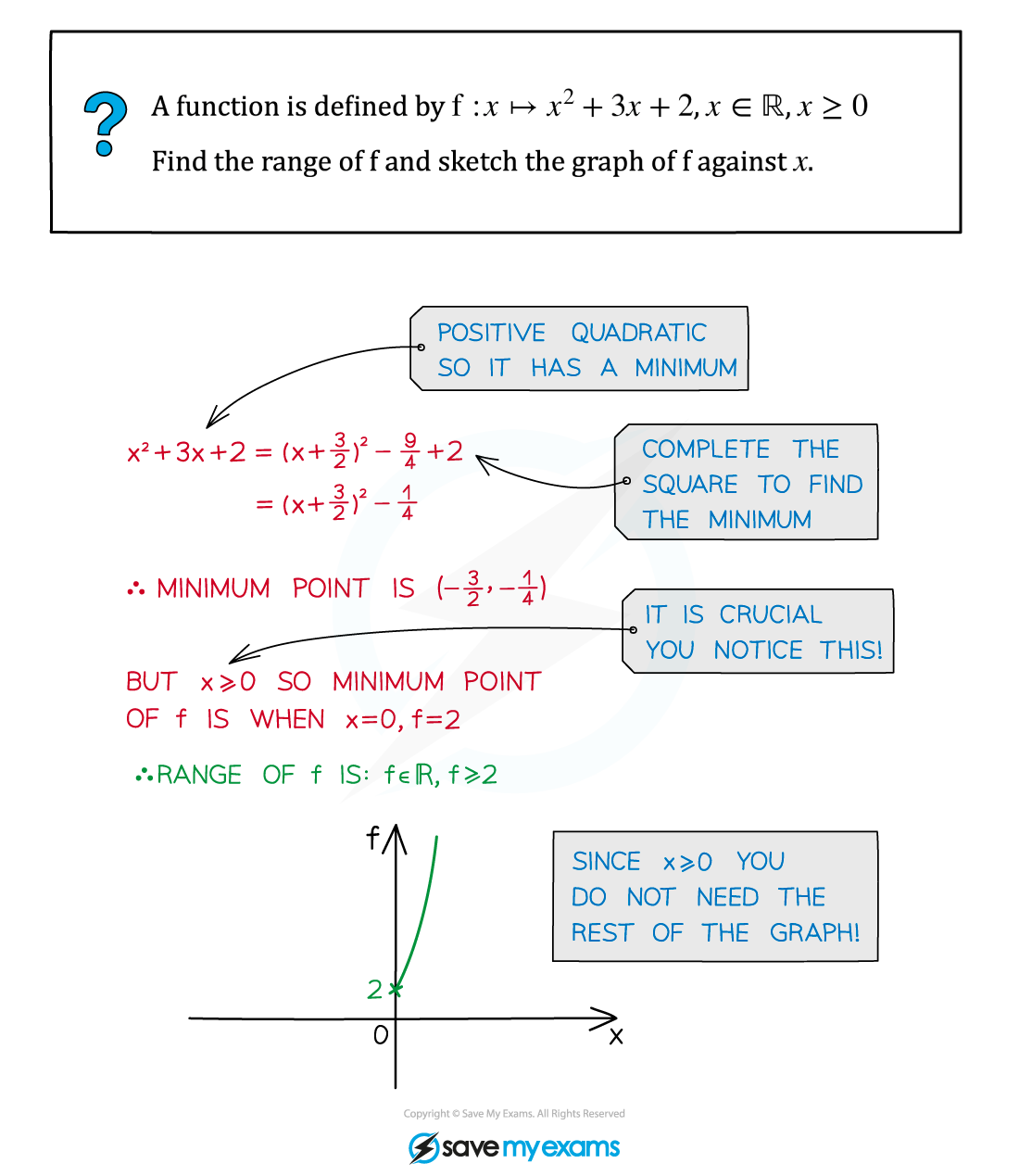
Worked Example

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
