The Light-Dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis (College Board AP® Biology): Study Guide
The light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages:
The light-dependent stage
The light-independent stage
The light-dependent reactions capture light energy and produce:
ATP
NADPH
The products of the light-dependent reactions are passed to the Calvin Cycle (light-independent reactions), where they are needed for the production of organic molecules via metabolic reactions
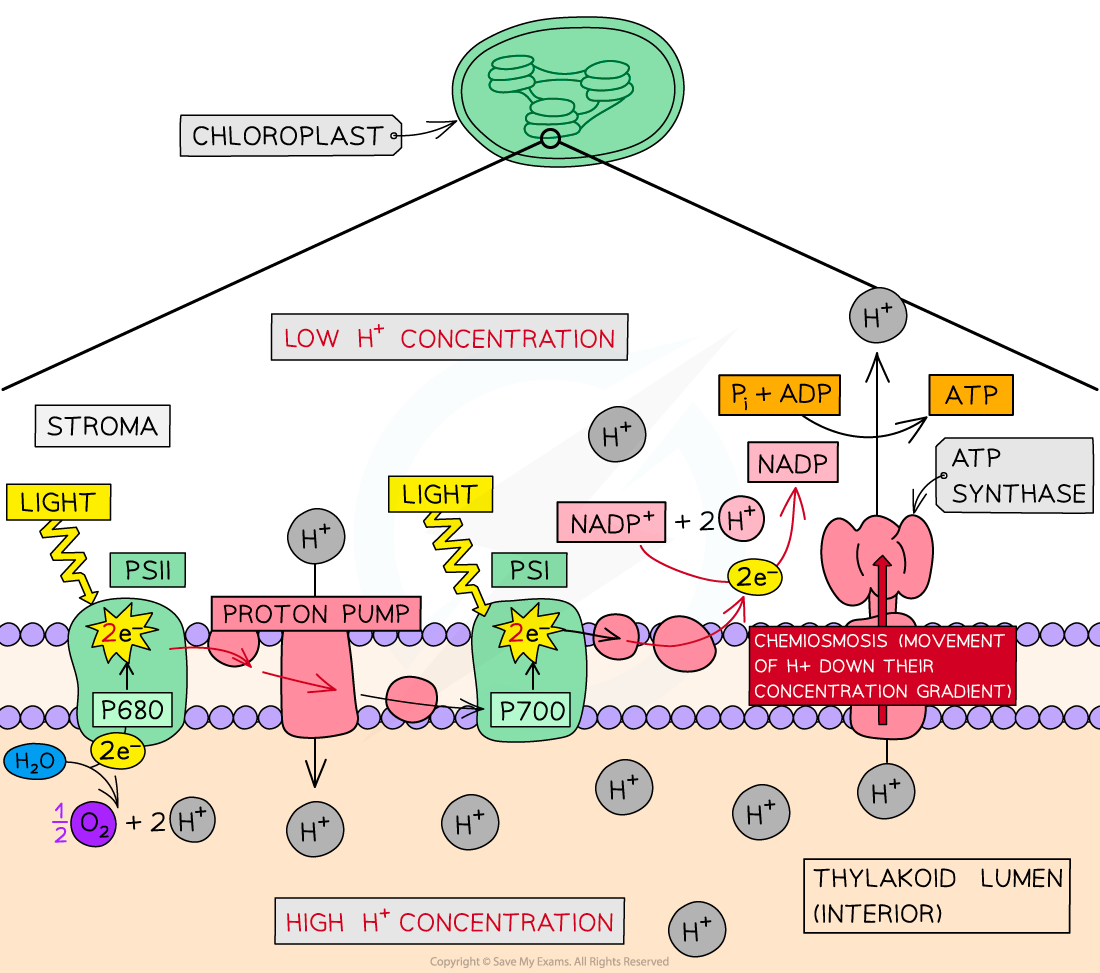
The electron transport chain
The electron transport chain is a series of electron carrier proteins embedded within the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts (it also occurs in mitochondria during cellular respiration, and across prokaryotic plasma membranes)
The events of the electron transport chain are as follows:
Light energy is absorbed by photosystems I and II
Light energy is transferred to electrons
Energised electrons are passed along the electron transport chain
The electron carriers are alternately reduced and oxidized as electrons are passed along the chain
Energy is released from the electrons as they pass down the ETC
The energy released is used to generate a proton gradient
Water is split, which provides the electrons to replace those lost from photosystem II
At the end of the electron transport chain, electrons combine with protons (hydrogen ions) and the carrier molecule NADP to produce NADPH:
2H+ + 2e- + NADP+ → NADPH
Lost electrons are replaced as:
electrons from photosystem II pass to photosystem I
electrons from photolysis pass to photosystem II
The proton gradient and ATP
The energy released as electrons pass along the ETC is used to actively transport protons (hydrogen ions) across the thylakoid membrane from the stroma to the thylakoid lumen
This creates an electrochemical gradient
There is a high concentration of protons in the thylakoid lumen and a low concentration in the stroma
The thylakoid membrane acts to separate the two regions, maintaining a concentration gradient
Protons return to the stroma by facilitated diffusion through transmembrane ATP synthase enzymes in a process called chemiosmosis
This process provides the energy needed to synthesize ATP by adding an inorganic phosphate group (Pi) to ADP
ADP + Pi → ATP
The process of ATP production described here is known as photophosphorylation
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The full names of the specific electron carriers in the electron transport chain are beyond the scope of your AP Exam. You need to know the name of the enzyme, ATP synthase, involved in chemiosmosis.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
