Congruence (Edexcel IGCSE Maths B): Revision Note
Exam code: 4MB1
Congruence
What is congruence?
Two shapes are congruent if they are identical in shape and size
One may be a reflection, rotation, or translation of the other
If one shape is an enlargement of the other, then they are not identical in size and so are not congruent
If all the angles are the same, then the shapes are similar
How do we prove that two shapes are congruent?
To show that two shapes are congruent you need to show that they are both the same shape and the same size
If a shape has been reflected, rotated or translated, then its image is congruent to it
Show that corresponding sides are the same length
Show that corresponding angles are the same size
You do not need to show that they are facing in the same direction
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Tracing paper can help in the exam if you are unsure whether two shapes are congruent:
Trace over one shape and then see if it fits exactly on top of the other
Only do this if the image is drawn to scale
Worked Example
Write down the letters of the two shapes below which are congruent to A.
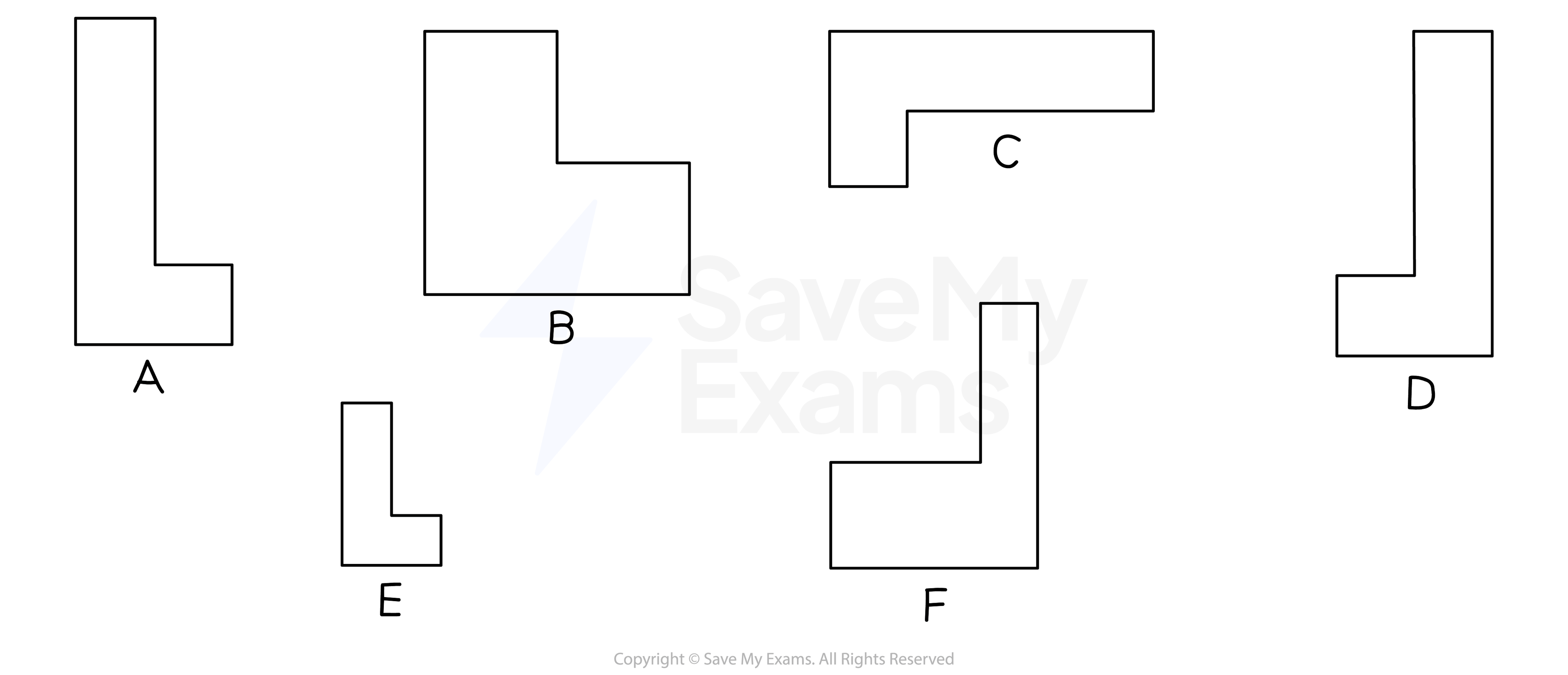
Answer:
Shapes C and D are congruent to A
Did this video help you?
Congruent triangles
What are congruent triangles?
Two triangles are congruent if they are the same size and shape
Although they may be reflections, translations or rotations of each other
All three angles and all three sides must be the same in both triangles
How do I prove that two triangles are congruent?
We only need to show that 3 of the 6 things are the same for both triangles
as long as they are the right three!
To do this we must use one of the 5 standard tests
Name | Description | Diagram |
SAS | Two sides and the angle between them |  |
ASA | Two angles and the side between them |  |
AAS | Any two angles and any side |  |
SSS | All three sides |  |
RHS | The hypotenuse and any other side for a right-angled triangle |  |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
AAA and SSA are not congruence conditions.
AAA (all three angles the same) shows that the triangles are similar, but is not enough to show that they are congruent
SSA (two sides and an angle not between the sides) is also not enough to prove congruence
Two triangles can meet the SSA condition without being congruent
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The course specification does not explicitly mention the AAS test. It has however been accepted in past paper mark schemes for proving congruence.
AAS and ASA are essentially equivalent
Because if you know two angles, you can always find the third one using 180° in a triangle
That converts 'AAS' to 'ASA'
Worked Example
Prove that triangles ABC and PQR are congruent.
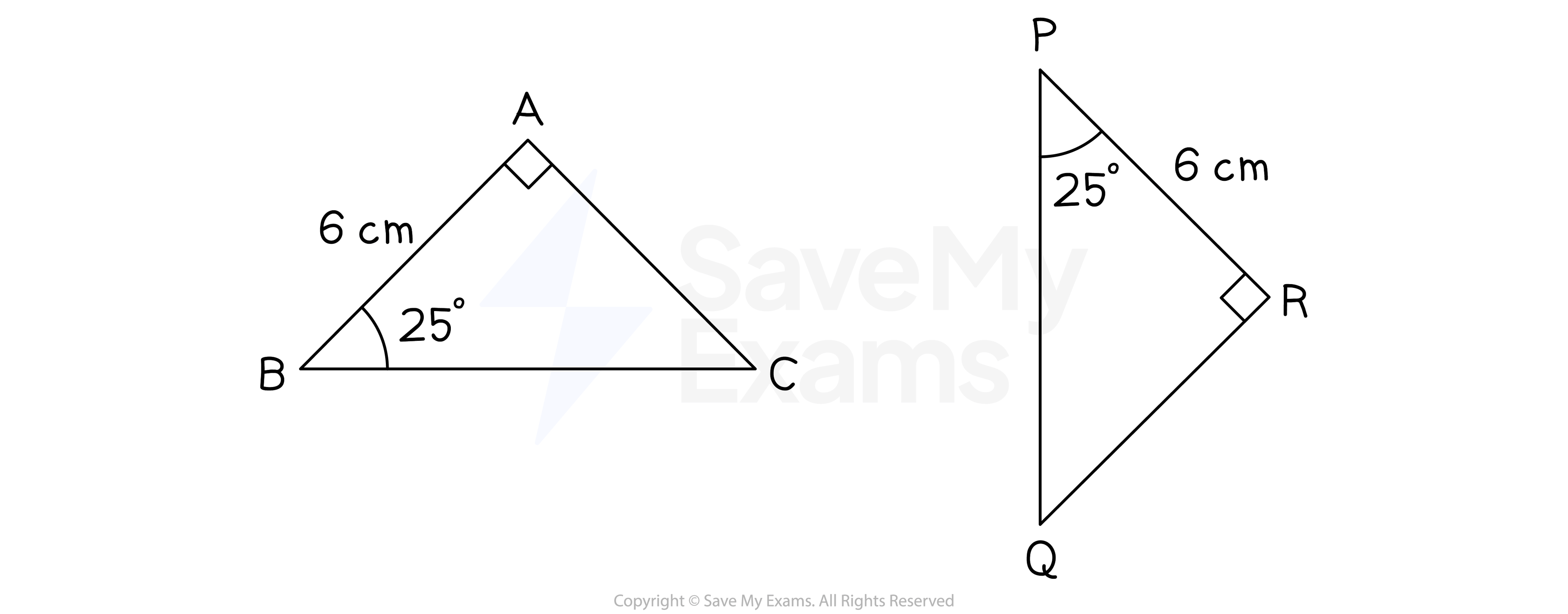
Answer:
Angle ABC and angle RPQ are both 25°
Angle BAC and angle PRQ are both 90°
Line PR and line AB are both 6cm
Two angles are the same, and the lengths between them are the same
Triangles are congruent by the ASA condition

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
