Determinant of a Transformation Matrix (Edexcel IGCSE Maths B): Revision Note
Exam code: 4MB1
Determinant of a transformation matrix
What does the determinant of a transformation matrix represent?
When a 2×2 matrix is used to represent a transformation
the determinant of the matrix is the area scale factor of the transformation
I.e. the area of a transformed shape is equal to
the area of the original shape
times the determinant of the transformation matrix
The determinant of a 2×2 matrix
is
Worked Example
A triangle has vertices with coordinates (1, -3), (7, -3) and (3, 1).
(a) Find the coordinates of the vertices of the image triangle when that triangle is transformed by the matrix .
Answer:
You can represent the triangle as a 2×3 matrix of vertices
This will be the coordinates of the vertices as column vectors, but written in a single matrix
To transform the triangle, multiply its matrix by the transformation matrix
Write the new vertices as coordinates
,
and
(b) Find the area of the image triangle.
Answer:
The original and transformed triangles look like this:
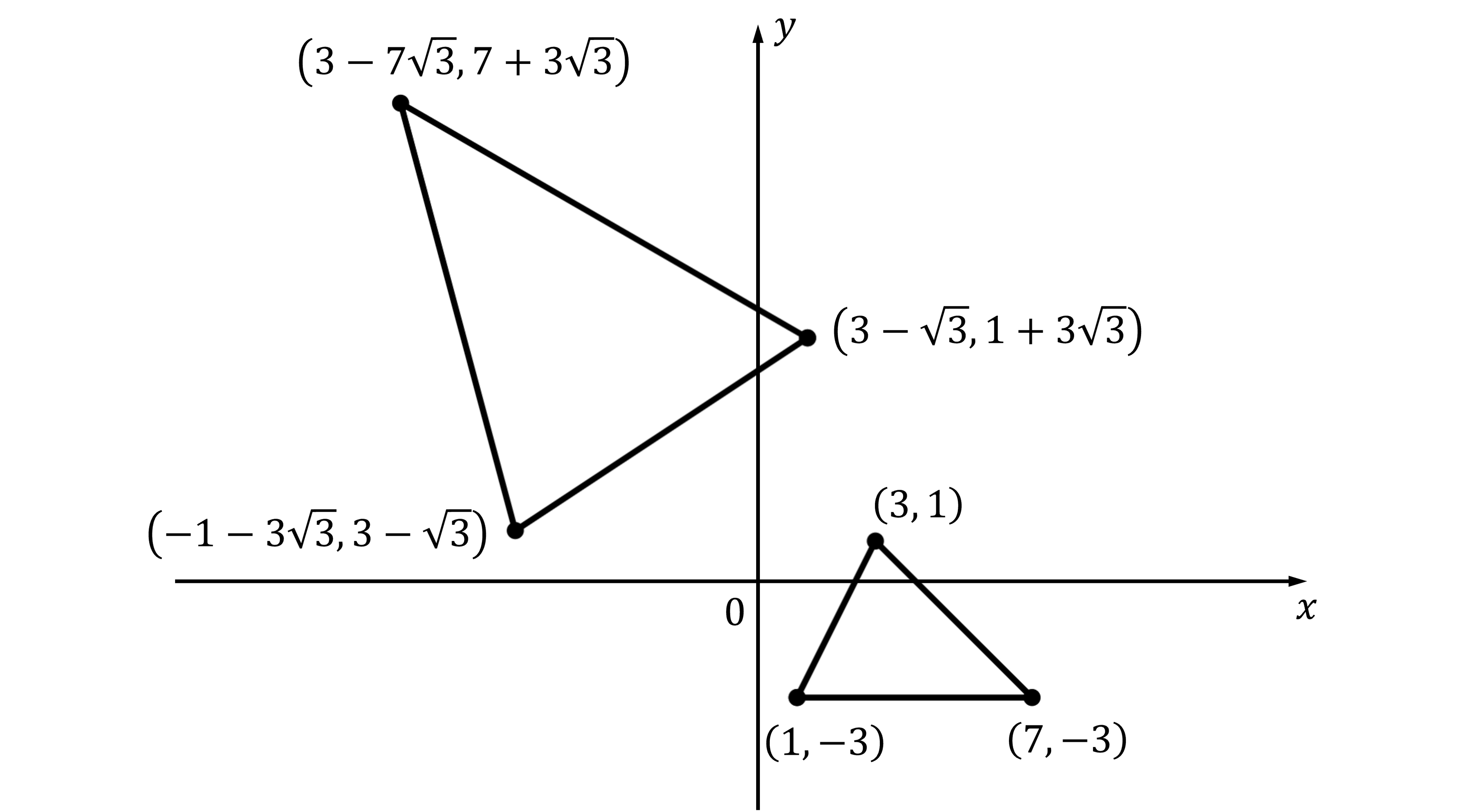
Trying to calculate the area of the transformed triangle directly would be quite challenging, to say the least!
However the area of the original triangle is easy to calculate
It has a base of 6, and a height of 4
Use
Find the determinant of the transformation matrix
The determinant of a 2×2 matrix
is
That is the area scale factor of the transformation
So multiply the original area by 4 to find the transformed area
Area of the image triangle is 48

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
