Modulus of a Vector (Edexcel IGCSE Maths B): Revision Note
Exam code: 4MB1
Did this video help you?
Modulus (magnitude) of a vector
How do I find the modulus of a vector?
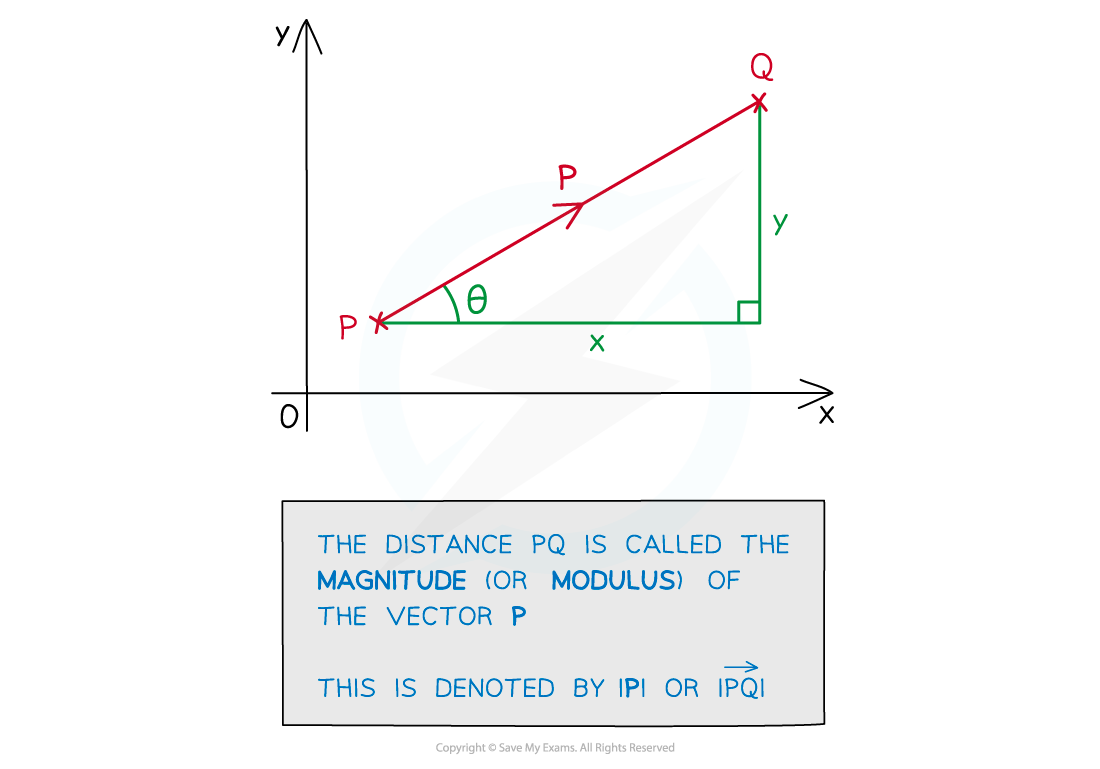
The modulus of a vector is its length (distance)
It is sometimes also called the magnitude
This is always a positive value
The direction of the vector is irrelevant
The modulus of
is written
The modulus of a is written |a|
Depending on the use of the vector, the modulus of a vector represents different quantities
For velocity, modulus would be speed
For a force, modulus would be the strength of the force (in Newtons)
In component form, the modulus is the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle
Use Pythagoras' theorem to find the modulus
The modulus of
is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If there is no diagram, sketch one!
You can sketch a vector and use it to form a right-angled triangle.
Worked Example
Consider two points and
.
(a) Write down the column vector .
Answer:
Find the horizontal and vertical distances between the two points
Subtract the x and y components of A from B
(b) Find the modulus of vector .
Answer:
Sketching a diagram of the vector can help
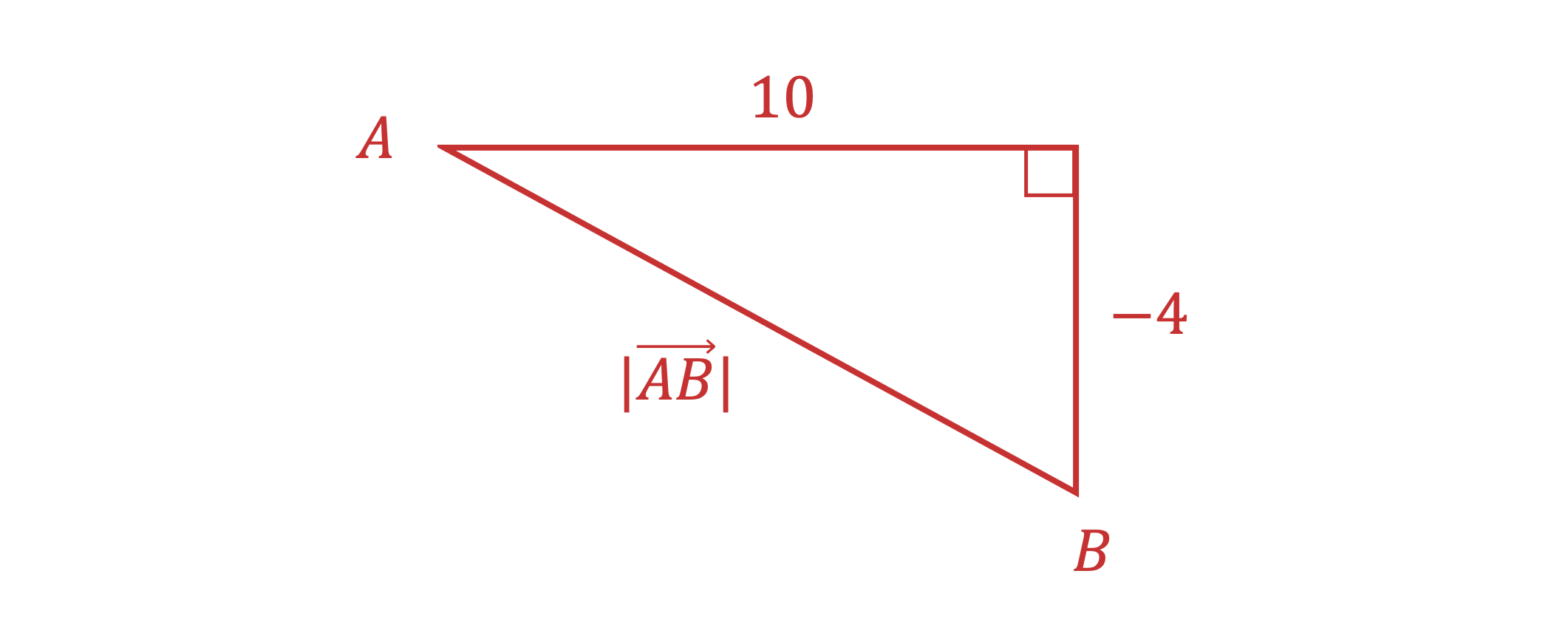
Apply Pythagoras' theorem to the x and y components of
(c) Briefly explain why .
Answer:
The modulus of a vector is it's 'size'
Direction of the vector is ignored
since both vectors have the same length
(d) Another vector, , has three times the modulus of vector
.
Write down a possible column vector for .
Answer:
Being three times means the vector
is three times longer
One way to find a vector is to multiply each component of the vector by 3 or -3
Another possible answer is

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
