Parallel Vectors & Unit Vectors (Edexcel IGCSE Maths B): Revision Note
Exam code: 4MB1
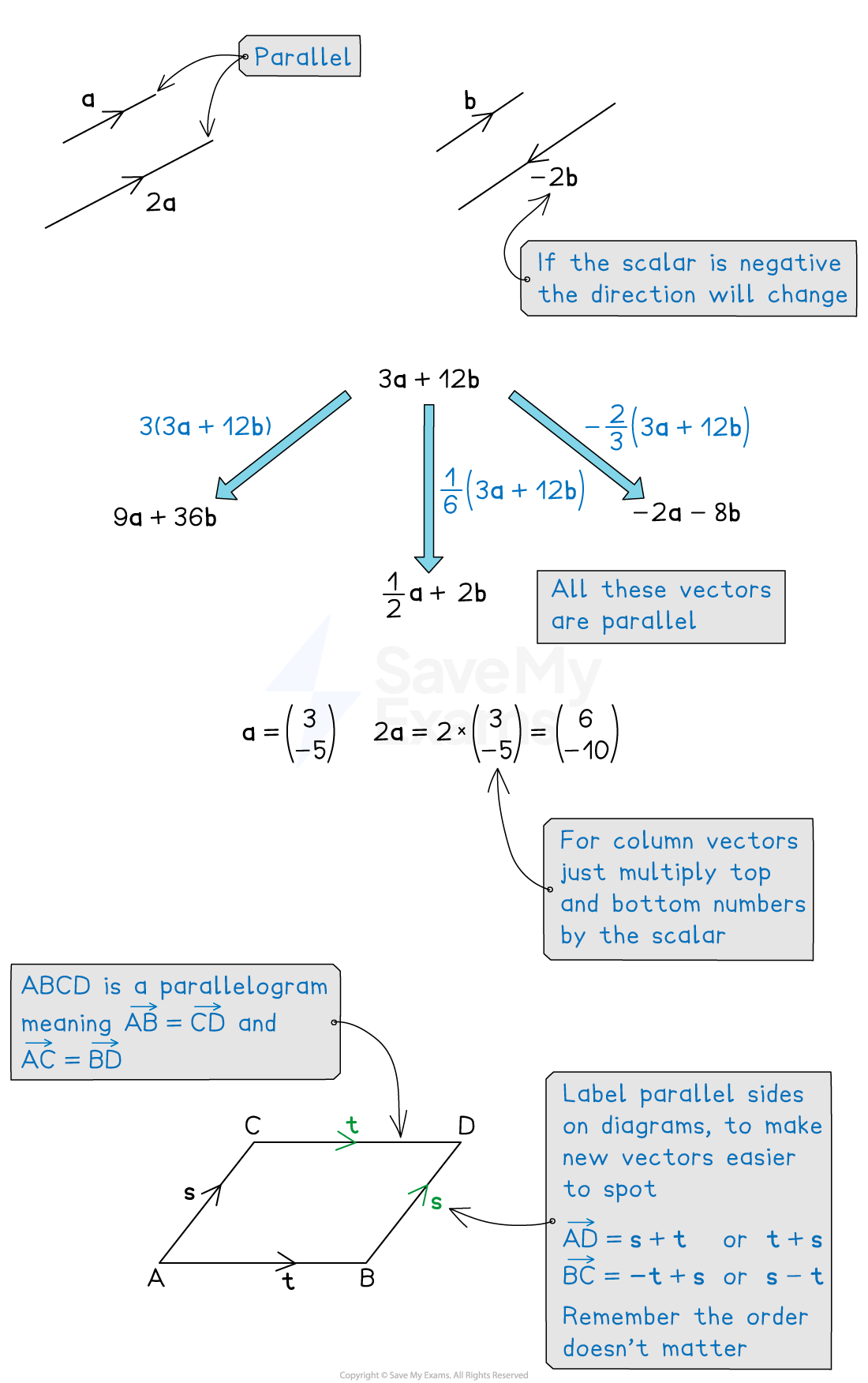
Parallel vectors
How can I tell if two vectors are parallel?
Two vectors are parallel if one is a scalar multiple of the other
This means that all components of the vector have been multiplied by a common constant (scalar)
For example,
and
are scalar multiples
The numbers in the first vector have each been multiplied by 2 to get the numbers in the second vector
Multiplying the components of a vector by a positive scalar changes the magnitude of the vector but not the direction
For example,
is double the length of
but in the same direction
Multiplying the components of a vector by a negative scalar reverses the direction
You can factorise a vector to help spot if two vectors are parallel
They are scalar multiples of the same vector so they are parallel
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are told that two vectors ( and
) are parallel, then it can be helpful to define a scalar to form an equation
.
Worked Example
Show that the vectors and
are parallel.
Answer:
Method 1
Show that one vector is a multiple of the other
, so the two vectors are parallel
Method 2
Show that both vectors are multiples of another vector
and
are both scalar multiples of
, so they are parallel to each other
Unit vectors
What is a unit vector?
A unit vector is a vector with a modulus (length) of 1
To find a unit vector that is in the same direction as the vector
divide the components of the vector by the modulus of the vector
I.e.
is a unit vector in the direction of vector
For example, a unit vector in the direction
is
Worked Example
Find a unit vector in the same direction as .
Answer:
Find the modulus of the vector
Divide each of the vector components by the modulus

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
