Structure of Biological Molecules (Edexcel IGCSE Science (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4SD0
Did this video help you?
Chemical Elements
Most of the molecules in living organisms fall into three categories: carbohydrates, proteins and lipids (fats and oils)
These all contain carbon and so are described as organic molecules
Molecule | Chemical elements |
|---|---|
Carbohydrate | Carbon (C), oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) |
Protein | All contain carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H) and nitrogen (N) |
Lipid | Carbon (C), oxygen (O) and hydrogen (H) |
Structure of Carbohydrates, Proteins & Lipids
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates contain the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
Carbohydrates can be small, simple sugars or more complex larger molecules
A monosaccharide is a simple sugar e.g. glucose (C6H12O6)
A disaccharide is made when two monosaccharides join together, e.g. maltose is formed from two glucose molecules joined together
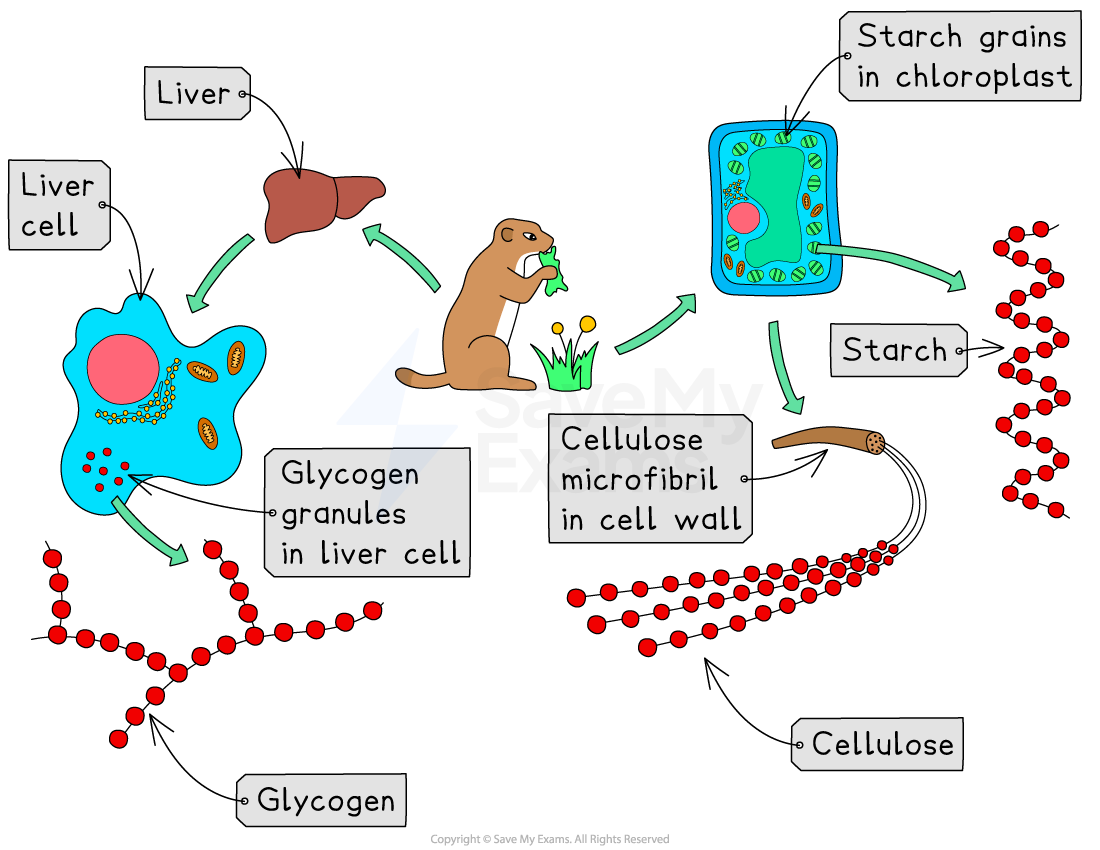
A large polysaccharide is formed when lots of monosaccharides join together
Starch, glycogen or cellulose are all formed when lots of simple glucose molecules join together
Polysaccharides are insoluble and therefore useful as storage molecules
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You don't need to know the terms monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharide for your exam, but you do need to know that starch and glycogen are large molecules formed from many glucose molecules (a simple sugar) joined together.
There is also a difference in how plants and animals store glucose: plants store glucose as starch molecules, whereas animals store glucose as glycogen molecules. Take care not to confuse the two!
Lipids
Lipids, like carbohydrates and proteins, are large molecules made up of smaller basic units: glycerol and fatty acids
Lipids may be solid at room temperature (solid lipids are also known as fats) or liquid at room temperature (liquid lipids are also known as oils )

One type of lipid found in the human body is a triglyceride; like all lipids it is formed from the smaller units glycerol and fatty acids joined together.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You don't need to know the structure of a triglyceride, just that lipids are large molecules formed from the smaller units glycerol and fatty acids, and that lipids contain the chemical elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O).
Proteins
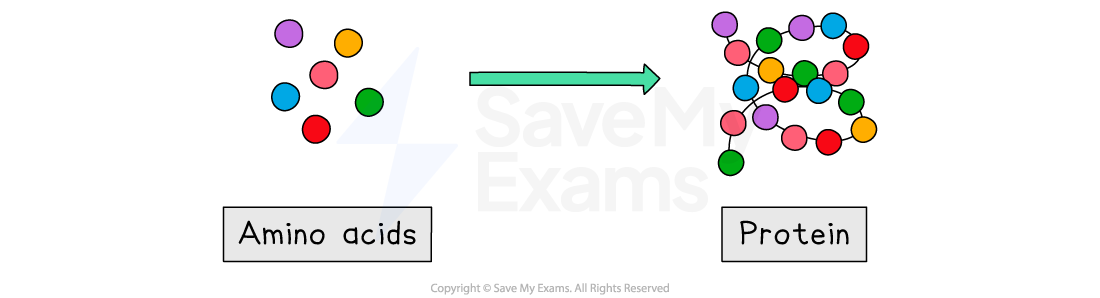
Proteins, like carbohydrates and lipids are large molecules formed from smaller molecules called amino acids
When amino acids are joined together a protein is formed
Amino acids can be arranged in any order, resulting in hundreds of thousands of different proteins
Each protein has a specific amino acid sequence which gives the overall protein molecule a particular shape; and the shape of a protein determines its function
Examples of proteins include enzymes, haemoglobin and keratin (a protein found in hair)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You must be able to recall the chemical elements found in the three biological molecules on this page, as well as what the smaller units are for each molecule. This knowledge links to a later topic in the course - the role of enzymes in human digestion - as all large biological molecules need to be broken down into their smaller units (by enzymes) so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
