The Human Eye: Structure (Edexcel IGCSE Science (Double Award)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4SD0
The Human Eye: Structure
The eye is a highly specialised sense organ containing receptor cells that allow us to detect the stimulus of light
The retina of the eye contains receptor cells sensitive to light
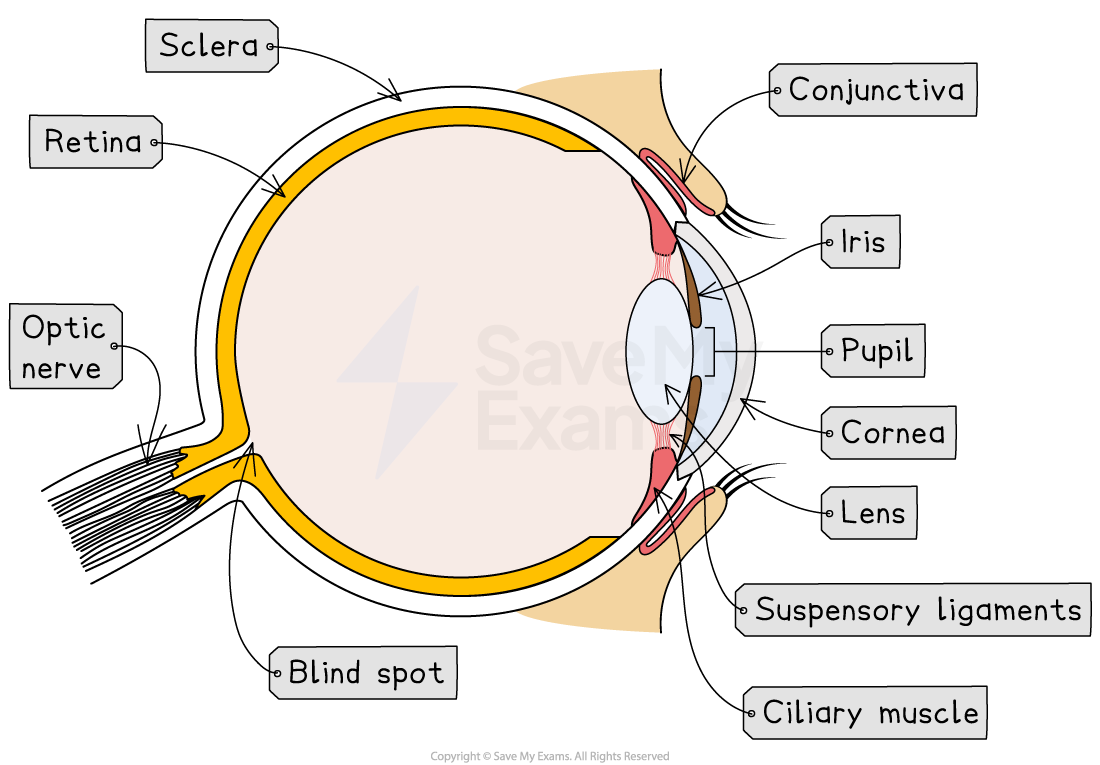
The structures of the eye
Conjunctiva - a clear membrane that covers the white of the eye and the inside of the eyelids; it lubricates the eye and provides protection from external irritants
Cornea - transparent, curved layer at the front of the eye that refracts light as it enters the eye
Sclera - the strong outer wall of the eyeball that helps to keep the eye in shape and provides a place of attachment for the muscles that move the eye
Pupil - circular opening in the centre of the iris that allows light to enter the eye
Iris - controls how much light enters the pupil
Lens - transparent disc that can change shape to focus light onto the retina
Ciliary muscle - a ring of muscle that contracts and relaxes to change the shape of the lens
Suspensory ligaments - ligaments that connect the ciliary muscle to the lens
Retina - contains receptor cells sensitive to light
Fovea - region of the retina that contains densely packed cones (allows eyes to see in good detail and colour)
Optic nerve - carries impulses between the eye and the brain
Blind spot - the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, where there are no light receptor cells
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you can identify the structures of the eye on a diagram because diagrams with labels are a very common form of exam question for this topic.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
