Parametric Differentiation (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9709
Did this video help you?
Parametric differentiation
How do I find dy/dx from parametric equations?
Ensure you are familiar with Parametric Equations – Basics first
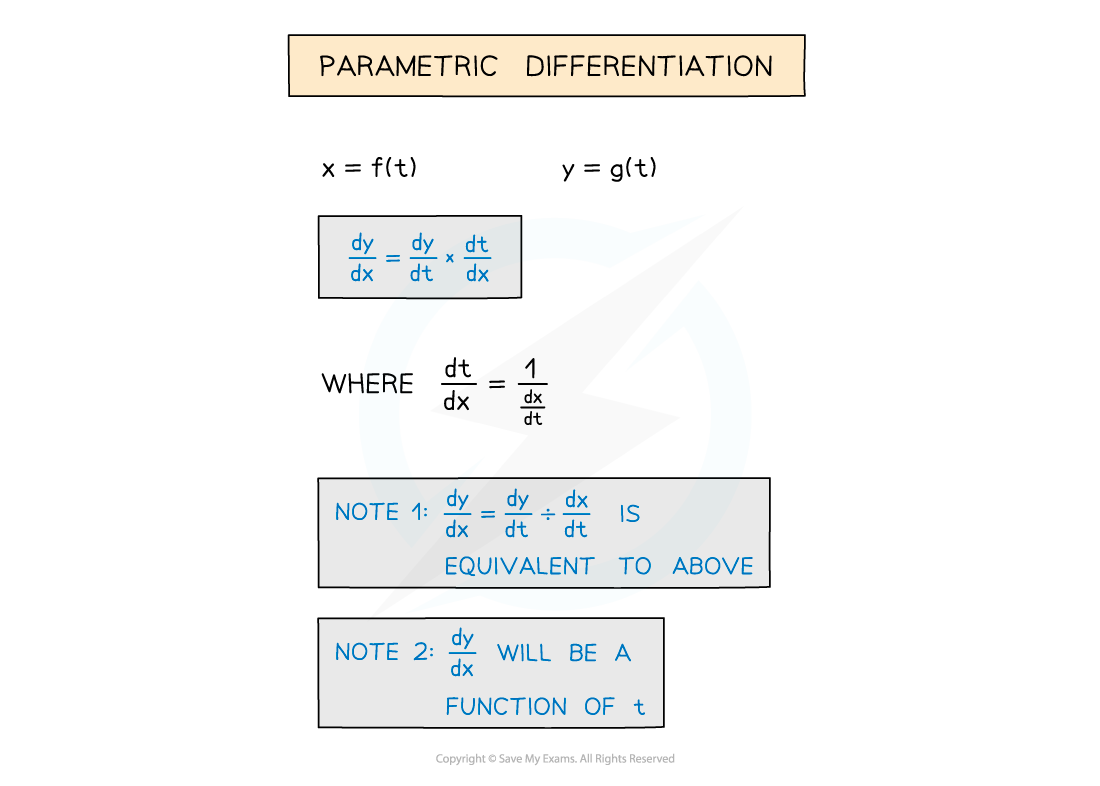
This method uses the chain rule and the reciprocal property of derivatives
Equivalently,
will be in terms of t – this is fine
Questions usually involve finding gradients, tangents and normals
The chain rule is always needed when there are three variables or more – see Connected Rates of Change
How do I find gradients, tangents and normals from parametric equations?
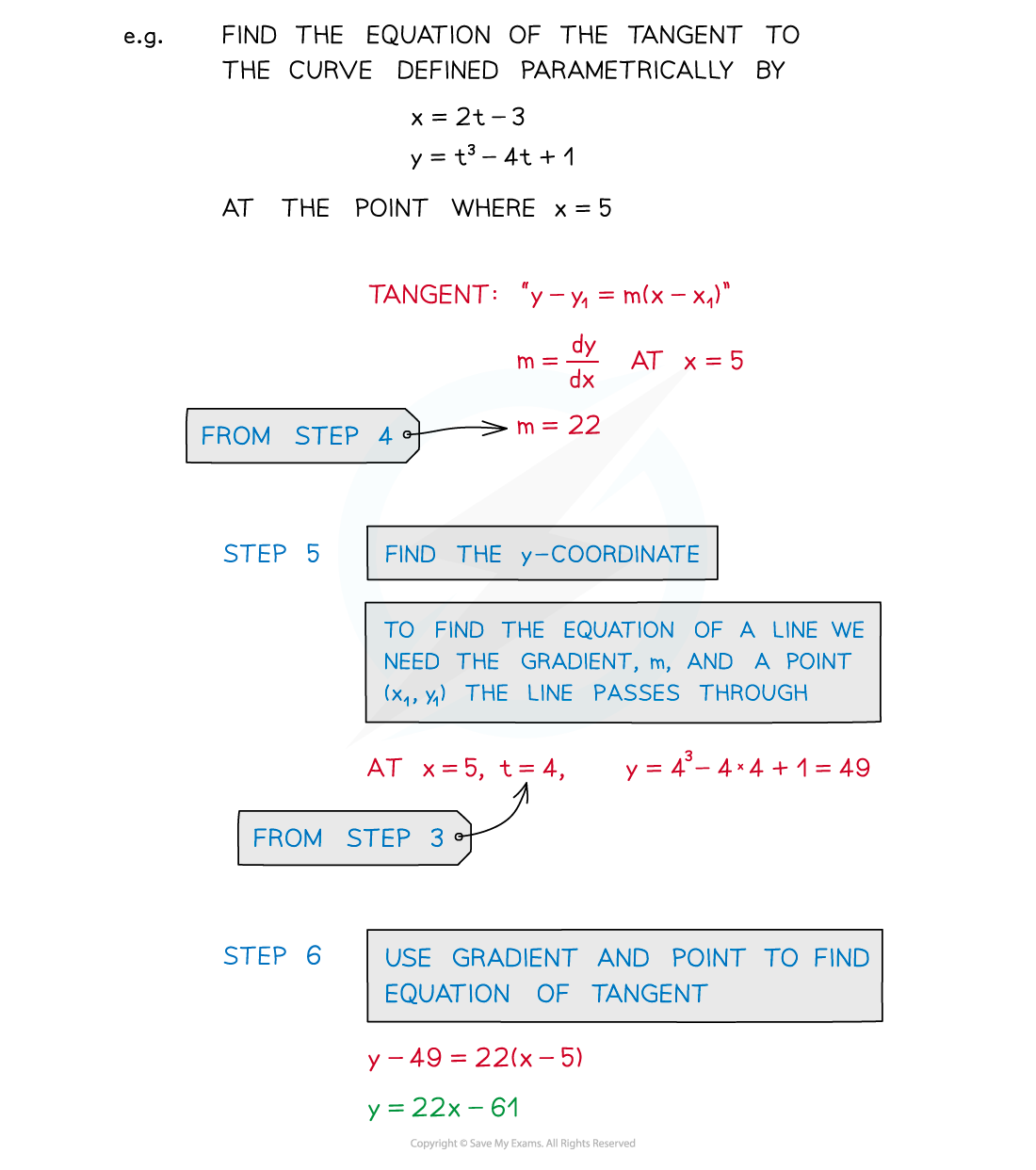
To find a gradient
STEP 1
Find dx/dt and dy/dtSTEP 2
Find dy/dx in terms of tUsing either dy/dx = dy/dt ÷ dx/dt
or dy/dx = dy/dt × dt/dx where dt/dx = 1 ÷ dx/dt
STEP 3
Find the value of t at the required pointSTEP 4
Substitute this value of t into dy/dx to find the gradient
To then go on to find the equation of a tangent
STEP 5
Find the y coordinateSTEP 6
Use the gradient and point to find the equation of the tangent
To find a normal...
STEP 7
Use perpendicular lines property to find the gradient of the normal m1 × m2 = -1STEP 8
Use gradient and point to find the equation of the normal y - y1 = m(x - x1)
How do I solve problems using parametric differentiation?
Questions may require use of tangents and normals as per the coordinate geometry sections
Find points of intersection between a tangent/normal and x/y axes
Find areas of basic shapes enclosed by axes and/or tangents/normals
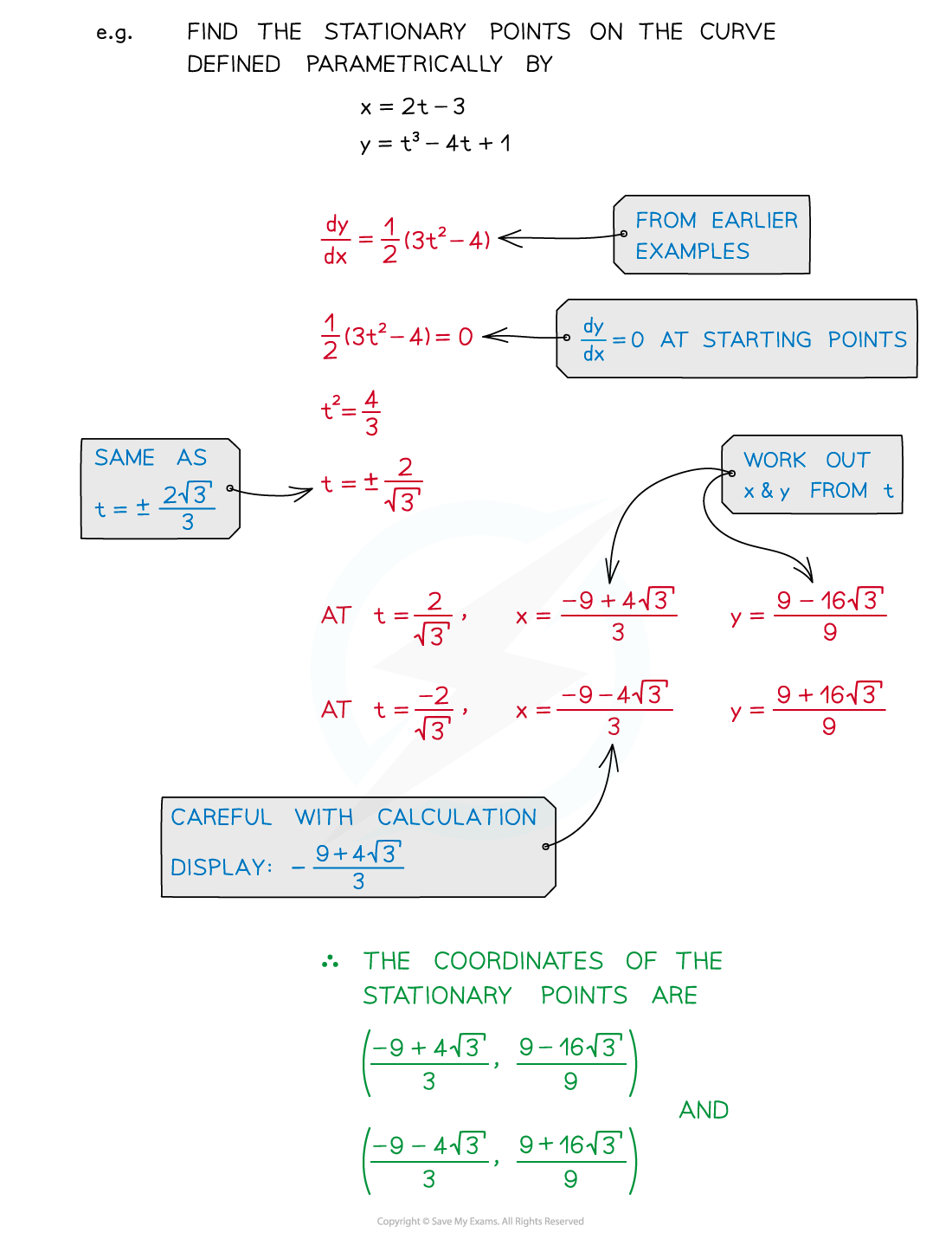
Find stationary points (dy/dx = 0)
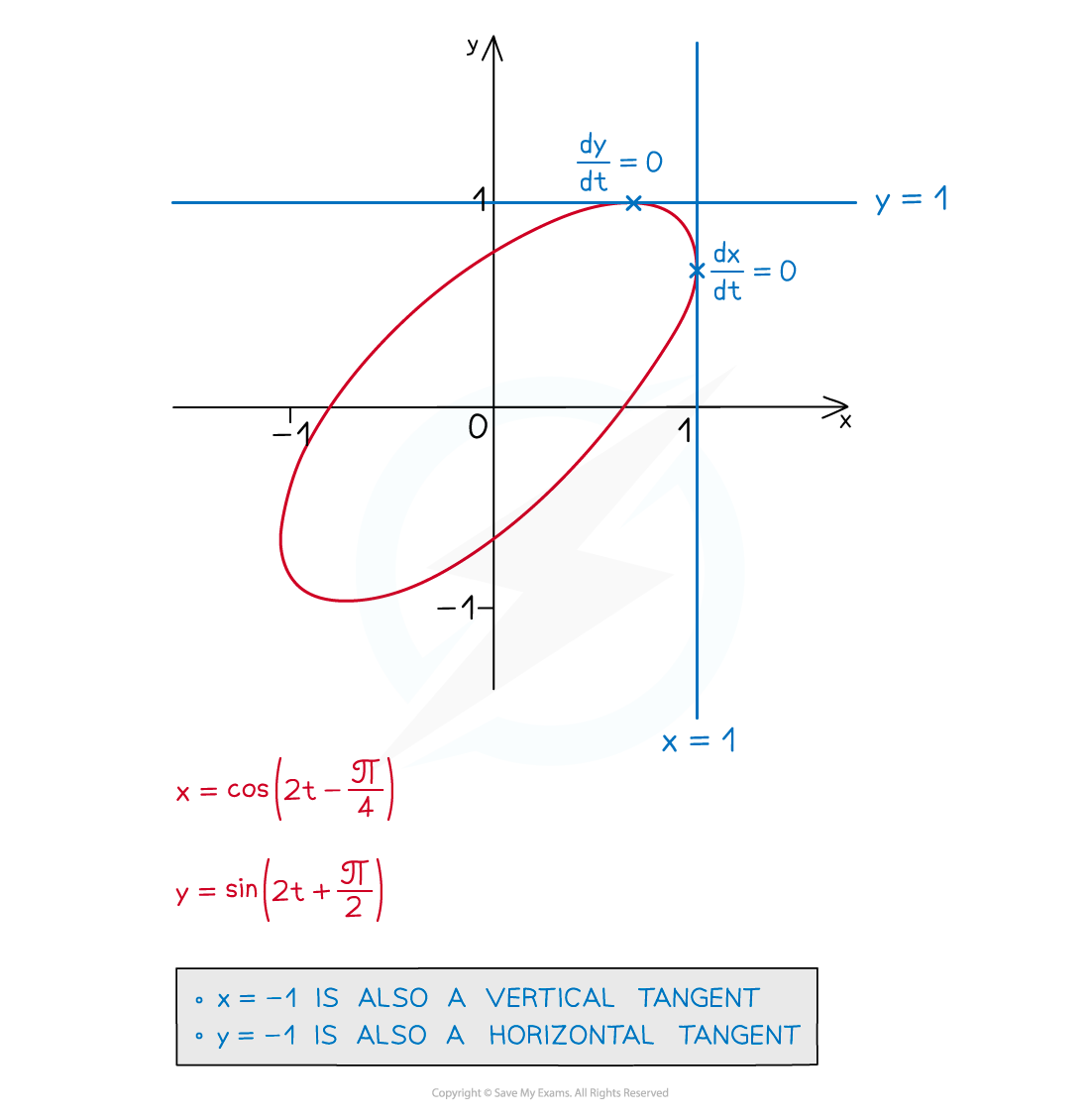
You may also be asked about horizontal and vertical tangents
At horizontal (parallel to the x-axis) tangents, dy/dt = 0
At vertical (parallel to y-axis) tangents, dx/dt = 0
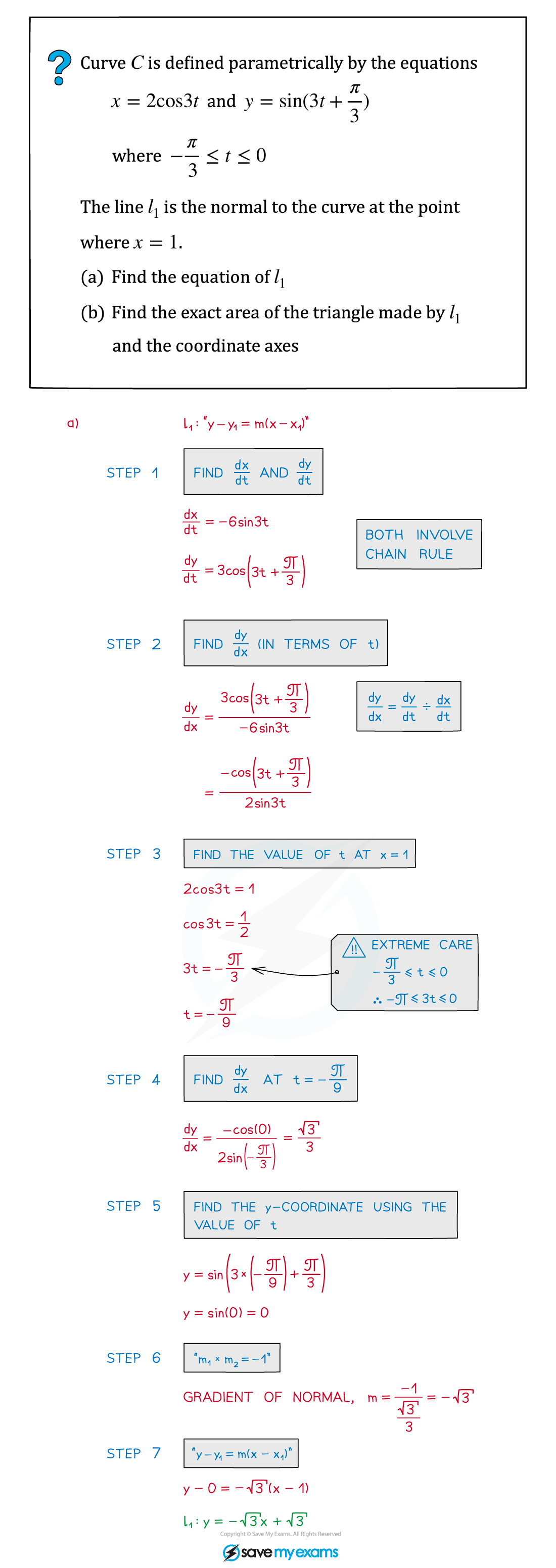
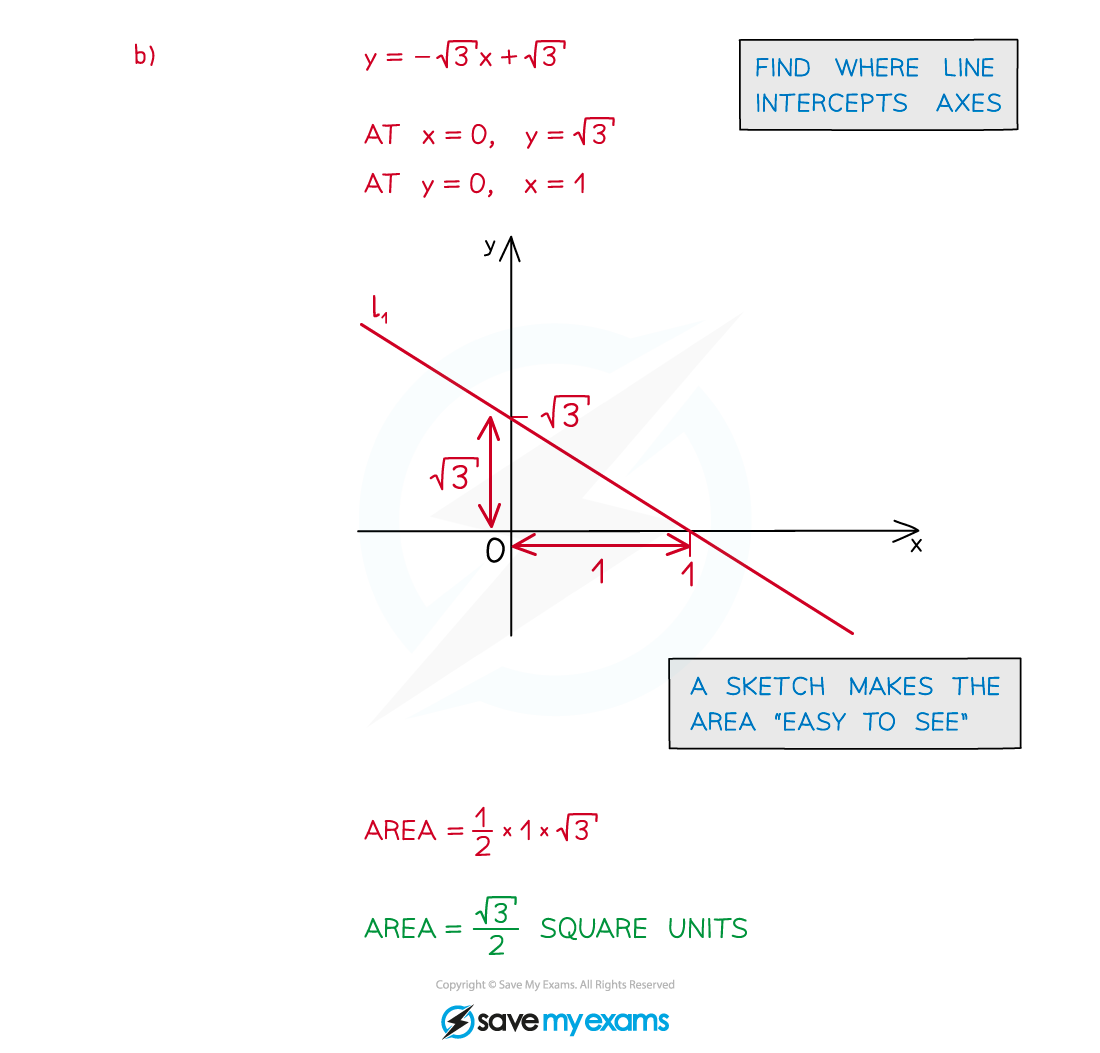
Worked Example

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
