Monomers & Covalent Bonds (College Board AP® Biology): Study Guide
Hydrolysis & dehydration synthesis
Polymers are large molecules that contain many repeated monomers
The term macromolecule is often used to describe biological polymers
Monomer | Polymer |
|---|---|
Monosaccharide, e.g. glucose | Polysaccharide, e.g. starch, glycogen, cellulose |
Amino acids | Polypeptides and proteins |
Nucleotides | Nucleic acids, e.g. DNA, RNA |
Many metabolic processes involve the breaking and making of biological macromolecules; this occurs via:
hydrolysis
dehydration synthesis
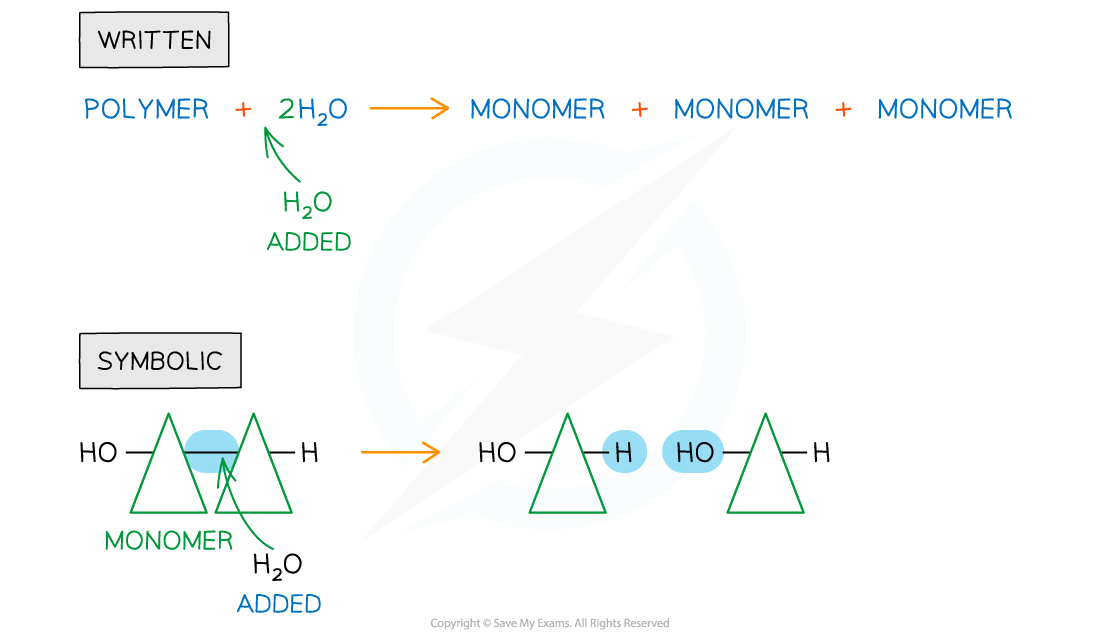
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction involving the cleaving of covalent bonds
This type of reaction breaks down larger molecules into smaller molecules
When water is added to the bond between monomers in a polymer, the bond is broken
The hydrogen ion from a water molecule is added to one monomer
The hydroxyl group of the water molecule is added to the other monomer
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that hydrolysis is a reaction during which molecules are split by the addition of water.
Hydro = water
Lysis = splitting
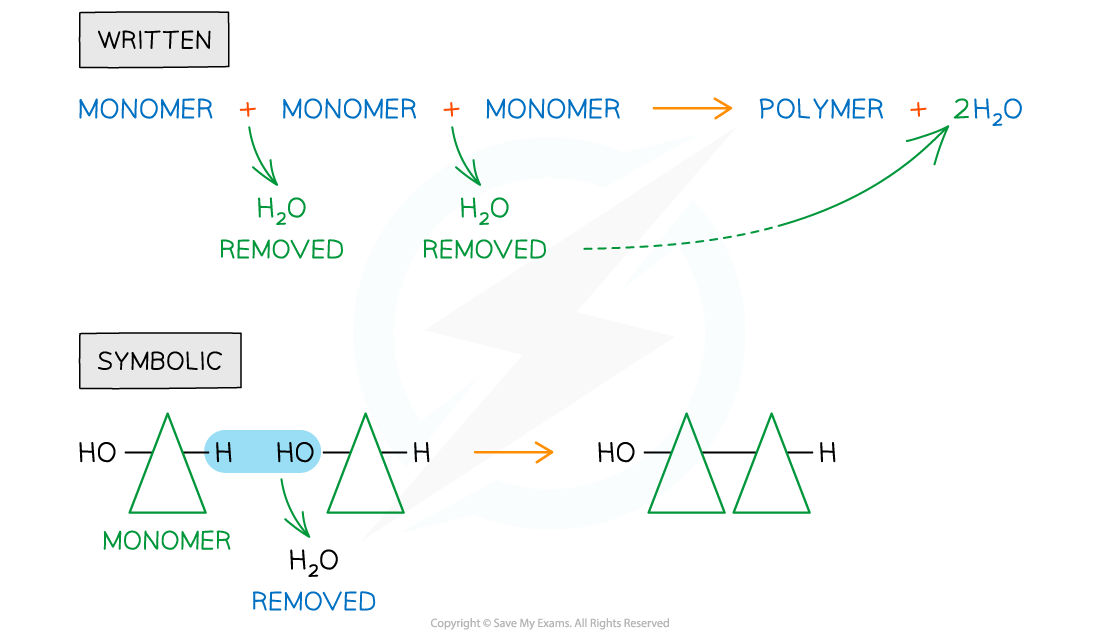
Dehydration synthesis
Dehydration synthesis is a chemical reaction during which covalent bonds are formed
This results in the joining of two smaller molecules to synthesize a larger molecule
A molecule of water is given off as a by-product, hence the term dehydration
A hydrogen ion is removed from one monomer
A hydroxyl group is removed from the other
The joining of many monomers via dehydration synthesis results in formation of a polymer; this is known as polymerization
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Dehydration synthesis is sometimes referred to as a condensation reaction.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
