The Blood (Edexcel IGCSE Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 4BI1
Written by: Lára Marie McIvor
Updated on
Did this video help you?
Components of Blood
Blood consists of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma
Over half of the volume of the blood is made up of plasma
The majority of the other half is made up of red blood cells
The remaining fraction consists of white blood cells and platelets

Blood micrograph

Composition of human blood
Components of the Blood Table
Component | Structure |
|---|---|
Red blood cells | Biconcave discs, no nucleus and contains haemoglobin |
White blood cells | Large cells containing a large nucleus; different types have slightly different structures and functions |
Platelets | Fragments of cells |
Plasma | Clear, straw-coloured aqueous solution |
Plasma
Plasma is a straw coloured liquid which the other components of the blood are suspended within
Plasma is important for the transport of many substances including:
Carbon dioxide - the waste product of respiration, dissolved in the plasma and transported from respiring cells to the lungs
Digested food and mineral ions - dissolved particles absorbed from the small intestine and delivered to requiring cells around the body
Urea - urea is a waste substance dissolved in the plasma and transported to the kidneys
Hormones - chemical messengers released into the blood from the endocrine organs (glands) and delivered to target tissues/organs of the body
Heat energy - heat energy (created in respiration) is transferred to cooler parts of the body or to the skin where heat can be lost
Did this video help you?
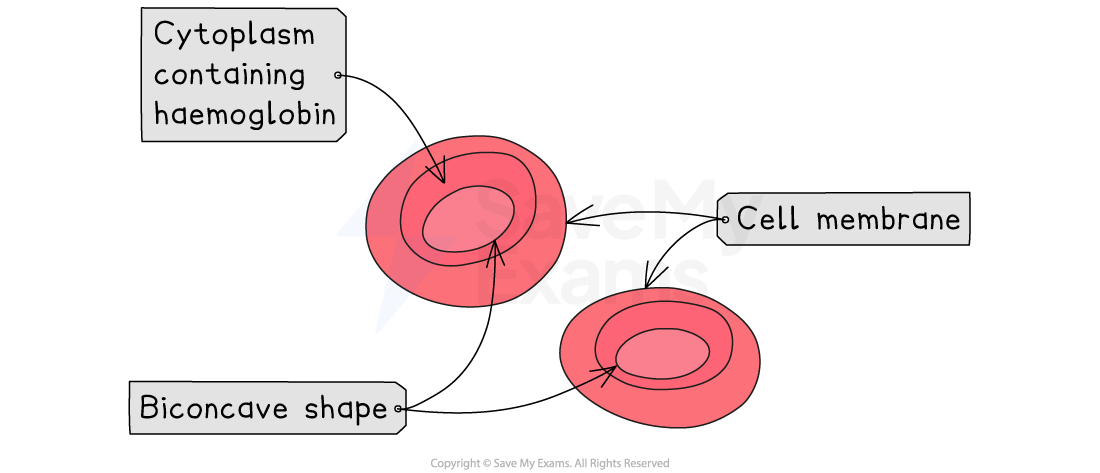
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells are specialised cells which carry oxygen to respiring cells
They are adapted for this function in three key ways:
Red blood cells are packed with haemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin
They have no nucleus which allows more space for haemoglobin to be packed in
Red blood cells have a biconcave disc shape, which means they are thinner in the middle than at the edges. This shape gives them a larger surface area to volume ratio, allowing oxygen to diffuse in and out quickly and efficiently.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
