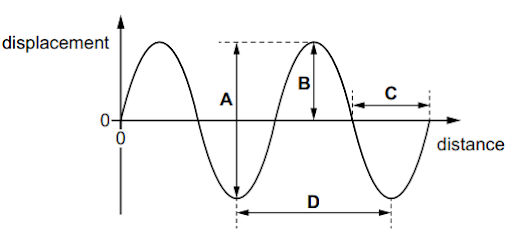
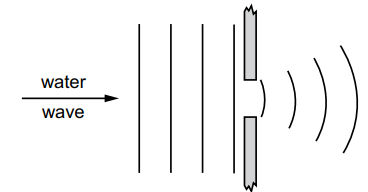
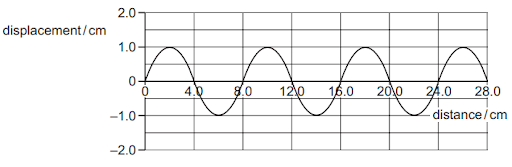
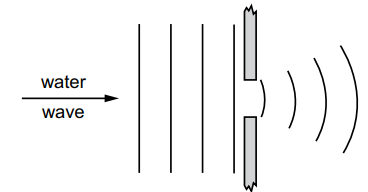
The following table shows some examples of waves
Which row correctly lists the nature of each of the wave types?
| Sound waves | Infrared waves | Red light waves |
A | transverse | longitudinal | transverse |
B | longitudinal | transverse | transverse |
C | longitudinal | longitudinal | transverse |
D | transverse | transverse | longitudinal |
Was this exam question helpful?