Nitrogen Cycle (Edexcel IGCSE Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 4BI1
Written by: Lára Marie McIvor
Updated on
The nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen is present as N2 gas in the atmosphere and within biological molecules, such as proteins, in the tissues of living organisms
Nitrogen is cycled through ecosystems via the nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation makes nitrogen available to living organisms
Nitrogen fixing bacteria convert N2 gas into ammonium compounds, which are then converted into nitrates in the soil
Nitrogen fixing bacteria include:
Free-living bacteria in the soil
Bacteria in the root nodules of leguminous plants (e.g. peas, beans, clover) which form a mutualistic relationship with the plant
Nitrogen can also be fixed by lightning or during the production of chemical fertilisers
After nitrogen fixation has occurred plants absorb nitrates from the soil to build plant proteins
Transfer of nitrogen between living organisms
Animals feed on plants, digest the proteins in the plant tissues, providing nitrogen to build animal proteins
Nitrogen may then be passed from one consumer to another up the food chain in the same way
Release of nitrogen from tissues
Nitrogen from dead organisms and metabolic waste products is returned to the soil as ammonia by decomposers (bacteria and fungi)
Ammonia reacts with water in the soil to form ammonium ions
Plants can’t absorb ammonium ions directly, so nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites, and then into nitrates, which can be taken up again by plants
The conversion of ammonium compounds to nitrates is known as nitrification, and can be summarised as follows:
ammonia → nitrites → nitrates
Denitrification
Denitrifying bacteria convert nitrates back into N₂ gas, returning nitrogen to the atmosphere. This process is known as denitrification
Denitrifying bacteria are active in anaerobic conditions, e.g. in waterlogged or compacted soil
Farmers reduce denitrification by ploughing the soil to increase aeration
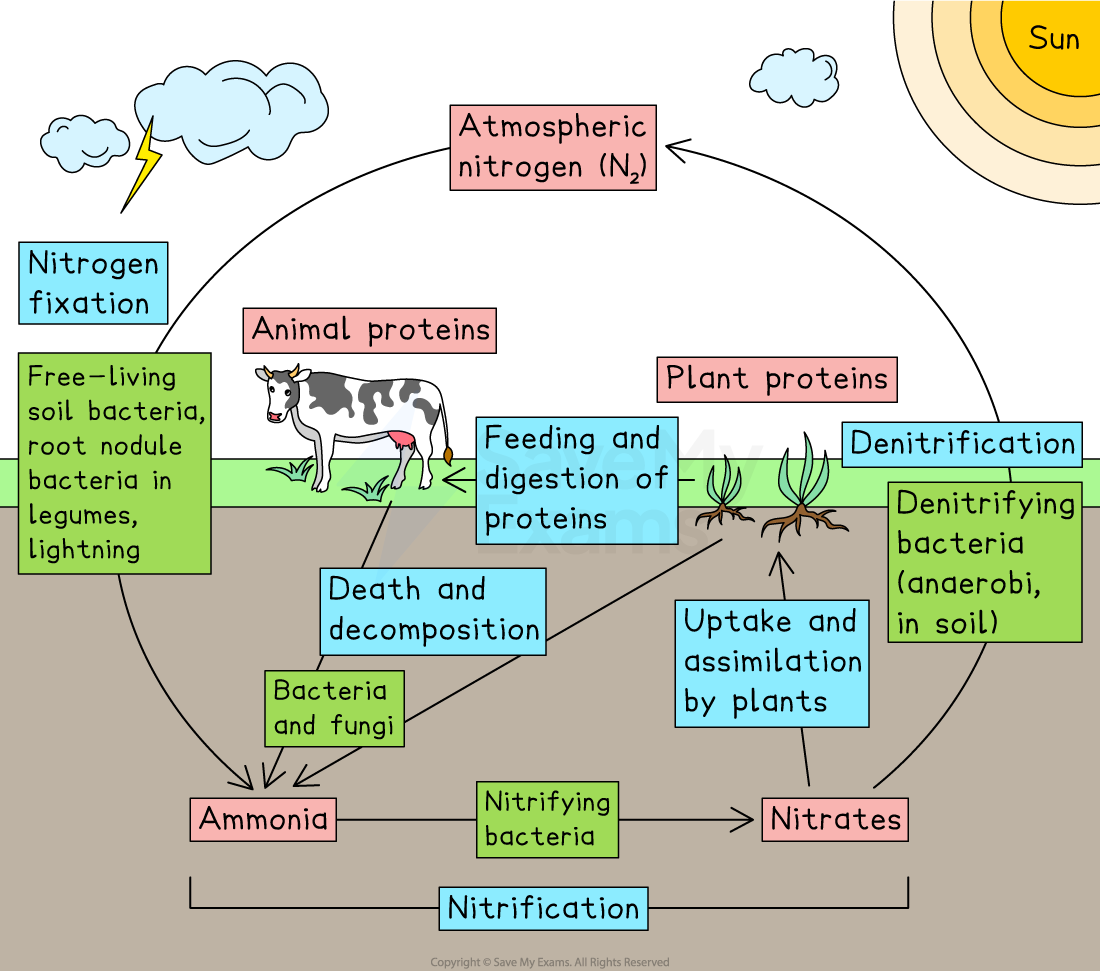
The nitrogen cycle involves nitrogen fixation, decomposition, nitrification and denitrification

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
