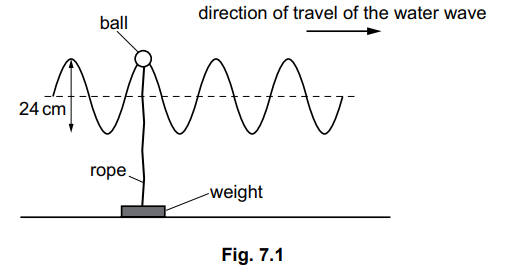
A ray of light refracts as it travels from air into glass, as shown in Fig.7.1.

(i) State which angle w, x, y or z, is the angle of refraction.
[1]
(ii) Light is a transverse wave. State another example of a transverse wave.
[1]
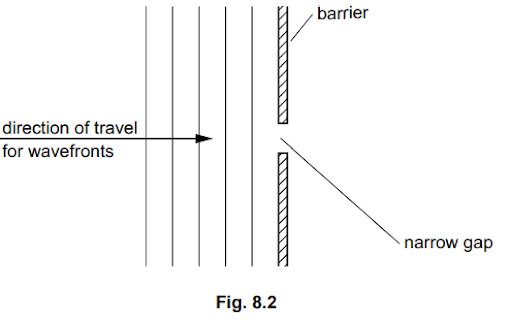
Fig.7.2 represents some wavefronts approaching a barrier with a narrow gap.

(i) On Fig.7.2, draw three wavefronts that have passed through the gap.
[2]
(ii) State the name of the effect in (b)(i).
[1]
Was this exam question helpful?