Uses of Monoclonal Antibodies (Cambridge (CIE) AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Use of monoclonal antibodies
Diagnostic uses of monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies can be used diagnostically for:
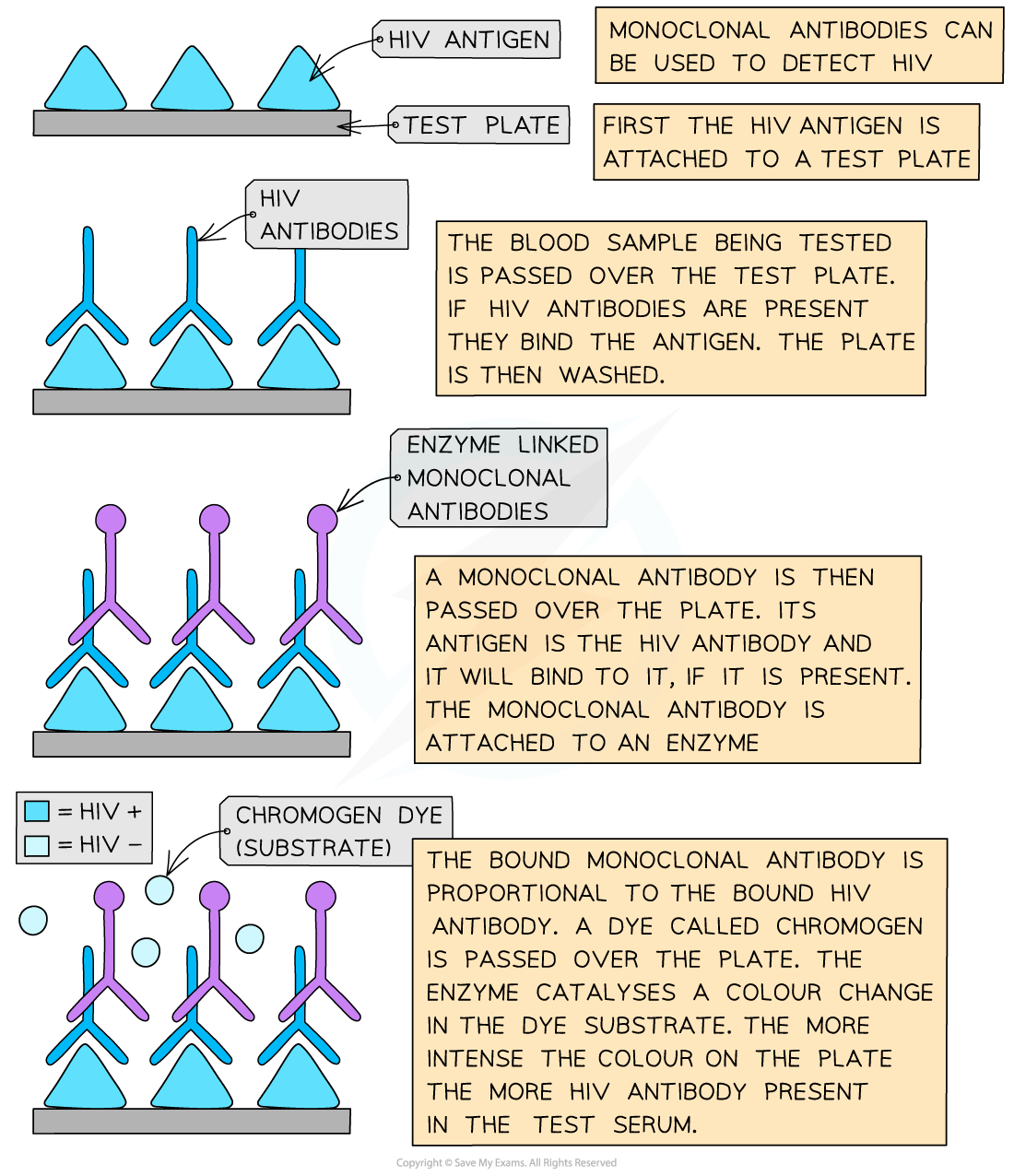
Diagnosing HIV
Detecting the presence of pathogens such as Streptococcus bacteria
Distinguishing between Herpes I and Herpes II virus
Detecting cancer cells
Monoclonal antibodies can also be used to locate the position of blood clots for patients thought to have deep vein thrombosis
This occurs by:
Injecting a mouse with human fibrin (the main protein found in blood clots)
This activates the plasma cells to produce antibodies against fibrin
These cells are collected from the mouse spleen
The plasma cells are then fused with tumour cells forming hybridomas that produce antifibrin antibodies
To detect where the antibodies are binding to fibrin molecules, a radioactive chemical (producing gamma radiation) is attached to the antibodies making them radioactively labelled
A gamma-ray camera is used to detect where these radioactively labelled antibodies have attached to a fibrin molecule, hence indicating where blood clots can be found
Generally monoclonal antibodies are used only once
Therapeutic uses of monoclonal antibodies
Therapeutically, monoclonal antibodies have multiple applications to include:
Treatment for the rabies virus, which can be potentially fatal
This is done by injecting purified antibodies
The prevention of transplanted organ rejection
This is done by intervening with the T-cells involved in the rejection process
Autoimmune therapies for allergic asthma and rheumatoid arthritis
Monoclonal antibodies are able to bind and deactivate factors involved in the inflammatory response
Treatment for diseases caused by the overproduction or inappropriate production of B-cells (e.g. leukaemia, multiple sclerosis and myasthenia gravis)
The antibody (rituximab) binds to cell surface receptor proteins on B-cells (not plasma cells) and causes the death of the cells
Prevention of blood clotting following angioplasty procedures
Monoclonal antibodies bind to receptors on the platelet surface thereby inhibiting fibrinogen from binding and subsequent clotting from ensuing
Targeted treatment of breast cancer
Herceptin is a monoclonal antibody used to treat breast cancer
It recognises receptor proteins on the surface of cancer cells and binds to them allowing the immune system to identify and destroy them
Treatment of melanoma (a type of skin cancer)
The antibody (ipilimumab) binds to a protein produced by T-cells (whose role is to reduce the immune response)
This results in the immune system remaining active against the cancer cells
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You do not need to know all the details for each example given on this page but you need to know specific examples of how monoclonal antibodies can be used as a diagnostic tool and for treatment. You can use a well-annotated diagram to explain how monoclonal antibodies can be used as a diagnostic tool.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?