Quadratic Trigonometric Equations (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Quadratic trigonometric equations
How do I solve quadratic trigonometric equations involving a single ratio?
STEP 1
Make a substitution equal to the trig ratioe.g. for
let
the equation becomes
STEP 2
Solve the new quadratic equationYou can factorise, complete the square, use the formula or use your GDC
or
STEP 3
Replace the variable with the substitution and reject any that do not have solutionsRemember the values of sin and cos range from -1 to 1
has no solutions as
STEP 4
Solve the trig equation(s) for the given interval
How do I solve trigonometric equations involving multiple ratios?
If your equation involves tan and another ratio
Use
to write the equation in terms of sin and cos only
e.g.
becomes
Get rid of any fractions
e.g.
Make the equation equal to zero
Factorise the expression
e.g.
Set each factor equal to zero and solve
e.g.
and
If your equation involves sin2 and/or cos2
Use
to write the equation in terms of only one ratio
e.g.
can be written as
Make the equation equal to zero
e.g.
becomes
Solve the quadratic trig equation
e.g.
and
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If there is a linear trig term and a quadratic trig term, then change the quadratic one to match the linear one. For example, if you have and
, then use
.
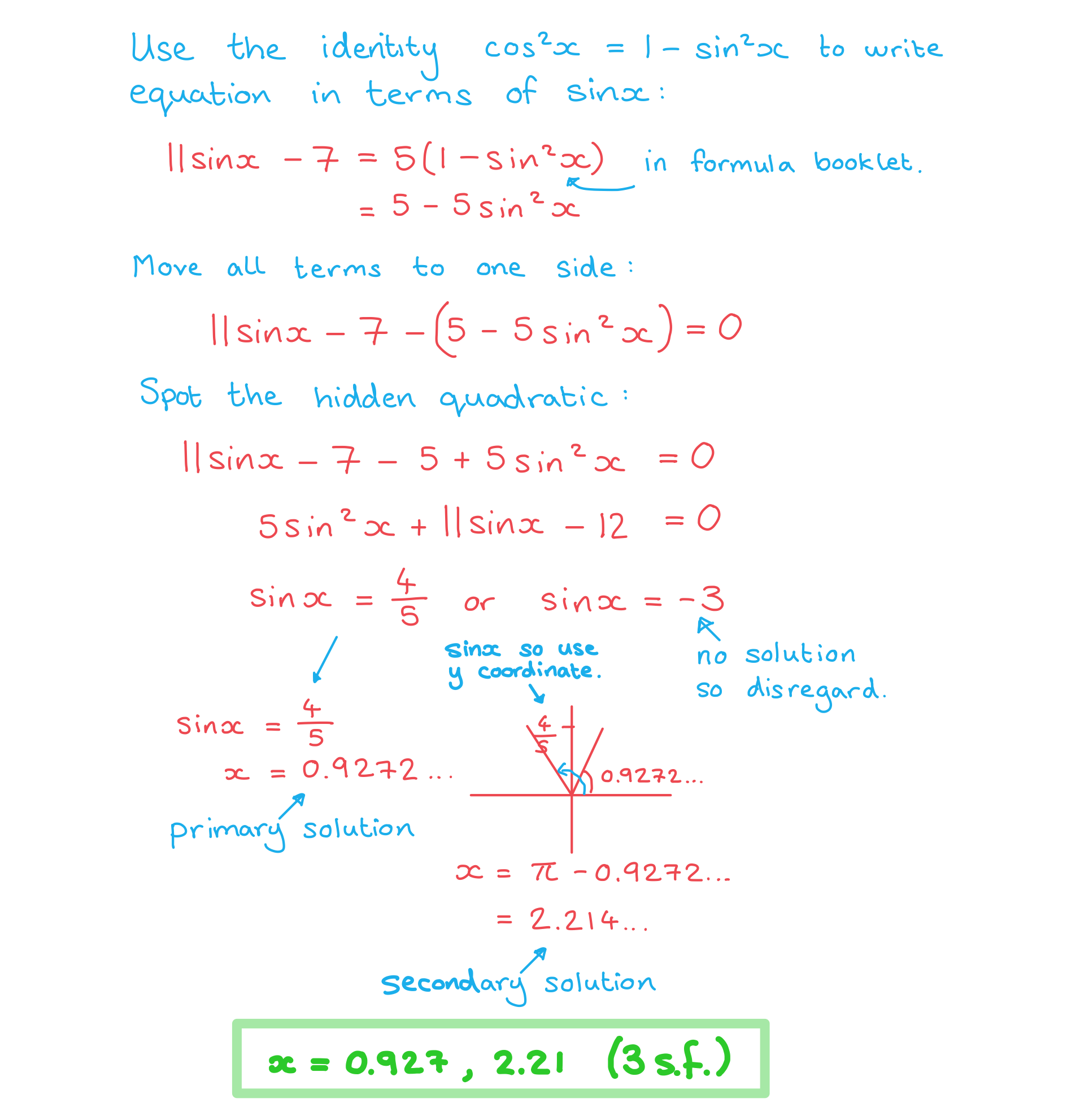
Worked Example
Solve the equation , finding all solutions in the range
.
Answer:

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
