Frequency & Phase of Trig Functions (DP IB Applications & Interpretation (AI)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Frequency & phase of trig functions
How are complex numbers related to sinusoidal functions?
A sinusoidal function is related to an exponential function with a complex argument
You can rewrite
in modulus-argument form
The relevant sinusoidal function is the real or imaginary part of the exponential function
For example,
Complex numbers are particularly useful when working with electrical currents or voltages as these follow sinusoidal wave patterns
AC voltages may be given in the form V = a sin(bt + c) or V = a cos(bt + c)
How can I add two sinusoidal functions which have the same frequencies?
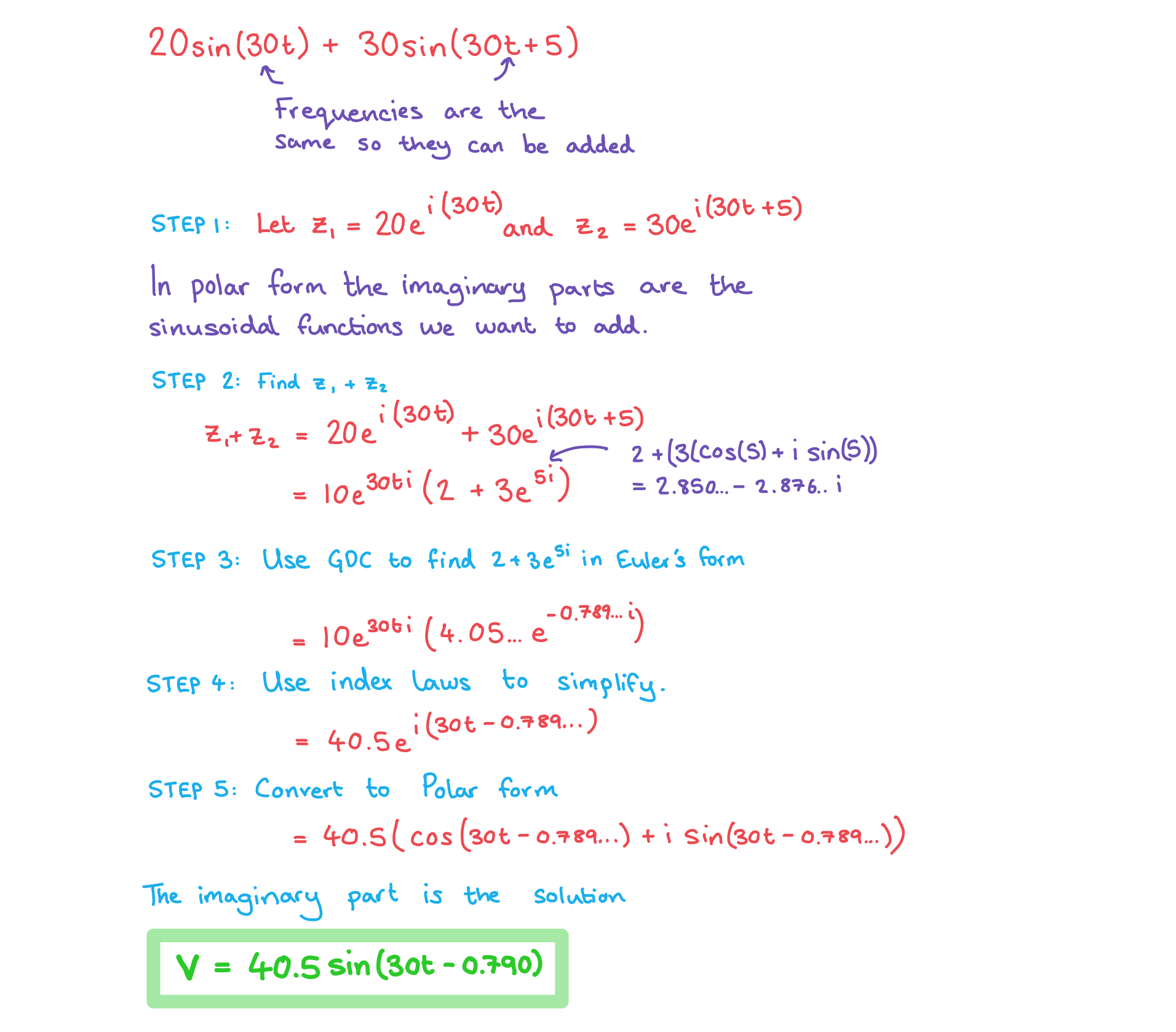
STEP 1
Identify the two related exponential functionse.g. for
use
and
STEP 2
Add the two functions together and factorisee.g.
STEP 3
Convert the term in the bracket into a single complex number in Euler's formUse your GDC to do this
e.g.
STEP 4
Simplify the whole expression and use the rules of indices to collect the powerse.g.
STEP 5
Convert into polar form and takeonly the imaginary part for sin
or only the real part for cos
e.g.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The frequency (coefficient of ) needs to be the same for this method to work, e.g. 2sin(3x + 1) can be added to 3sin(3x - 5) using this method but not 2sin(5x + 1).
Worked Example
Two AC voltage sources are connected in a circuit. If and
find an expression for the total voltage in the form
.
Answer:

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
