Total Internal Reflection (Oxford AQA IGCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9203
Critical Angle
The relationship between refractive index, n, and critical angle, c, is:
The equation can be rearranged to make sin c the subject:
The larger the refractive index of a material, the smaller the critical angle
When light is shone at the boundary between a more dense and a less dense medium, different angles of incidence result in different angles of refraction
As the angle of incidence is increased, the angle of refraction also increases
Until the angle of incidence reaches the critical angle
When the angle of incidence = critical angle then:
Angle of refraction = 90°
The refracted ray is refracted along the boundary between the two materials
When the angle of incidence < critical angle then:
the ray is refracted and exits the material
When the angle of incidence > critical angle then:
the ray undergoes total internal reflection
Angle of refraction, critical angle and reflection

Worked Example
Opals and diamonds are transparent stones used in jewellery. Jewellers shape the stones so that light is reflected inside.
Compare the critical angles of opal and diamond and explain which stone would appear to sparkle more.
The refractive index of opal is about 1.5
The refractive index of diamond is about 2.4
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Refractive index of opal, no = 1.5
Refractive index of diamond, nd = 2.4
Step 2: Write out the equation relating critical angle and refractive index
Step 3: Calculate the critical angle of opal (co)
Step 4: Calculate the critical angle of diamond (cd)
Step 5: Compare the two values and write a conclusion
Total internal reflection occurs when the angle of incidence of light is larger than the critical angle (i>c)
In opal, total internal reflection will occur for angles of incidence between 42° and 90°
The critical angle of diamond is lower than the critical angle of opal (co>cd)
This means light rays will be totally internally reflected in diamond over a larger range of angles (25° to 90°)
Therefore, more total internal reflection will occur in the diamond, hence it will appear to sparkle more than the opal
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In your exam, you are not required to recall the values of critical angles for different materials.
When calculating the value of the critical angle using the above equation:
First use the refractive index, n, to find sin(c)
Then use the inverse sine function (sin–1) to find the value of c
Total Internal Reflection
Total internal reflection is a special case of refraction that occurs when:
The angle of incidence within the denser medium is greater than the critical angle
Total internal reflection follows the law of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
A denser medium has a higher refractive index
For example, the refractive index of glass, ng > the refractive index of air, na
Light rays inside a material with a higher refractive index are more likely to be totally internally reflected
Worked Example
A glass cube is held in contact with a liquid and a light ray is directed at a vertical face of the cube. The angle of incidence at the vertical face is 39° and the angle of refraction is 25° as shown in the diagram. The light ray is totally internally reflected for the first time at X.
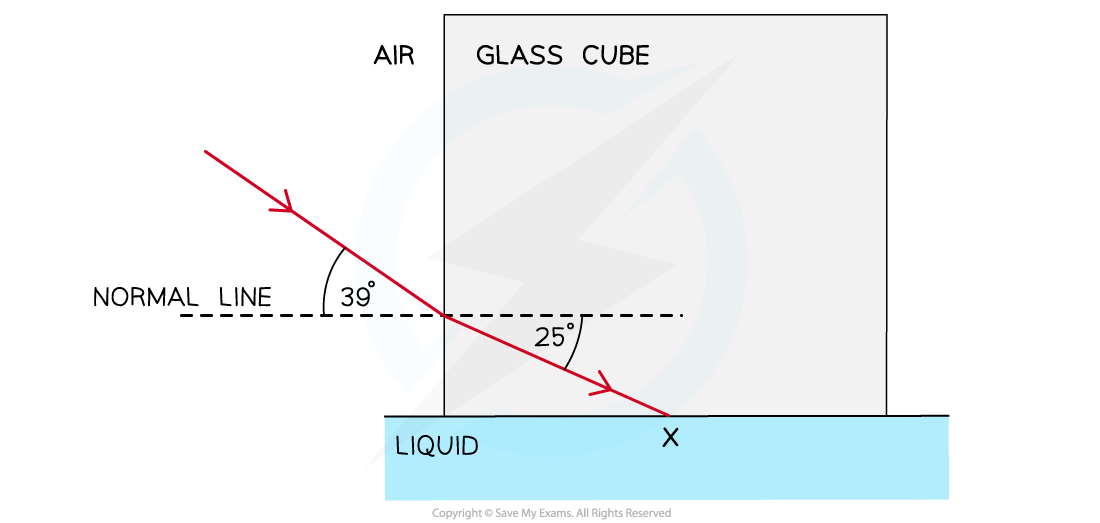
Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray beyond X to the air.
You should include the values of any angles you draw.
Answer:

Step 1: Draw the reflected ray at the glass-liquid boundary
When a light ray is reflected, the angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Therefore, the angle of incidence (or reflection) is 90° – 25° = 65°
First, draw in the normal as a dotted line
Then draw in the reflected ray at an angle of 65° from the normal
Step 2: Draw the refracted angle at the glass-air boundary
At the glass-air boundary, the light ray refracts away from the normal
Due to the reflection occurring at the exact centre point of the glass block, the light rays are symmetrical on both sides
Uses of Total Internal Reflection
Visible light and infrared can be transmitted through optical fibres by total internal reflection
Total internal reflection in an optical fibre

In an optical fibre, the denser medium is the glass that forms the fibre
The air outside the fibre is the less dense medium
Optical fibres in medicine
Optical fibres are used in medicine to see within the human body
An endoscopy is a medical procedure that uses an endoscope to look inside the body
An endoscope contains a camera on a long, thin flexible tube containing an optical fibre
It can be used to obtain images of the digestive tract by insertion of the endoscope
Endoscopes allow doctors to:
Identify the exact location of a problem
Suggest the correct treatment
Treat a patient more quickly
Provide more effective medicine
An endoscope

Optical fibres in communication
Optical fibres can be used to transmit:
Landline telephone signals
Internet signals
Cable television signals
In these systems, electrical signals are converted to light pulses that travel at high speeds along the optical fibre
Slower systems still use the old copper cables for some sections of the transmission
Optical fibres have many advantages over copper cables:
They use less energy to transmit the signal
They need fewer boosters to increase the signal
There is no interference with nearby cables
They are difficult to intercept
Their mass is lower, so they are easier to install
Fibre optic and copper cables


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
