Chain Reactions (Oxford AQA IGCSE Combined Science Double Award): Revision Note
Exam code: 9204
Chain Reactions
For fission to occur, a nucleus must first absorb one neutron
The nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei (called daughter nuclei) of roughly equal size as well as two or three neutrons which move away at high speed
Each of these new neutrons can start another fission reaction, which again creates further excess neutrons
This process is called a chain reaction
Chain reaction analogy

Controlled chain reactions
In a nuclear reactor, a chain reaction is required to keep the reactor running
The kinetic energy of the fission products is transferred to water, causing it to boil
The steam from this is used to generate electricity
For the reactor to work safely in a stable state, the number of free neutrons in the reactor needs to be kept constant
This means some neutrons must be removed from the reactor
To do this, nuclear reactors contain control rods
Structure of a nuclear reactor

Control rods are made of a material, such as boron, which can absorb neutrons without becoming dangerously unstable
The number of neutrons absorbed is controlled by varying the depth of the control rods in the fuel rods
Lowering the rods further decreases the rate of fission, as more neutrons are absorbed
Raising the rods increases the rate of fission, as fewer neutrons are absorbed
This is adjusted automatically so that, on average, only one neutron produced by each fission event goes on to cause another fission event
In the event the nuclear reactor needs to shut down, the control rods can be lowered all the way to absorb all of the neutrons so no further reactions can take place
Uncontrolled chain reactions
Because each new fission reaction transfers energy, uncontrolled chain reactions can be dangerous
The number of neutrons available increases quickly, so the number of reactions does too
A nuclear weapon uses an uncontrolled chain reaction to release a huge amount of energy in a short period of time as an explosion
Worked Example
The diagram shows the nuclear fission process for an atom of uranium-235.
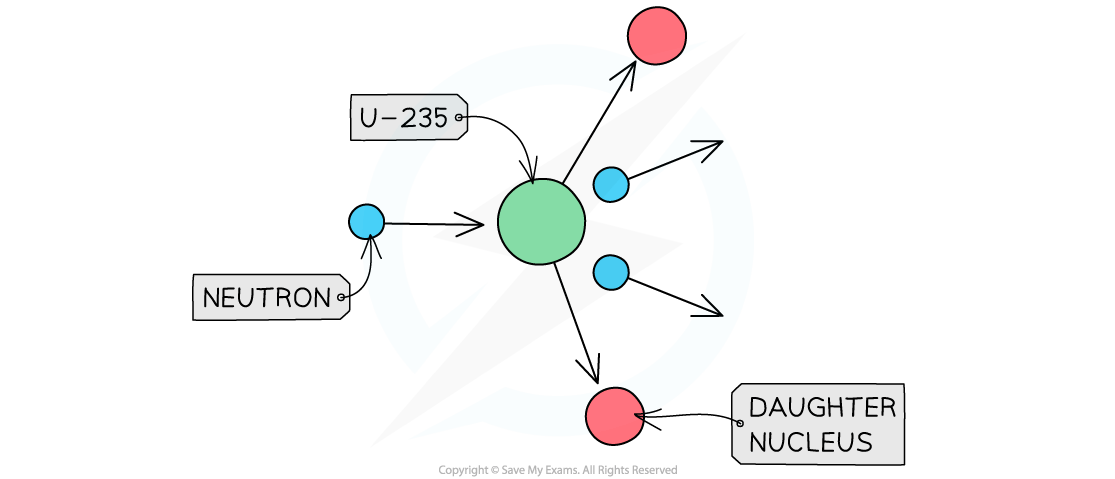
Complete the diagram to show how the fission process starts a chain reaction.
Answer:

Step 1: Draw the neutrons to show that they hit other U-235 nuclei
It is the neutrons hitting the uranium-235 nuclei which causes the fission reactions
The daughter nuclei do not need to be shown, only the neutrons and uranium-235 nuclei
Step 2: Draw the splitting of the U-235 nuclei to show they produce two or more neutrons
The number of neutrons increases with each fission reaction
Each reaction requires one neutron but releases two
More reactions happen as the number of neutrons increases
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to be able to draw and interpret diagrams of nuclear fission and chain reactions. Generally, things move to the right as time goes on in these diagrams, but it is important to read all the information carefully on questions like this. If you have to draw a diagram in an exam remember that the clarity of the information is important, not how pretty it looks!

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
