ADH & Composition of Urine (Edexcel IGCSE Biology (Modular)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4XBI1
The Role of ADH
Osmoregulation is the maintenance of water and salt levels within the body
The nephrons have a crucial role in osmoregulation; most water absorption from the filtrate occurs from the collecting duct
The amount of water that is reabsorbed is controlled by the hormone ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
Maintenance of body water levels is an example of negative feedback
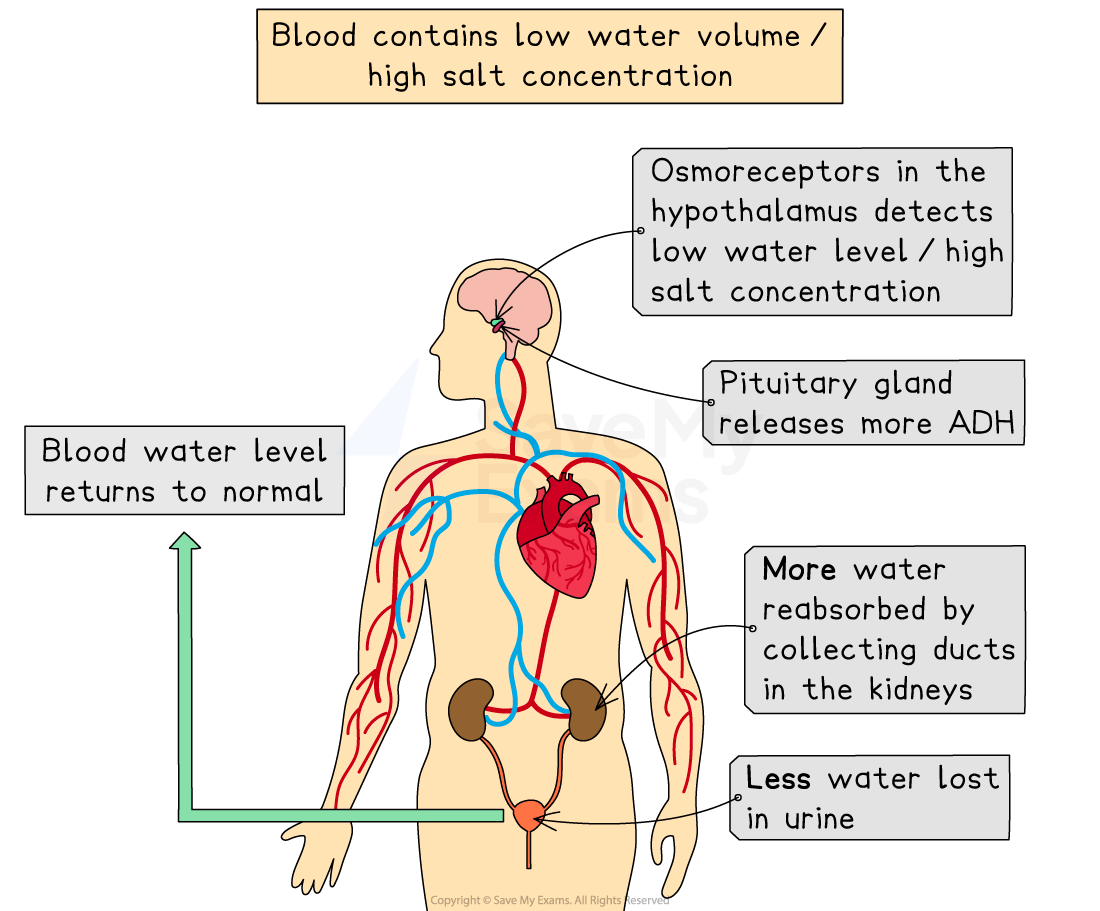
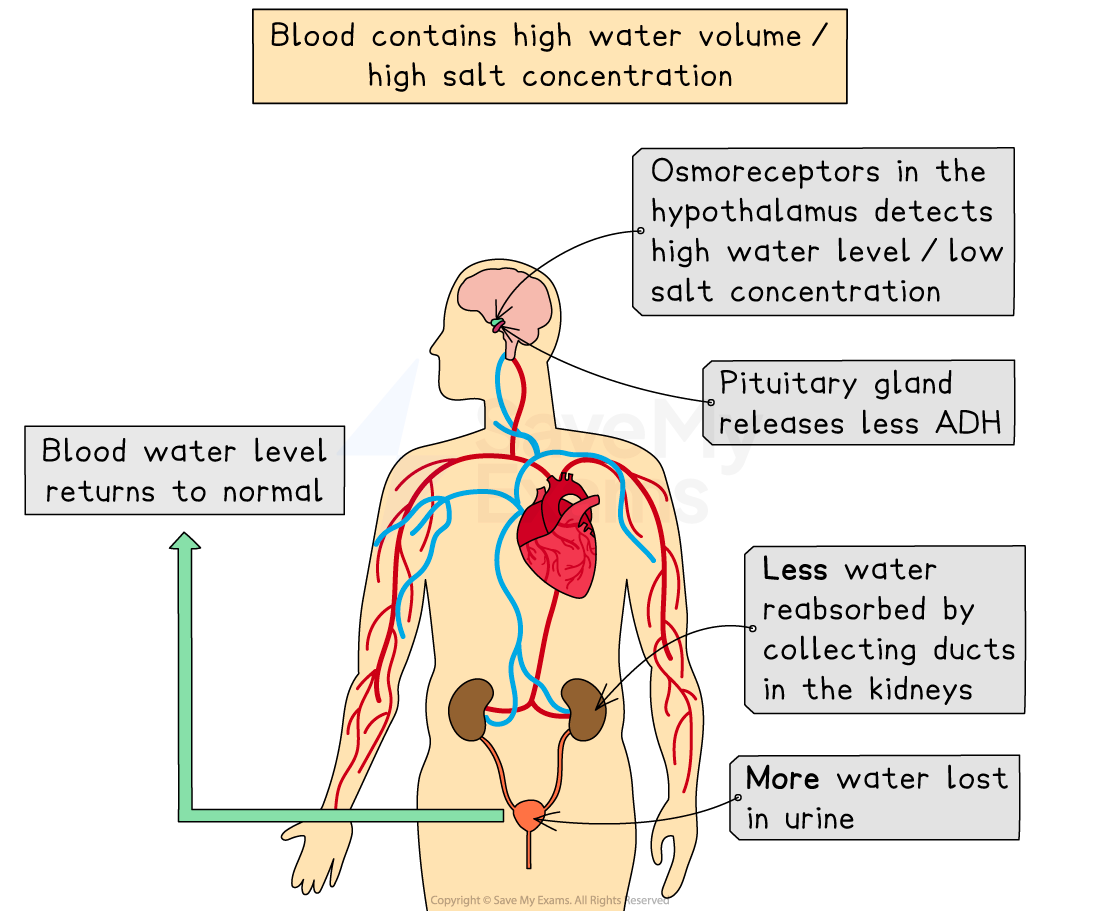
Changes in blood water levels are detected by osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus in the brain
The hypothalamus sends signals to the pituitary gland, which releases ADH
ADH affects the permeability of the collecting duct to water
If the water potential of the blood is too high (too much water):
The pituitary gland in the brain releases less ADH
The collecting ducts become less permeable to water
Less water is reabsorbed from the collecting ducts
A larger volume of dilute urine is produced
If the water potential of the blood is too low (too little water):
The pituitary gland in the brain releases more ADH
The collecting ducts become more permeable to water
More water is reabsorbed from the collecting ducts
A smaller volume of concentrated urine is produced
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You must remember the key phrase "ADH increases the permeability of the collecting duct to water" for your exams. Mark schemes will expect you to use this exact terminology.
Remember that blood with a low water level will have a high salt (or solute) concentration and blood with a high water level will have a low salt (or solute) concentration. Technically it's better to refer to "water potential" rather than "water level".
The Composition of Urine
Urine produced by the kidneys contains a mixture of
urea
excess ions
excess water
The colour and quantity of urine produced in the body can change quickly
Large quantities of urine are usually pale yellow in colour because it contains a lot of water and so the urea is less concentrated
Small quantities of urine are usually darker yellow / orange in colour because it contains little water and so the urea is more concentrated
There are various reasons why the concentration of urine will change, including:
Water intake - the more fluids drunk, the more water will be removed from the body and so a large quantity of pale yellow, dilute urine will be produced
Temperature - the higher the temperature the more water is lost in sweat and so less will appear in the urine, meaning a smaller quantity of dark yellow, concentrated urine will be produced
Exercise - the greater the level of exercise, the more water is lost in sweat and so less will appear in the urine, meaning a smaller quantity of dark yellow, concentrated urine will be produced

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
