Micropropagation (Edexcel IGCSE Biology (Modular)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4XBI1
Micropropagation
Tissue culture is a process in which very small (micro) pieces of plants ('tissue') are grown (‘cultured’) using nutrient media
Because they are initially grown in Petri dishes on nutrient agar we say they are grown ‘in vitro’ – outside a living organism
Large numbers of genetically identical plants can be produced using micropropagation
The stages of micropropagation are:
Small pieces are cut from the plant to be cloned - these pieces are known as explants
The surface of the explants are sterilised using a disinfectant followed by a rinse with sterile water
Sterilised explants are transferred to a sterile petri dish containing sterile nutrient agar
The growth medium encourages the explant cells to grow and divide into small masses of cells (known as a callus)
Each callus is transferred to a fresh growth medium that contains a range of plant growth regulators (hormones). The presence of these hormones causes the callus to develop roots, stems and leaves, forming a plantlet
Plantlets can be transferred to individual potting trays and develop into plants
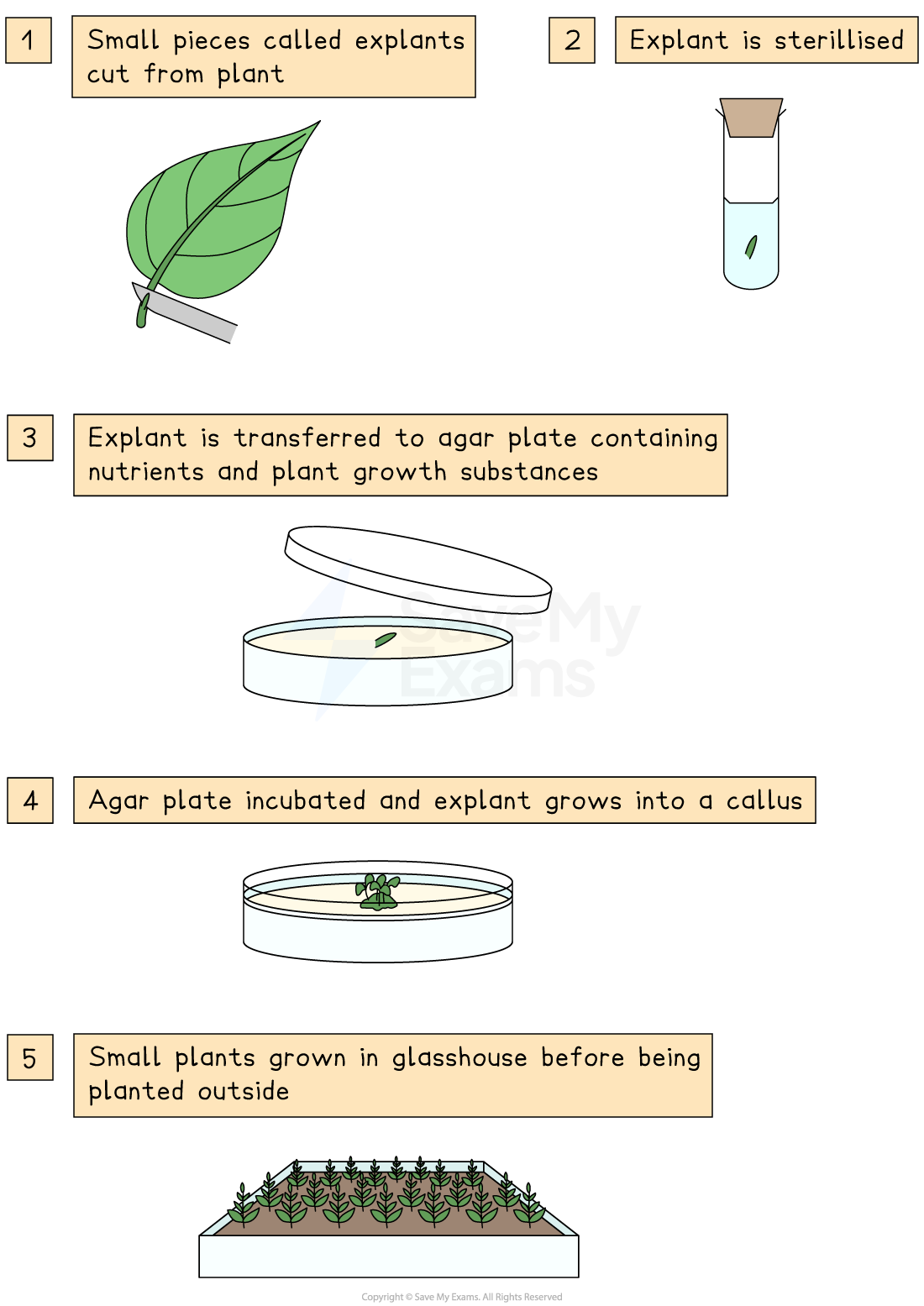
The steps of micropropagation to reproduce cloned plants
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is possible small pieces of plant tissue (explants) to grow into whole new individual plants because plant cells can differentiate into all different specialised cell types throughout a plants life.
The same cannot occur in animals - small pieces of animal tissue cannot grow into new individuals. This is because only stems cells found in animal embryos can differentiate into all of the specialised cell types required to make a whole new individual.
Commercial use of micropropagation
Advantages of micropropagation
Advantages of micropropagation include:
The production of (many) genetically identical clones of plants with desirable traits
Commercial benefits:
Can produce plants cheaply and in large quantities per square metre
Fast production: plantlets grow into mature plants quicker than from seeds
Can be done at any time of year, without any seasonal limitations on growth
Ensures plants are disease-free (as they're grown in a sterile lab) and if the original plant has a trait for disease resistance, this trait is preserved in all the cloned plantlets
Another advantage is micropropagation is that is can can be used in conservation to preserve rare plant species
Disadvantages of micropropagation
There are a number of drawbacks to using micropropagation:
Trained personnel and a sterile laboratory are required
All the plants produced are genetically identical and so will all be vulnerable to the same diseases and pests (the lack of genetic variation makes them less able to adapt to environmental change)

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
