Representing Vectors as Diagrams (Edexcel IGCSE Maths A (Modular)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4XMAF/4XMAH
Vector diagrams
How can I represent a vector visually?
A vector has both a size (magnitude) and a direction
You need to draw a line to show the size of the vector
You also need to draw an arrow to show the direction of the vector
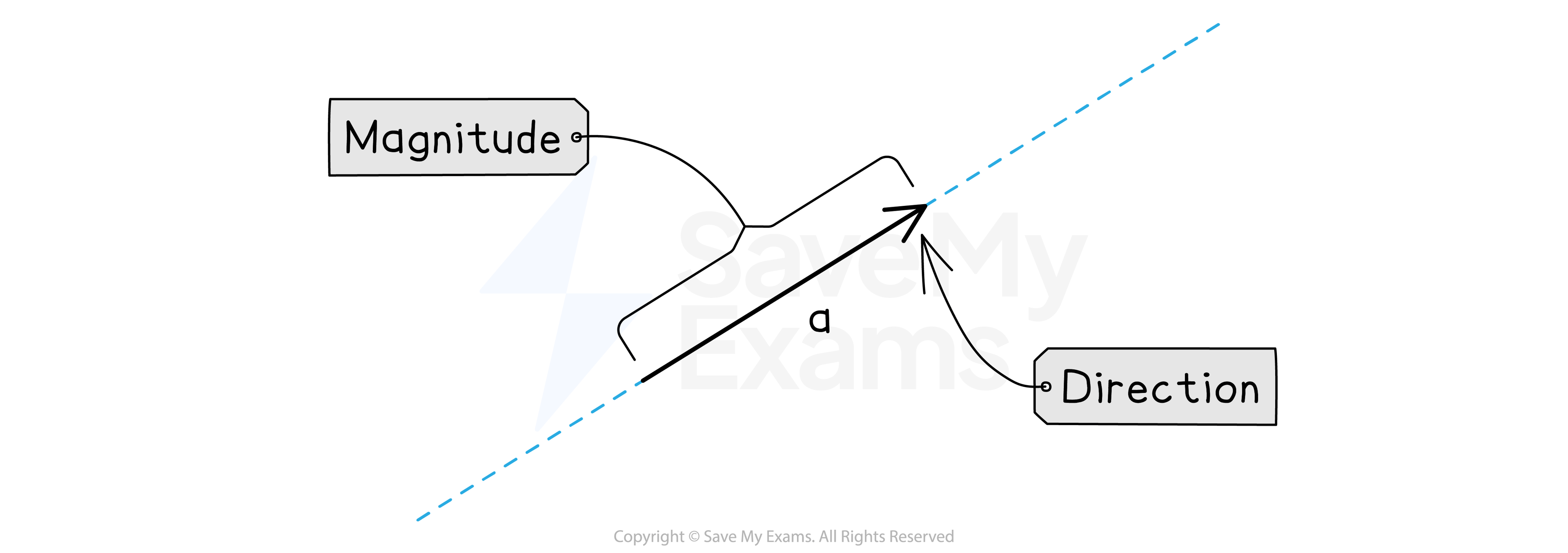
Vectors are written in bold when typed to show that they are a vector and not a scalar
When writing a vector in an exam you should underline the letter to show it is a vector
when typed and
when handwritten
You will not lose marks if you forget to underline vectors
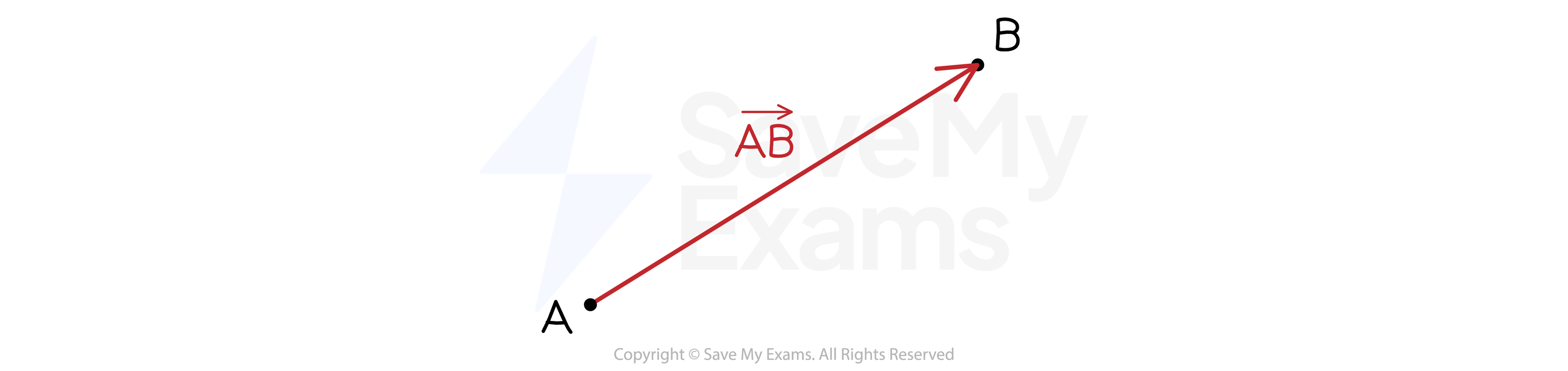
If a vector starts at A and ends at B we can write it as
Here the arrow will point toward B
Vector
will have the same length but point toward A
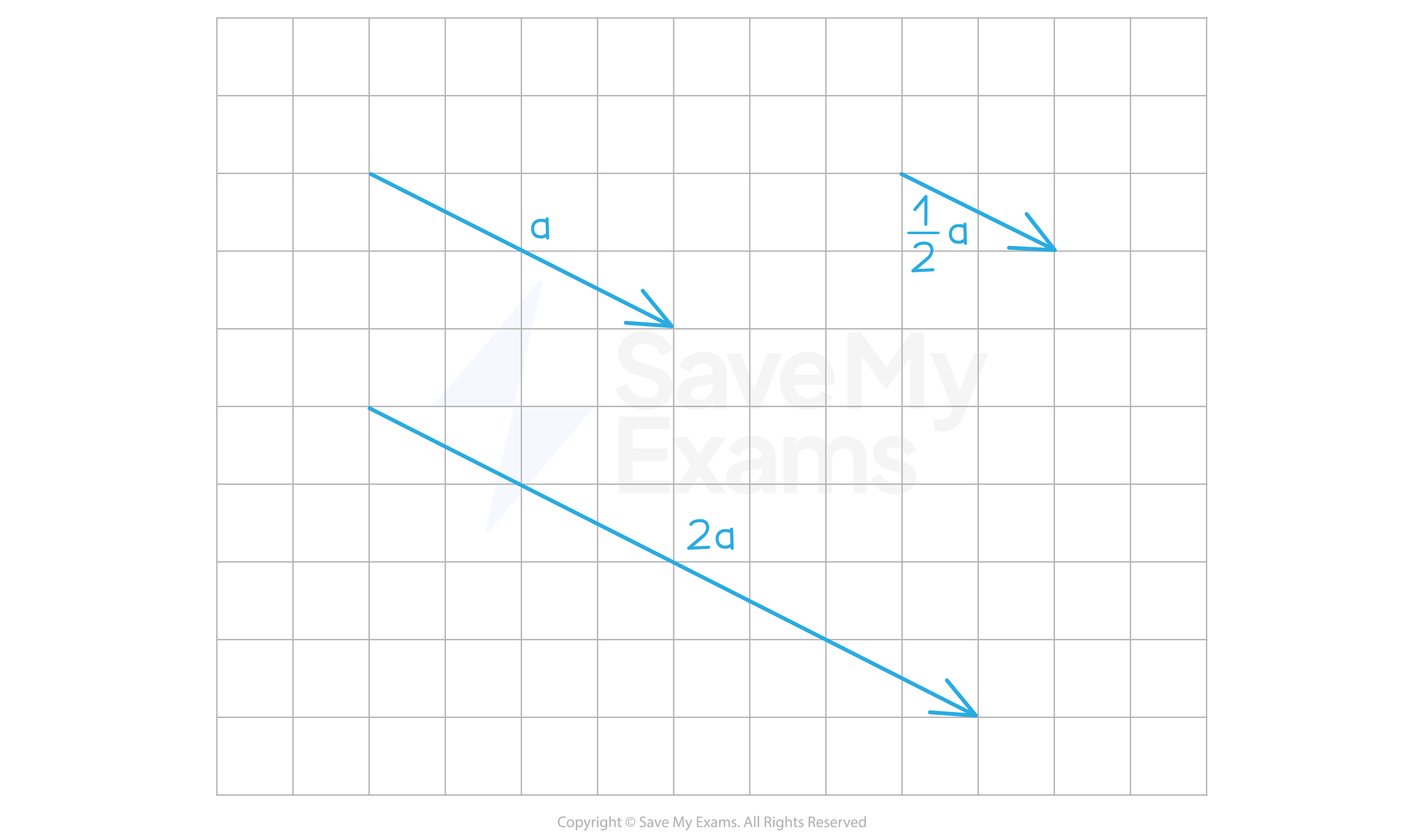
What happens when a vector is multiplied by a scalar?
When you multiply a vector by a positive scalar:
The direction stays the same
The length of the vector is multiplied by the scalar
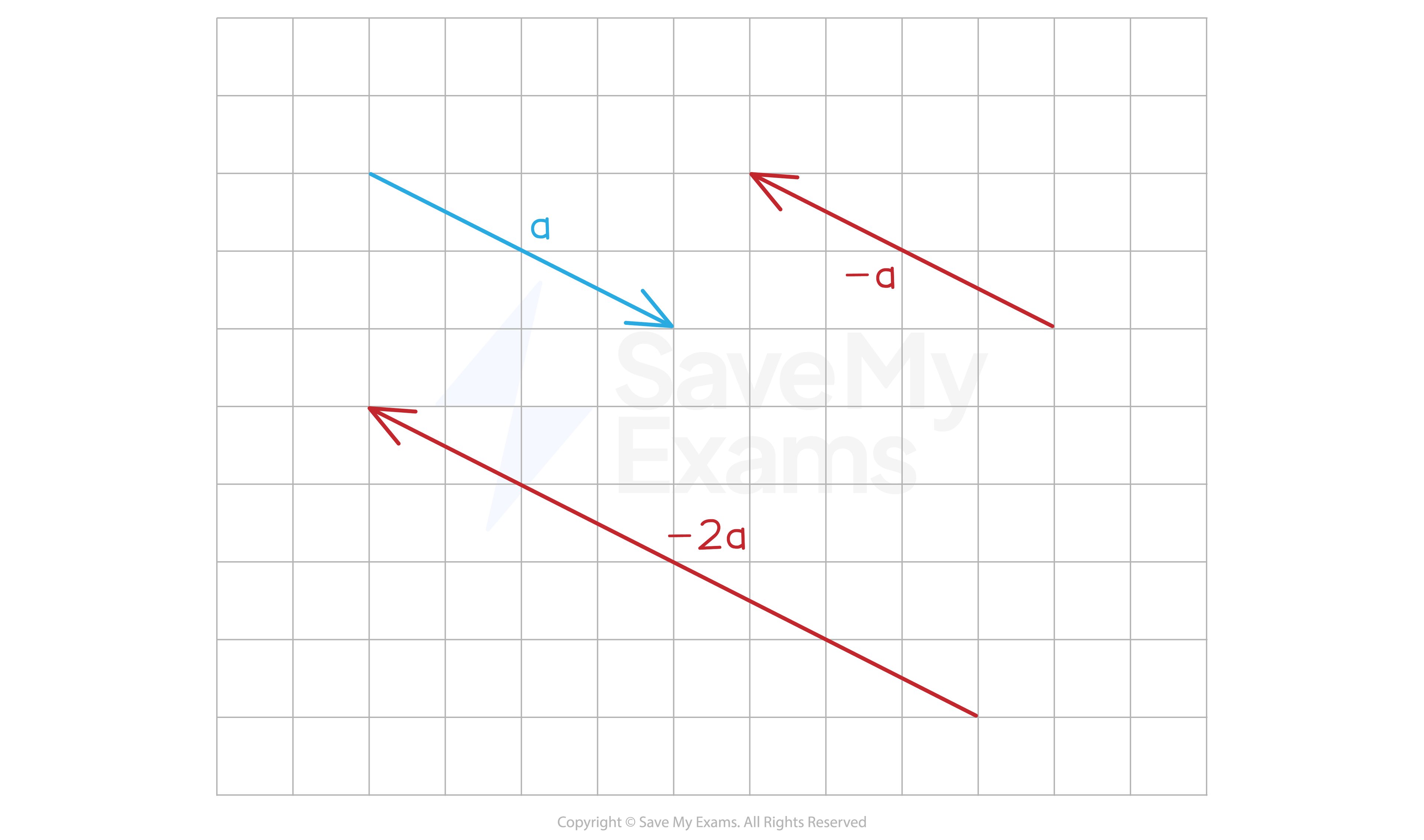
When you multiply a vector by a negative scalar:
The direction is reversed
The length of the vector is multiplied by the number after the negative sign
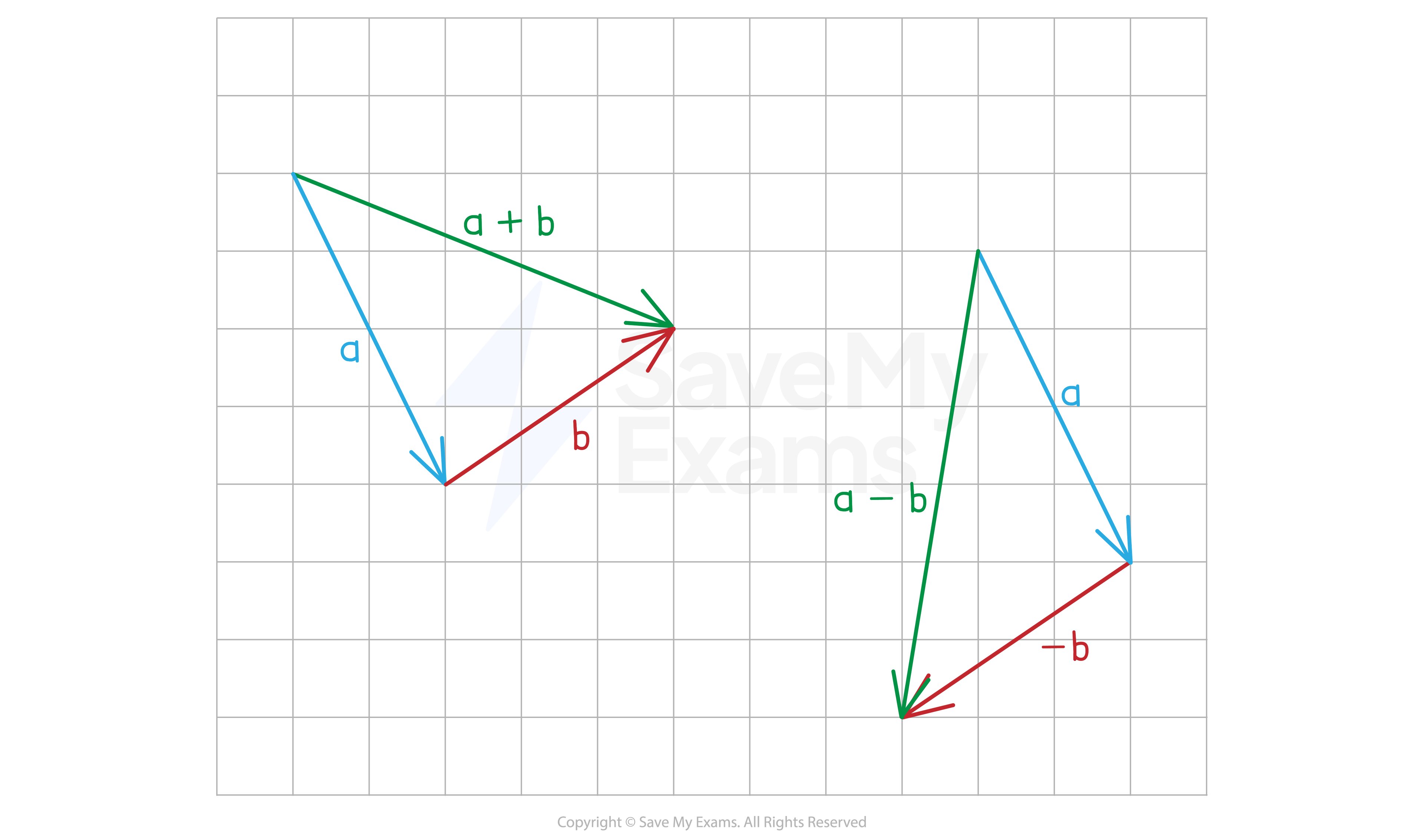
What happens vectors are added or subtracted?
To draw the vector
Draw the vector
Draw the vector
starting at the endpoint of
Draw a line that starts at the start of
and ends at the end of
To draw the vector
Draw the vector
Draw the vector
starting at the endpoint of
Draw a line that starts at the start of
and ends at the end of

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
