Gene Mutations (Cambridge (CIE) AS Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Gene mutations & their effect on polypeptides
A gene mutation is a change in the sequence of base pairs in a DNA molecule that may result in an altered polypeptide
As the DNA base sequence determines the sequence of amino acids that make up a protein, mutations in a gene can sometimes lead to a change in the polypeptide that the gene codes for
Most mutations do not alter the polypeptide or only alter it slightly so that its structure or function is not changed
This is because the genetic code is degenerate
There are different ways that a mutation in the DNA base sequence can occur:
Insertion of nucleotides
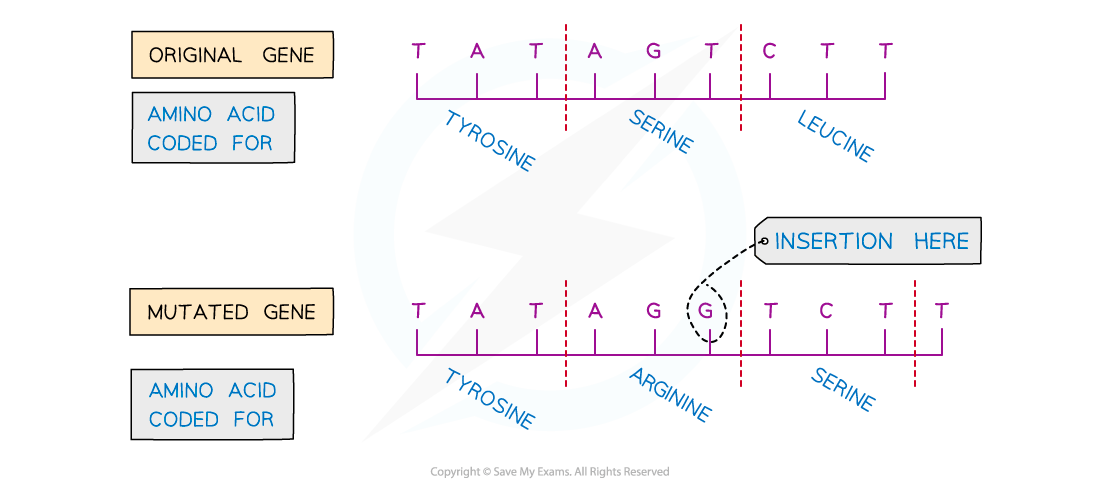
A mutation that occurs when a nucleotide (with a new base) is randomly inserted into the DNA sequence is known as an insertion mutation
An insertion mutation changes the amino acid that would have been coded for by the original base triplet, as it creates a new, different triplet of bases
An insertion mutation also has a knock-on effect by changing the triplets (groups of three bases) further on in the DNA sequence
This is sometimes known as a frameshift mutation
This may dramatically change the amino acid sequence produced from this gene and therefore the ability of the polypeptide to function
Deletion of nucleotides
A mutation that occurs when a nucleotide (and therefore its base) is randomly deleted from the DNA sequence
Like an insertion mutation, a deletion mutation:
Changes the amino acid that would have been coded for
Has a knock-on effect by changing the groups of three bases further on in the DNA sequence
This is another type of frameshift mutation
This may dramatically change the amino acid sequence produced from this gene and therefore the ability of the polypeptide to function
Substitution of nucleotides
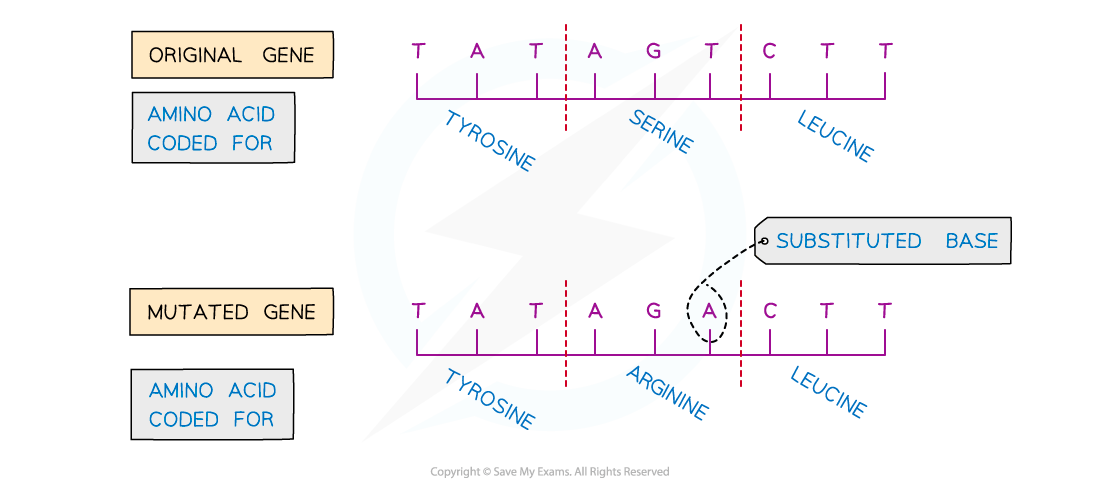
A mutation that occurs when a base in the DNA sequence is randomly swapped for a different base
Unlike an insertion or deletion mutation, a substitution mutation will only change the amino acid for the triplet (a group of three bases) in which the mutation occurs
It will not have a knock-on effect (it is not a frameshift mutation)
The effect of gene mutations on polypeptides
Most mutations do not alter the polypeptide or only alter it slightly so that its appearance or function is not changed
However, a small number of mutations code for a significantly altered polypeptide with a different shape
This may affect the ability of the protein to perform its function
For example:
If the shape of the active site on an enzyme changes, the substrate may no longer be able to bind to the active site
A structural protein (like collagen) may lose its strength if its shape changes

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
