Circular Orbits (AQA GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 8463
Written by: Katie M
Updated on
Did this video help you?
Orbital Motion
There are many orbiting objects in our solar system
They each orbit a different type of planetary body
Orbiting bodies in the Solar System
Orbiting body | What it orbits |
|---|---|
Planet | Sun |
Moon | Planet |
Comet | Sun |
Asteroid | Sun |
Artificial satellite | Any larger body in the Solar System |
A smaller body or object will orbit a larger body
In order to orbit a body such as a star or a planet, there has to be a force pulling things towards that body
Gravity provides this force
The gravitational force exerted by the larger body on the orbiting object is always attractive
Therefore, the gravitational force always acts towards the centre of the larger body
The gravitational force is the centripetal force as it will cause the body to move and maintain a circular path

Gravitational attraction causes the Moon to orbit around the Earth
Circular motion in an orbit
Planets travel around the Sun in orbits that are (approximately) circular
Objects moving in circular orbits move at a constant speed, but their direction is constantly changing
A change in direction indicates a change in velocity, and a change in velocity indicates acceleration
Therefore, if an object in orbit is constantly changing direction, then its velocity is constantly changing, and hence, it must be accelerating
A resultant force is needed to cause an acceleration
This resultant force is gravity, which must act at right angles to the instantaneous velocity of the object to create a circular orbit
This is always towards the centre of the orbit
The instantaneous velocity of the object is the velocity at a given time
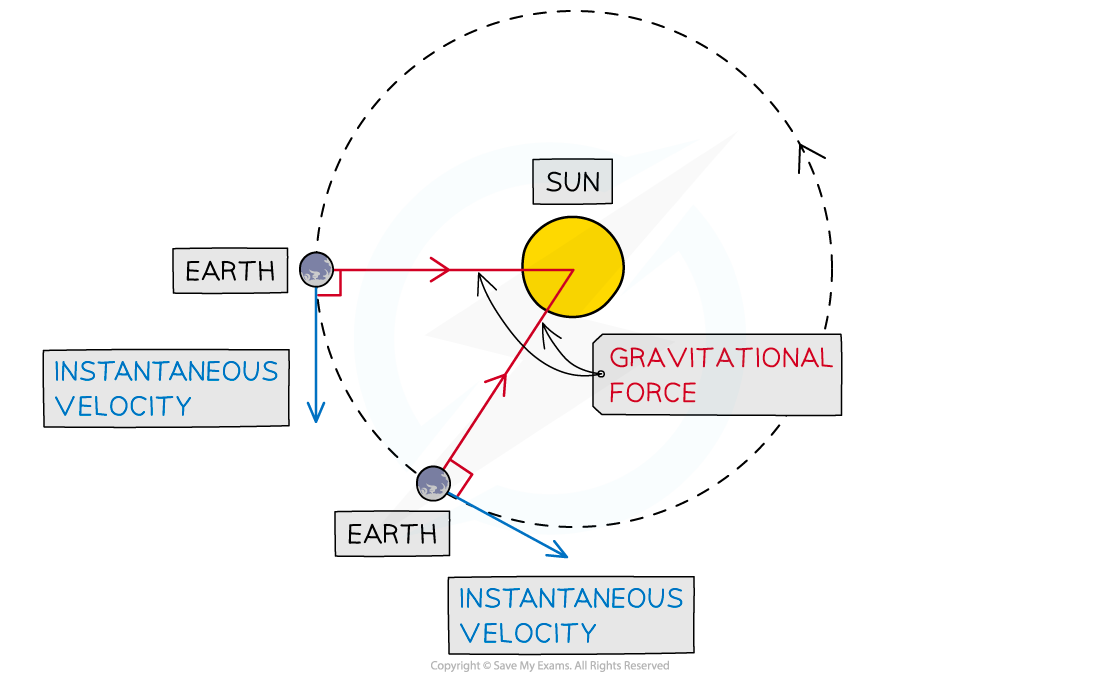
The direction of the instantaneous velocity and the gravitational force at different points of the Earth’s orbit around the sun
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When you are describing the motion of an object in orbit, make sure you describe the correct terminology. Recall that:
speed is a scalar quantity, as it has a magnitude (size) only
velocity is a vector quantity, as it has both a magnitude (size) and a direction.
Did this video help you?
Circular Orbits
Planets
There are several similarities in the way different planets orbit the Sun:
Their orbits are all slightly elliptical (stretched circles) with the Sun at one focus (approximately the centre of the orbit)
They all orbit in the same plane
They all travel the same direction around the Sun
There are also a few differences:
They orbit at different distances from the Sun
They orbit at different speeds
They all take different amounts of time to orbit the Sun

Orbit of planets around the Sun
Moons
Moons will orbit planets in a circular path
Some planets will have more than one moon
The closer the moon is to the planet:
the shorter the time it will take to orbit
the greater the speed in the orbit
Artificial satellites
A satellite needs to travel at a specific speed to maintain a circular orbit at a particular distance from the object it is orbiting
If the speed of the satellite is too large:
the radius of the orbit will increase, and the satellite will move into a higher orbit, further from the object it is orbiting
the satellite may leave the object's gravitational field altogether, but only if the speed is fast enough, or a continuous force acts on it, such as propulsion
If the speed of the satellite is too small:
the radius of the orbit will decrease, and the satellite will move into a lower orbit, closer to the object it is orbiting
the satellite may spiral inwards towards the object, but only if a continuous force acts on it, such as atmospheric drag

The speed of an artificial satellite is affected by its orbital radius
If an artificial satellite in a stable orbit is to change the radius at which it is orbiting, then its speed must change
If the satellite is moved further away from the object to an orbit with a larger radius:
the force of gravity decreases
the orbital speed decreases
the orbital period increases
If the satellite is moved closer to the object to an orbit with a smaller radius:
the force of gravity increases
the orbital speed increases
the orbital period decreases

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
