Practical: Factors Affecting Transpiration (Edexcel IGCSE Biology (Modular)): Revision Note
Exam code: 4XBI1
Did this video help you?
Practical: Factors Affecting Transpiration
We can investigate the effect of different environmental conditions (such as temperature, humidity, light intensity and wind movement) on the rate of transpiration using a piece of apparatus called a potometer
There are two types of potometer
A mass potometer measures a change in mass of a plant as a measure of the amount of water that has evaporated from the leaves and stem
A bubble potometer measures the uptake of water by a stem as a measure of the amount of water that is being lost by evaporation consequently pulling water up through the stem to replace it


There are two different types of potometer that could be used to investigate the effect of environmental conditions on transpiration
Investigating the effect of light intensity on transpiration using a bubble potometer
Apparatus
Potometer (bubble or mass potometer)
Timer
Lamp
Ruler
Plant
Method
Set up experiment:
Cut a shoot underwater (to prevent air entering the xylem) and place in potometer
Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram and make sure it is airtight, using petroleum jelly to seal any gaps
Dry the leaves of the shoot (as wet leaves will affect the results)
Remove the capillary tube from the beaker of water to allow a single air bubble to form and place the tube back into the water
Investigate light intensity:
Place a lamp 10 cm from the leaf
Allow the plant to adapt to the new environment for 5-10 minutes
Record the starting position of the air bubble (in mm)
Start a timer and leave for 30 minutes
Record the end position of the air bubble (in mm)
Repeat:
Reset the air bubble by opening the tap of the reservoir to move the bubble back
Repeat for the same light distance two more times
Change the light intensity by moving the lamp (eg. move lamp to 20 cm, 40 cm)
Repeat the steps above for the same shoot, adjusting the lamp and reseting the air bubble each time
Calculate the rate of transpiration:
Calculate the distance moved by air bubble (mm) = end position - start position
Divide the distance the bubble travelled by the time period (30 minutes in this experiment)
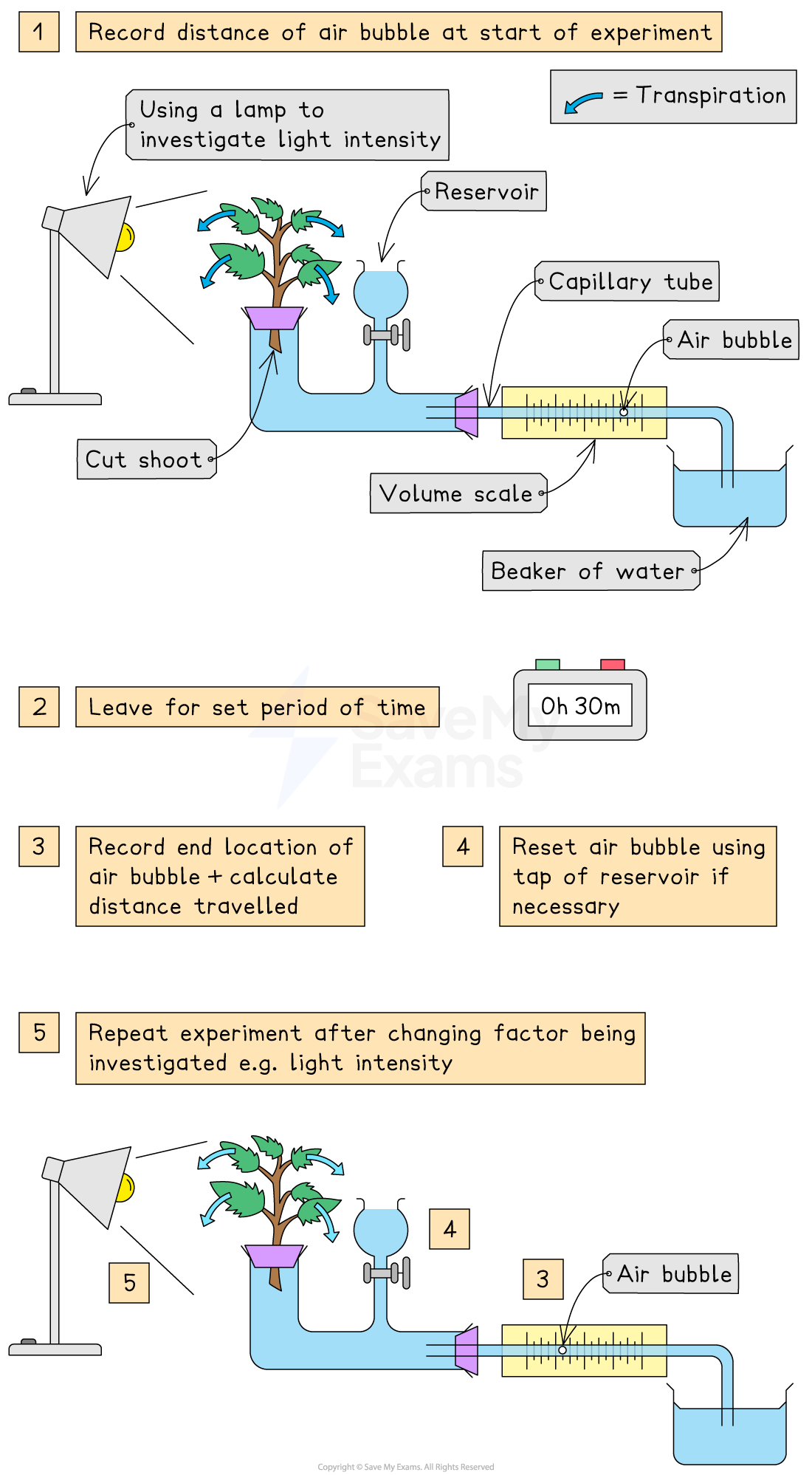
Investigating transpiration rates using a potometer
Results
Lamp distance (cm) | Distance moved by air bubble (mm) | Rate of transpiration |
|---|---|---|
10 | 32 | 1.07 |
20 | 24 | 0.80 |
40 | 12 | 0.40 |
The closer the lamp (and the higher the light intensity), the higher the rate of transpiration
This is shown by the bubble moving a greater distance in the 30-minute time period when the lamp was 10 cm from the plant (the highest light intensity)
In bright light, more stomata open to allow more carbon dioxide into the leaf for photosynthesis
The more stomata that are open, the greater the evaporation of water vapour from the leaf
Limitations
The main limitation to this practical is the fact that the other factors that can affect the rate of transpiration (especially temperature) cannot be satisfactorily controlled
For example, the lamp will heat the plant when at the closest distance to the plant for the highest light intensity, which means both light intensity and temperature are affecting the rate of transpiration, rather than just light intensity
The air humidity and air movement in the room are likely to be variable
Other limitations include:
Imperfect seals resulting in leaks
Solution: Ensure that all equipment fits together rightly around the rubber bungs and assemble underwater to help produce a good seal
The plant cutting has a blockage
Solution: Cut the stem underwater and assemble equipment underwater to minimise opportunities for air bubbles to enter the xylem
Further experiments:
Other environmental factors can be investigated in the following ways:
Airflow: Set up a fan or hairdryer
Humidity: Spray water in a plastic bag and wrap around the plant
Temperature: Temperature of room (cold room or warm room)
Using CORMS

The CORMS prompt
In this investigation, there are several different variations of the method depending on which environmental factor you are testing. However, if testing the effect of light intensity, the CORMS would look like this:
Change - change the intensity of the light
Organisms - plants used in each repeat should be the same species, size, age, number of leaves
Repeat - repeat the investigation several times to ensure results are reliable
Measurement 1 - measure the distance travelled by the bubble
Measurement 2 - ...in 30 minutes (calculate the rate of transpiration)
Same - control the temperature, wind speed and humidity of the environment

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
