Gradient of a Line (SQA National 5 Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: X847 75
Determining the gradient of a straight line between two points
What is the gradient of a line?
The gradient is a measure of how steep a straight line is
A gradient of 3 means:
For every 1 unit to the right, go up by 3
A gradient of -4 means:
For every 1 unit to the right, go down by 4
A gradient of 3 is steeper than a gradient of 2
A gradient of -5 is steeper than a gradient of -4
A positive gradient means the line goes upwards (uphill)
Bottom left to top right
A negative gradient means the line goes downwards (downhill)
Top left to bottom right
How do I find the gradient of a line?
Find two points on the line and draw a right-angled triangle
Then
Or, in short,
The rise is the vertical length of the triangle
The run is the horizontal length of the triangle
Put the correct sign on your answer
Positive for uphill lines
Negative for downhill lines
You can also find gradient of a line between two points,
and
Use the formula
How do I draw a line with a given gradient?
To draw the gradient
The rise is 2
The run is 3
It is positive (uphill)
Move 3 units to the right and 2 units up
To draw the gradient
make it a fraction,
The rise is 5
The run is 1
It is negative (downhill)
Move 1 unit to the right and 5 units down
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A lot of students forget to make their gradients negative for downhill lines!
Worked Example
Find the gradient of the line that goes through the points and
.
Answer:
Use the formula with
-2
Worked Example
Find the gradient of the line shown in the diagram below.
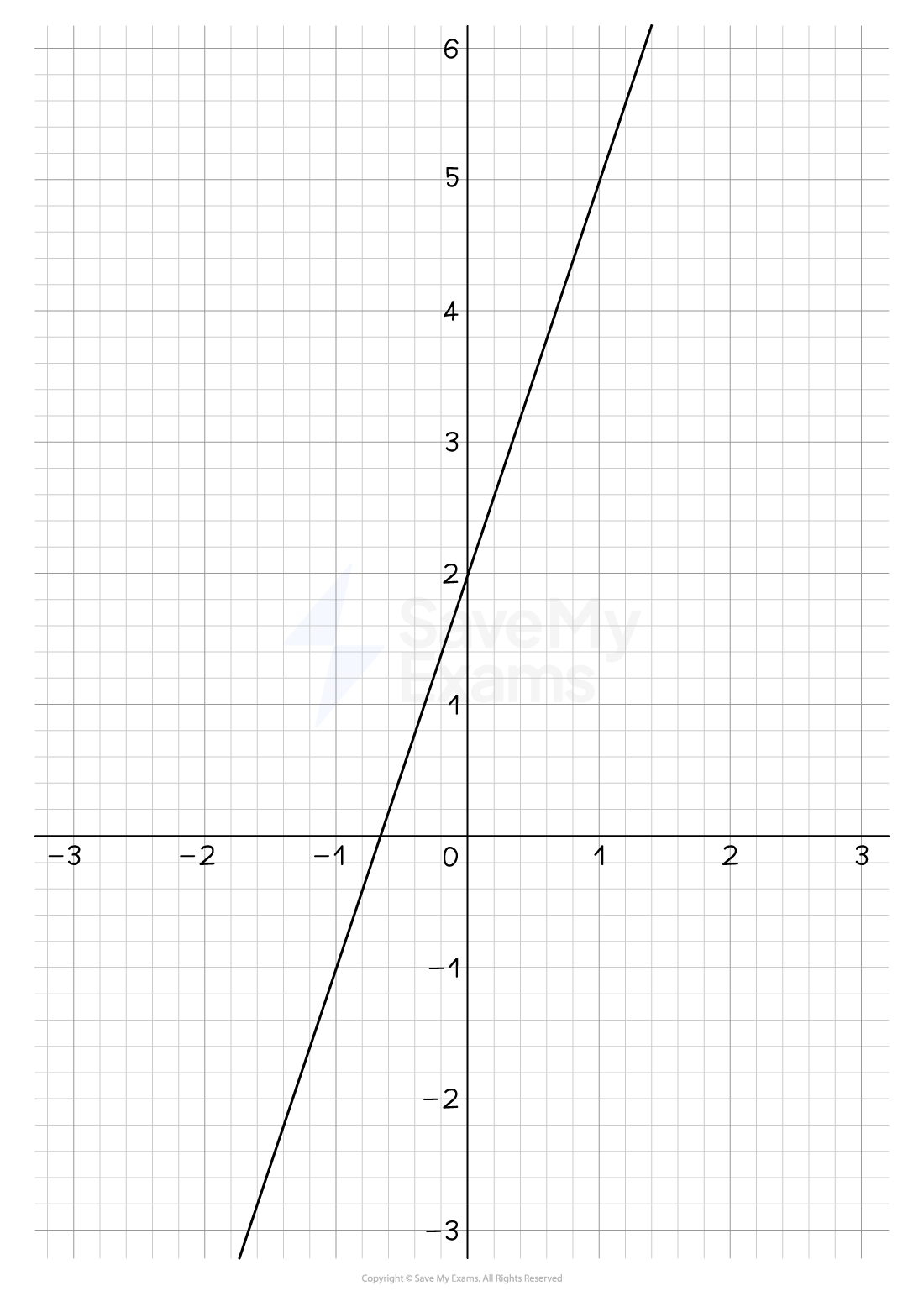
Answer:
Find two points that the line passes through
Use the grid to draw a right-angled triangle
Find the 'rise' (vertical length) and 'run' (horizontal length)
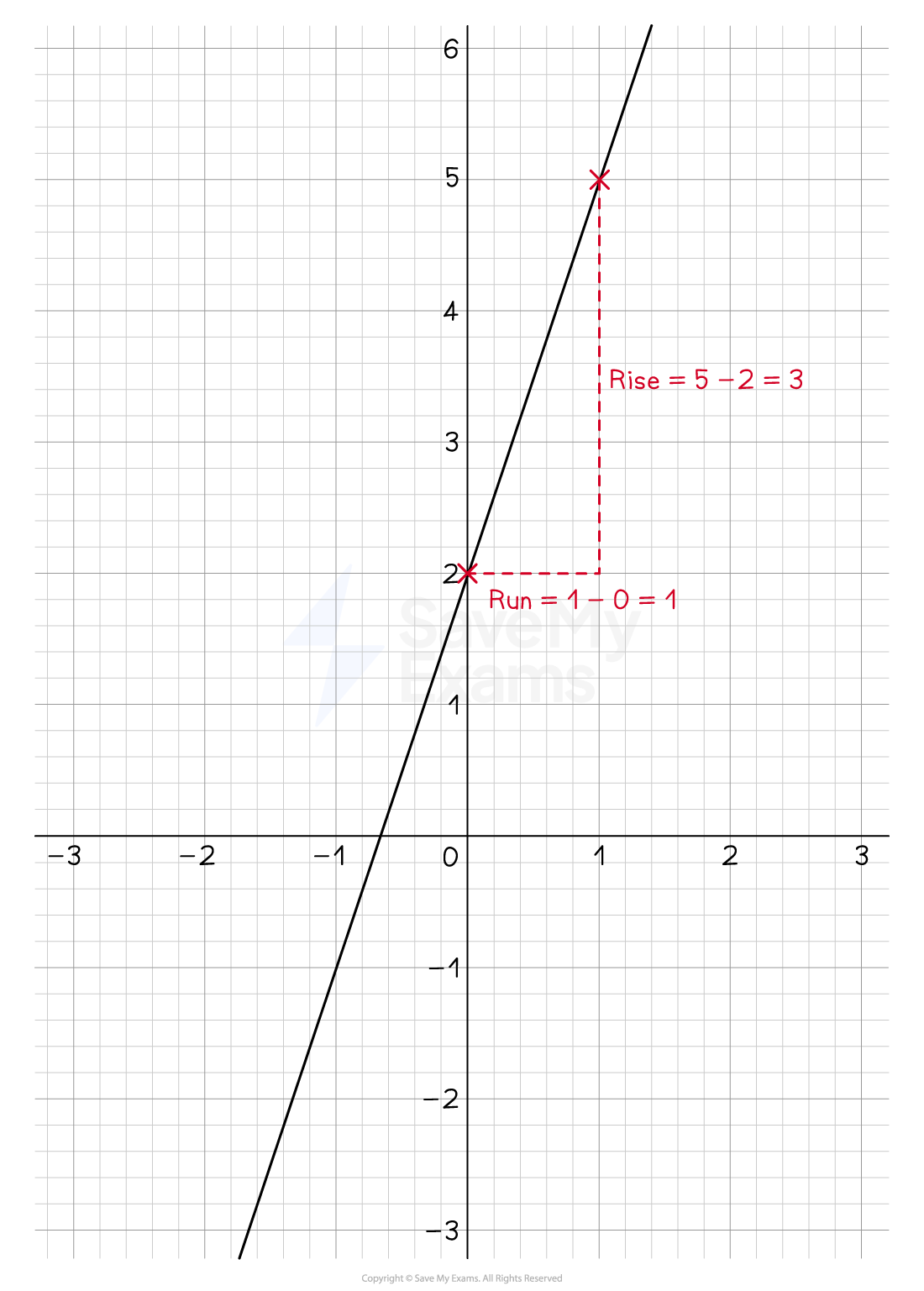
Work out the fraction
Look to see if the line is uphill or downhill
uphill, so the gradient is positive
The gradient is 3
Worked Example
Draw the line with a gradient of −2 that passes through (0,1).
Answer:
Mark on the point (0, 1)
-2 is the fraction
The rise is 2, the run is 1, the line goes downhill (so 1 across, 2 down)
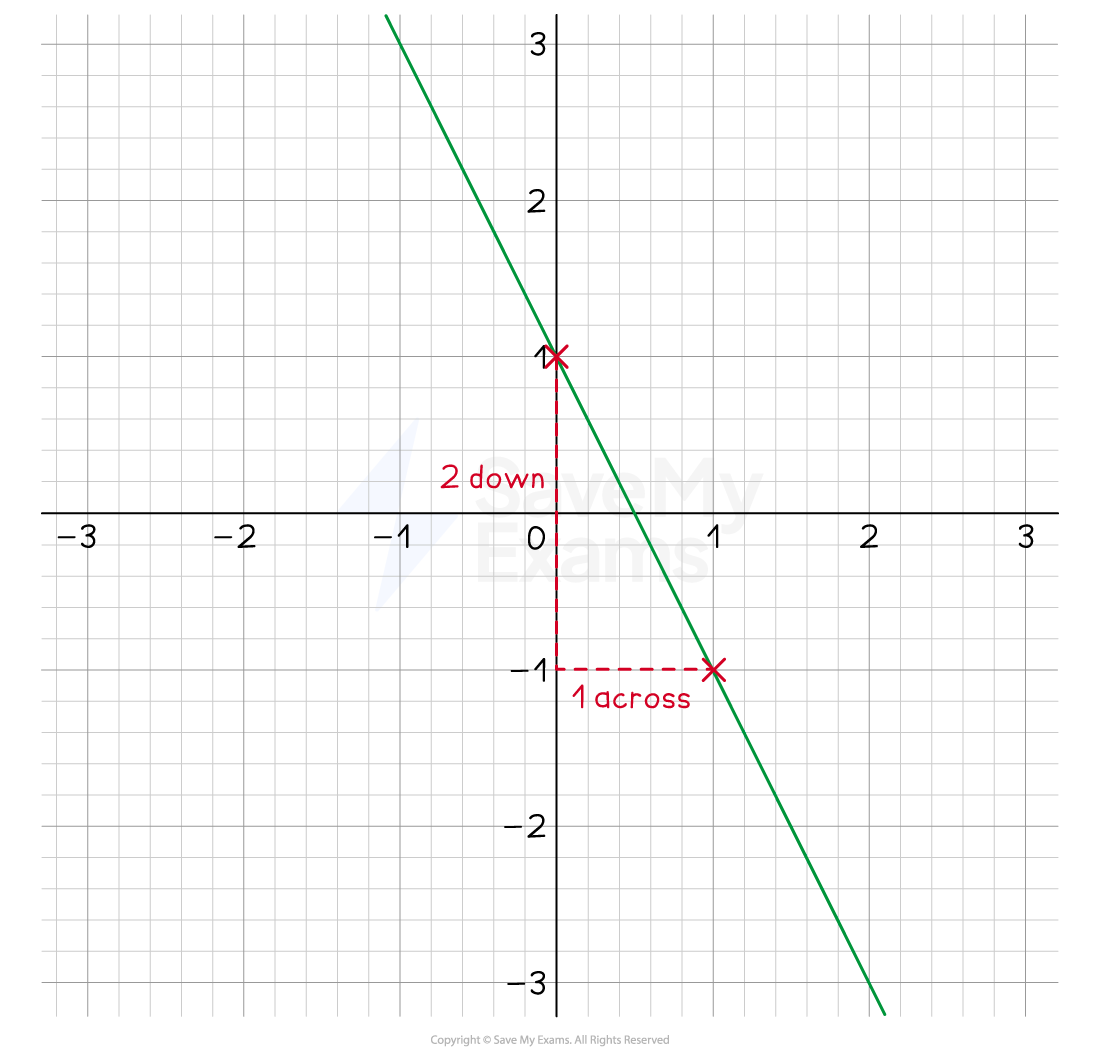
Worked Example
Draw the line with a gradient of that passes through (0,-1).
Answer:
Mark on the point (0,-1)
The rise is 2, the run is 3, the line goes uphill (so 3 across, 2 up)
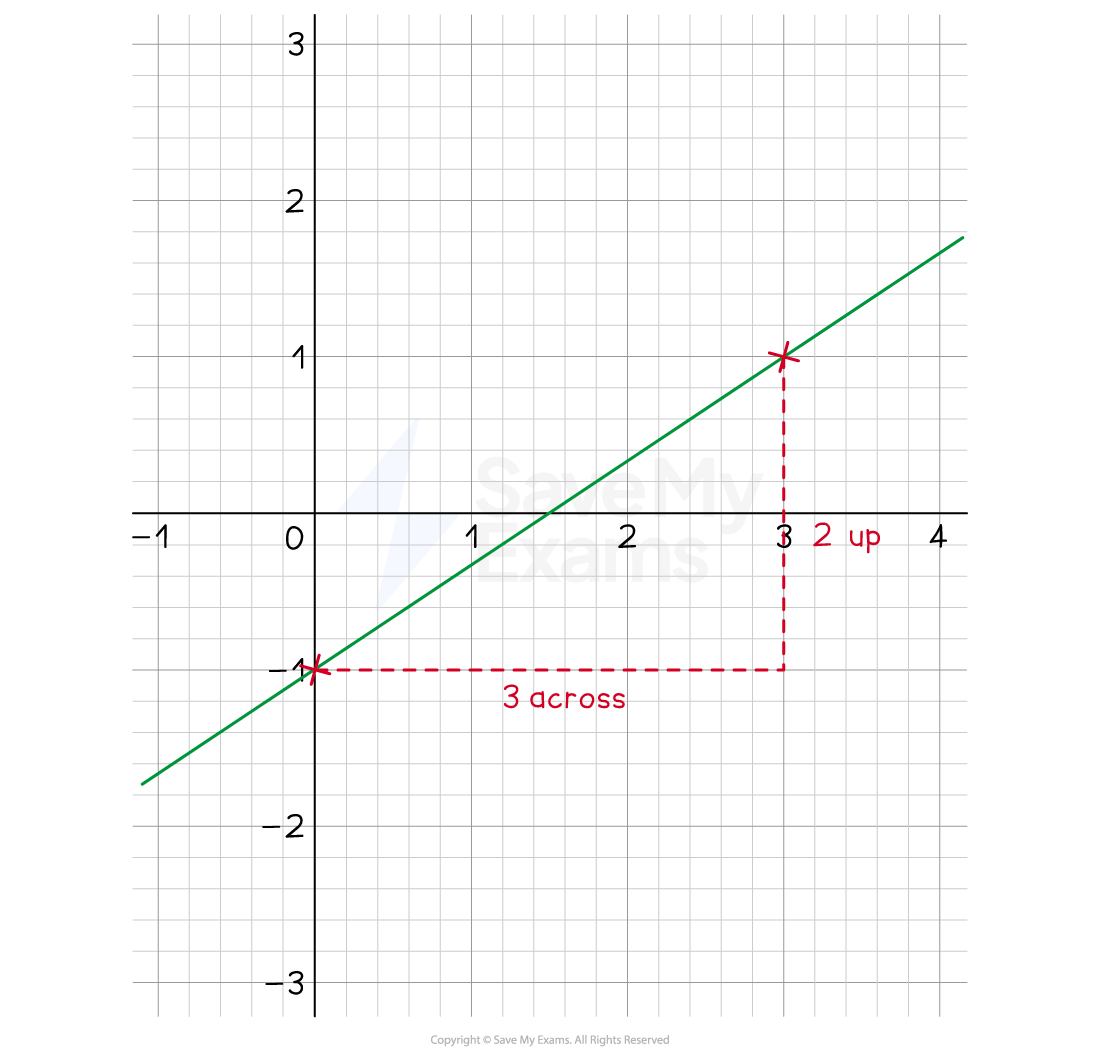

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?