Triangles & Quadrilaterals (SQA National 5 Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: X847 75
Angles in triangles and quadrilaterals
What are the angle sums of triangles and quadrilaterals?
The angles inside any triangle will add up to 180°
The angles inside any quadrilateral (four-sided shape) will add up to 360°
How can I find a missing angle in a triangle or quadrilateral if I know all the other angles?
To find a missing angle in a triangle
subtract all the other angles from 180°
To find a missing angle in a quadrilateral
subtract all the other angles from 360°
Worked Example
ABCD is a quadrilateral.
Point E lies on AD.
Angle BAE is 32°.
Angle ABE is 42°.
Angle BCD is 59°.
Angle CDE is 125°.
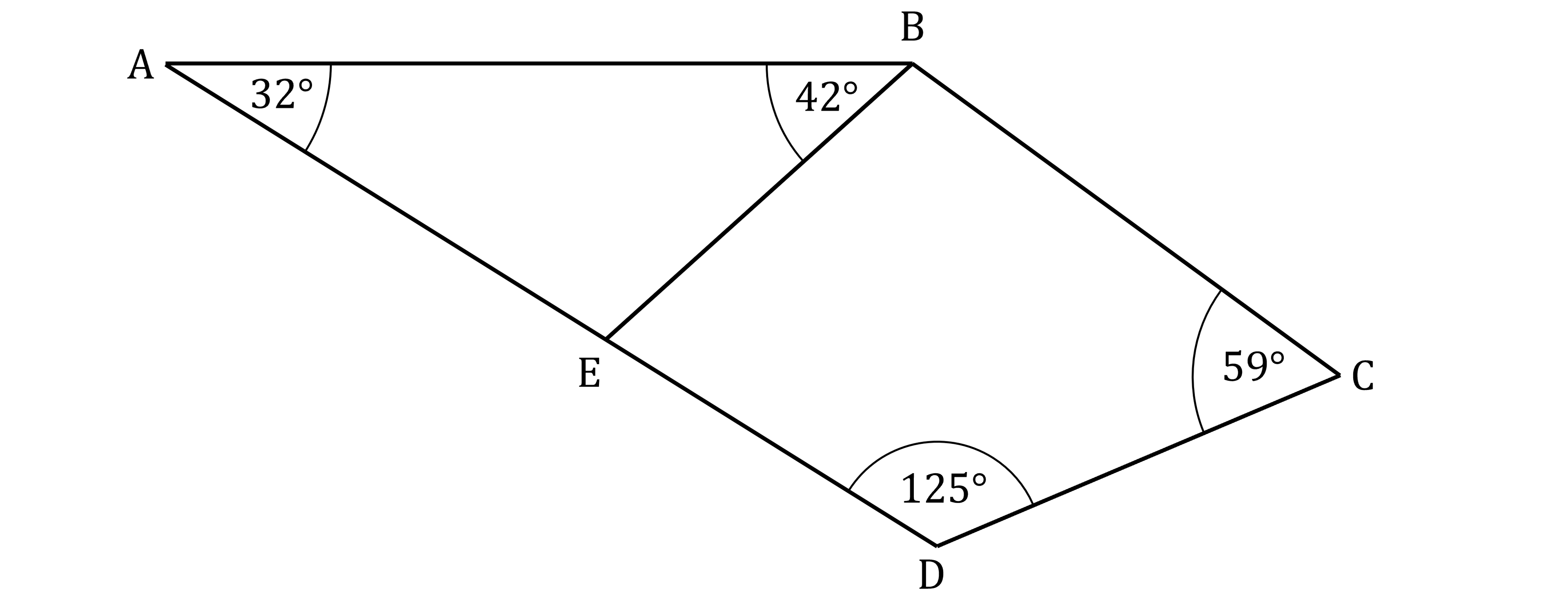
Calculate the size of angle CBE.
Answer:
Angle AEB is the 'missing angle' in triangle ABE
Angles AEB and BED lie on a straight line
So they must add up to 180°
Now you know three of the angles in quadrilateral BCDE
Angle CBE is the 'missing angle' in the quadrilateral
Angle CBE = 102°
Other properties of triangles and quadrilaterals
You should be familiar with the properties of different types of triangles and quadrilaterals from your National 4 Maths course.
The key properties are summarised below.
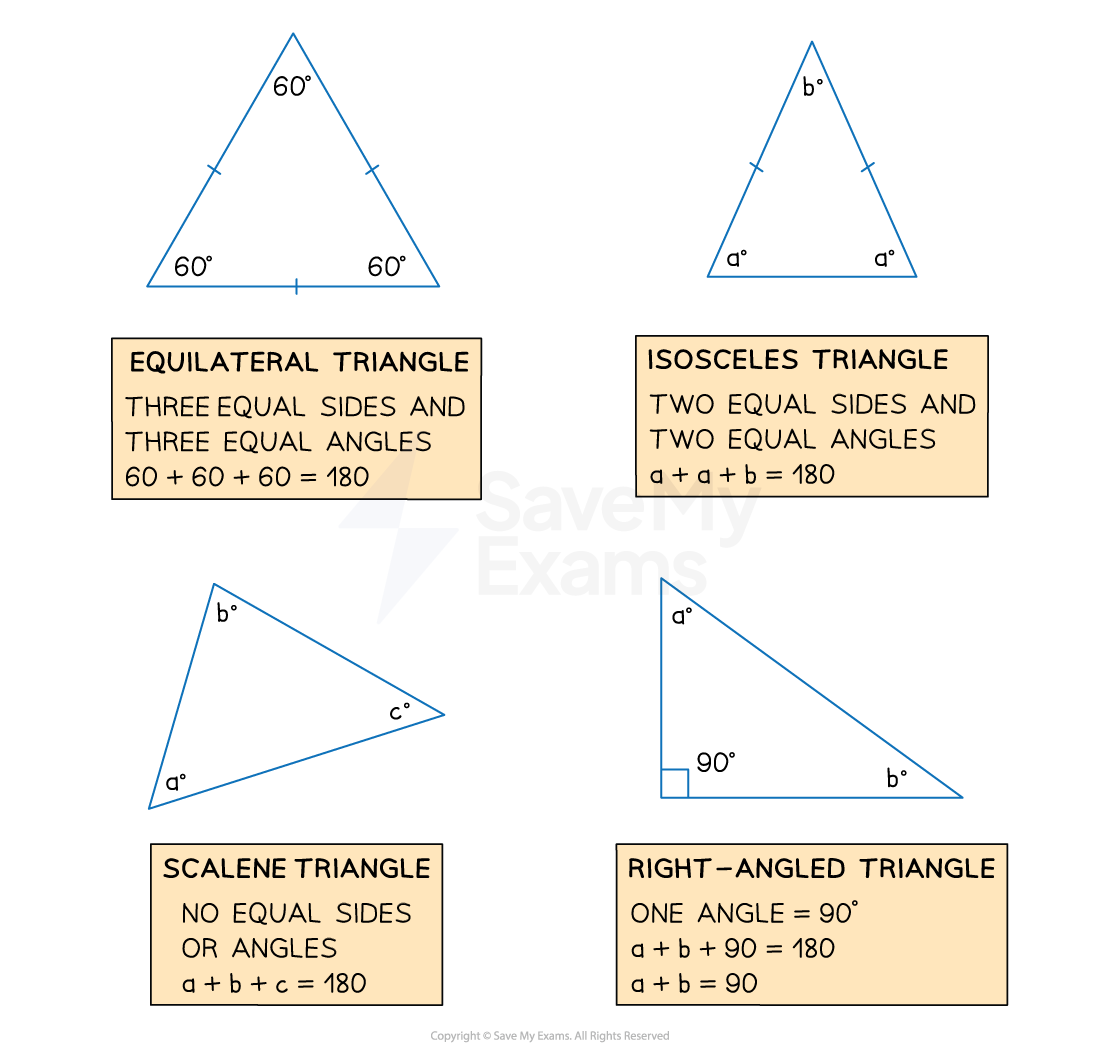
What are the names of the different types of triangles?
You should know the names and properties of the different types of triangles
An equilateral triangle has 3 equal sides and 3 equal angles
An isosceles triangle has 2 equal sides and 2 equal angles
A right-angled triangle has one 90° angle
A scalene triangle has 3 sides all of different lengths
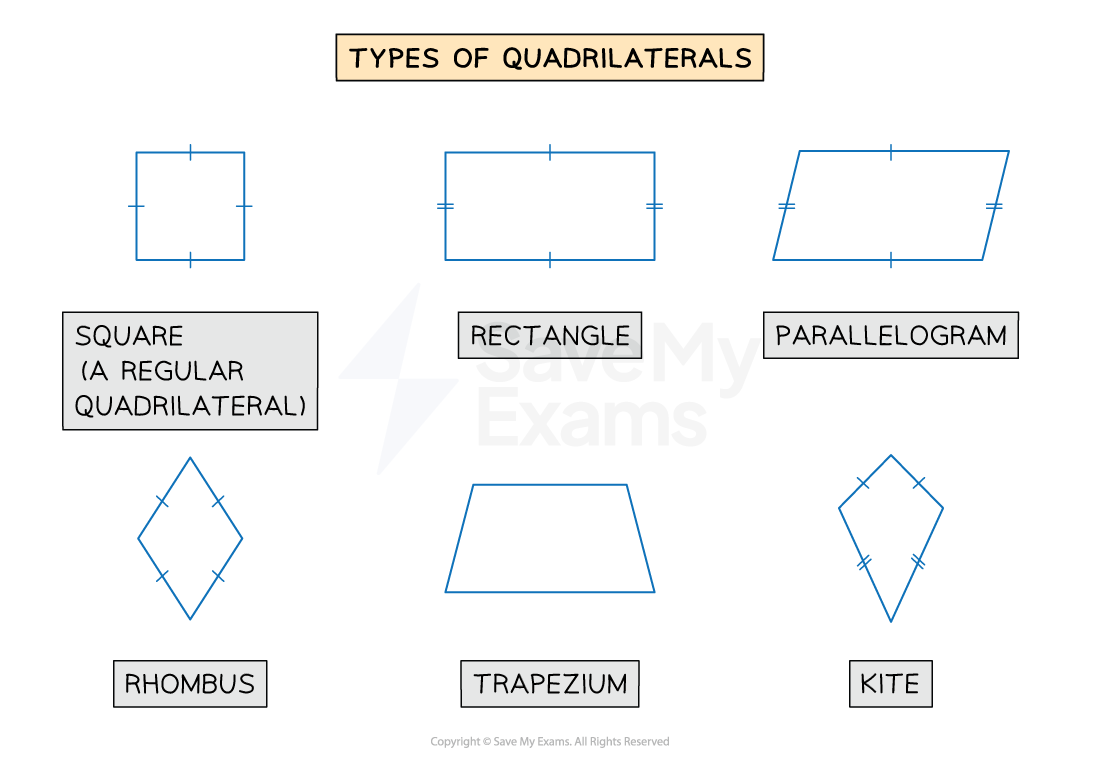
What are the names of the different types of quadrilaterals?
You should know the names and properties of the different types of quadrilaterals
These are squares, rectangles, parallelograms, rhombuses, trapeziums and kites
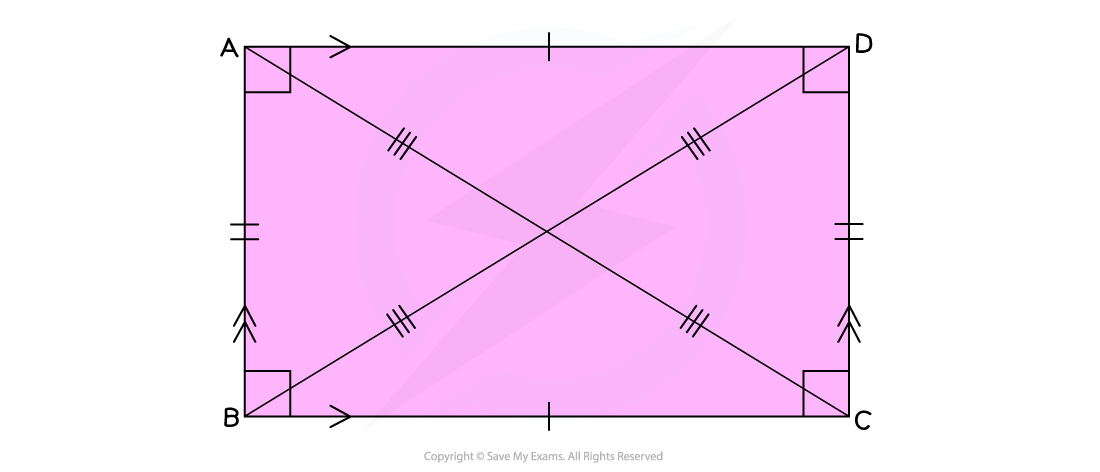
What are the properties of rectangles and squares?
Rectangles and squares have four equal right angles (90°)
Rectangles have two pairs of equal length, parallel sides
Squares are just regular rectangles; all four of their sides are equal
The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other at the centre of the rectangle
This means that they cut each other in half
The intersecting diagonals form two pairs of angles at the centre
In a square, all four of these angles will be equal to 90°
Pythagoras’ theorem can be used to find the length of the diagonal of a square or rectangle
The diagonal forms the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle
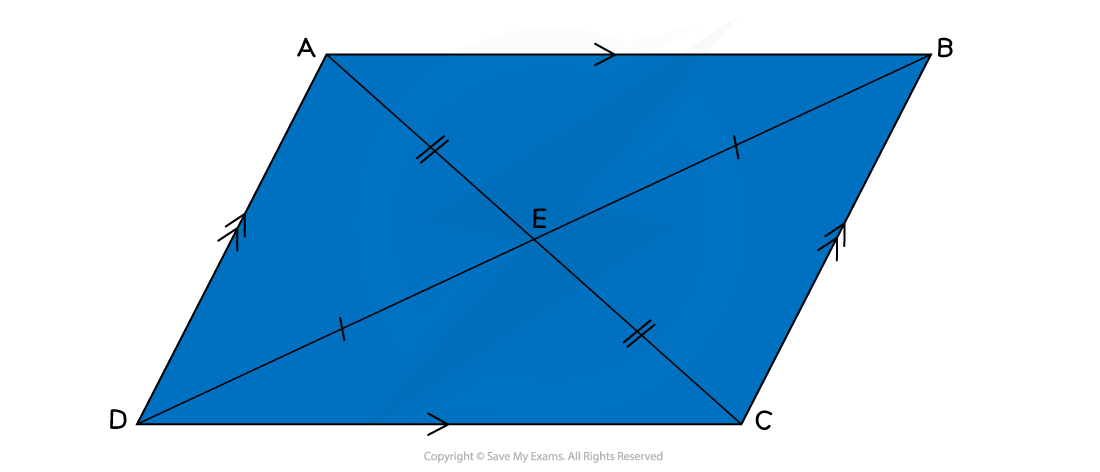
What are the properties of parallelograms and rhombuses?
Parallelograms and rhombuses (rhombi) have two pairs of equal, opposite, angles
Parallelograms and rhombuses have two pairs of opposite, parallel sides
Rhombuses have four sides of the same length
This means a rhombus is a regular parallelogram
A square is also a regular rhombus
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, forming two pairs of opposite angles
The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles (90°)
This means that they cut each other in half
The diagonals will not be of equal length
On the diagram below, the diagonal AC is shorter than the diagonal DB
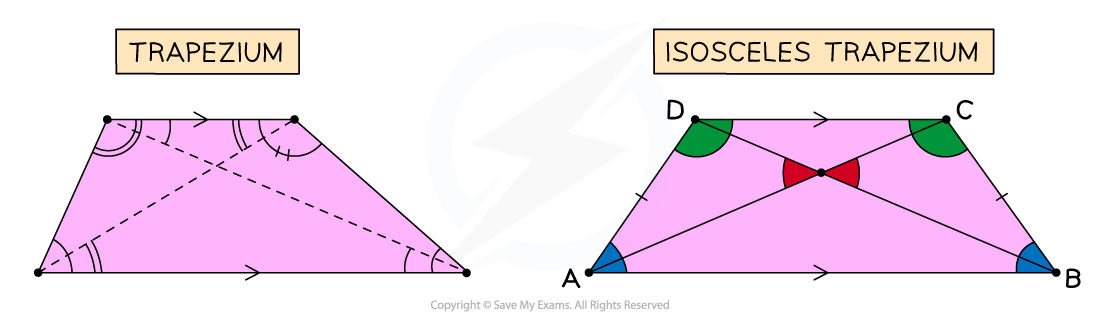
What are the properties of trapeziums?
Trapeziums have one pair of opposite, parallel sides
These are not of equal length
Trapeziums may not have any equal angles
As with all quadrilaterals, the angles add up to 360°
If a trapezium has a line of symmetry, it is classed as isosceles
Isosceles trapeziums have two pairs of equal angles
The non-parallel sides in an isosceles trapezium will be equal length
An isosceles trapezium has two diagonals of equal length
What are the properties of kites?
Kites have one line of symmetry, known as their main diagonal
The angles opposite the main diagonal are equal
These are angles ABC and ADC on the diagram below
The diagonals of a kite bisect each other at right angles (90°)
This means that they cut each other in half
The diagonals will not be of equal length
Kites have no parallel sides
Kites have two pairs of equal length, adjacent sides

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember the key properties of each shape.
You may need to use these facts to help work out more tricky geometry or vector problems

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?