Converse of Pythagoras' Theorem (SQA National 5 Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: X847 75
Using the converse of Pythagoras' theorem
What is Pythagoras' theorem?
You should be familiar with Pythagoras' theorem from your National 4 Maths course
The theorem gives a formula that links the lengths of the three sides of a right-angled triangle
Pythagoras' theorem states that
is the length of the hypotenuse
The hypotenuse is the longest side, and is always opposite the right angle
and
are the lengths of the two shorter sides
It does not matter which is labelled
and which is labelled

What is the converse of Pythagoras' theorem?
If you know that a triangle is right-angled, then you can use Pythagoras' theorem to find a missing side if you know the other two sides
If the triangle is right-angled, then
The converse of Pythagoras' theorem can be used to show whether or not a triangle is right-angled if you know the three side lengths
If
, then the triangle is right-angled
If
, then the triangle is not right-angled
How do I use the converse of Pythagoras' theorem to determine whether or not a triangle is right-angled?
For example: A triangle has side lengths of 5 cm, 12 cm and 14 cm. Determine whether or not the triangle is right-angled
Work out the values of
and
Make sure that you use the longest side as
It doesn't matter which of the other two sides is
, and which is
If the two values are equal, then the triangle is right-angled
If the two values are not equal, then the triangle is not right-angled
Here
Therefore the triangle is not right-angled
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Students have tended to lose a lot of marks on these questions in past papers.
In particular, do not start by substituting the three sides into .
So in the example above, do not write
You will lose a mark for doing this, even if everything else is correct
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In exams, converse Pythagoras questions have tended to appear in the context of 'real-life' scenarios.
Look out for questions where you are asked to determine whether two things are perpendicular
Be sure to answer in the context of the question
Worked Example
A ladder is leaned against a wall built on horizontal ground as shown in the diagram.
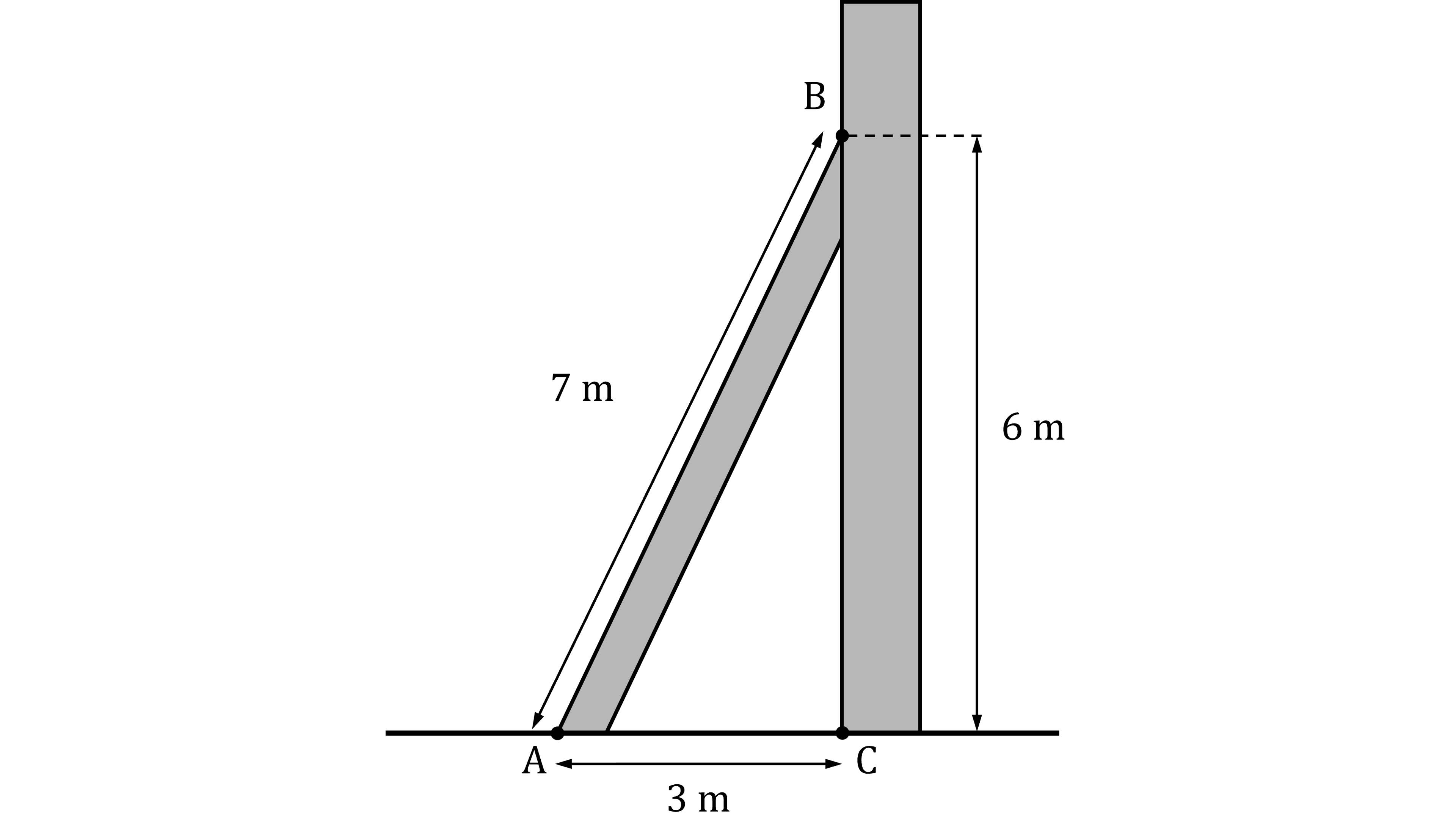
The edge of the ladder, AB, is 7 metres long.
C is at the foot of the wall.
A is 3 metres from C.
B is 6 metres from C.
Determine whether the wall is perpendicular to the ground.
Justify your answer.
Answer:
You need to determine whether or not angle ACB is a right angle
If it is, then the wall is perpendicular to the ground
If it is not, then the wall is not perpendicular to the ground
Use the converse of Pythagoras' theorem
Let
, because the 7 m side is the longest side of the triangle
and
will be 3 and 6 (which is which isn't important)
Calculate
Calculate
State that those are not equal
Because they are not equal, the triangle is not a right-angled triangle
This means angle ACB is not a right angle
Which means the wall isn't perpendicular to the ground
Write your conclusion, giving a justification and answering in the context of the question
The wall is not perpendicular to the ground, because angle ACB is not a right angle

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?