Pythagoras' Theorem in 3D (SQA National 5 Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: X847 75
Using Pythagoras' theorem in 3D
How do I use Pythagoras' theorem in a 3D shape?
You can often find right-angled triangles within 3D shapes
If two sides of the triangle are known, you can use Pythagoras’ theorem
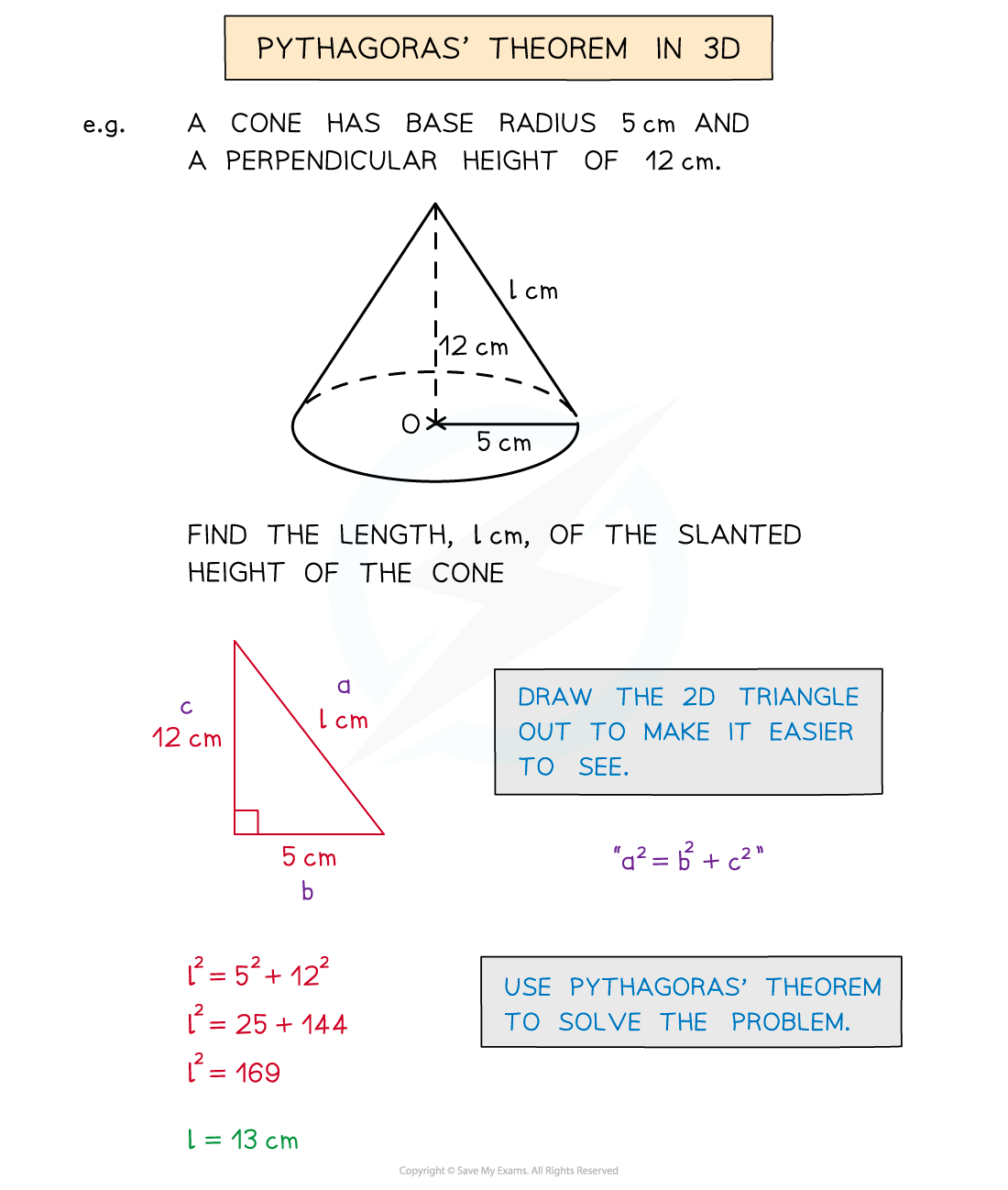
Is there a 3D version of the Pythagoras' theorem formula?
There is a 3D version of Pythagoras’ theorem:
is the distance between two points
and
are the distances in the three different perpendicular directions between the two points
A typical example of using this is to find the length of one of the diagonals that goes across the inside of a cuboid
In exam questions this is referred to as a space diagonal
You may also see people refer to it as an 'interior diagonal' or 'body diagonal'

However, all 3D situations can be broken into two 2D problems
Form two right-angle triangles
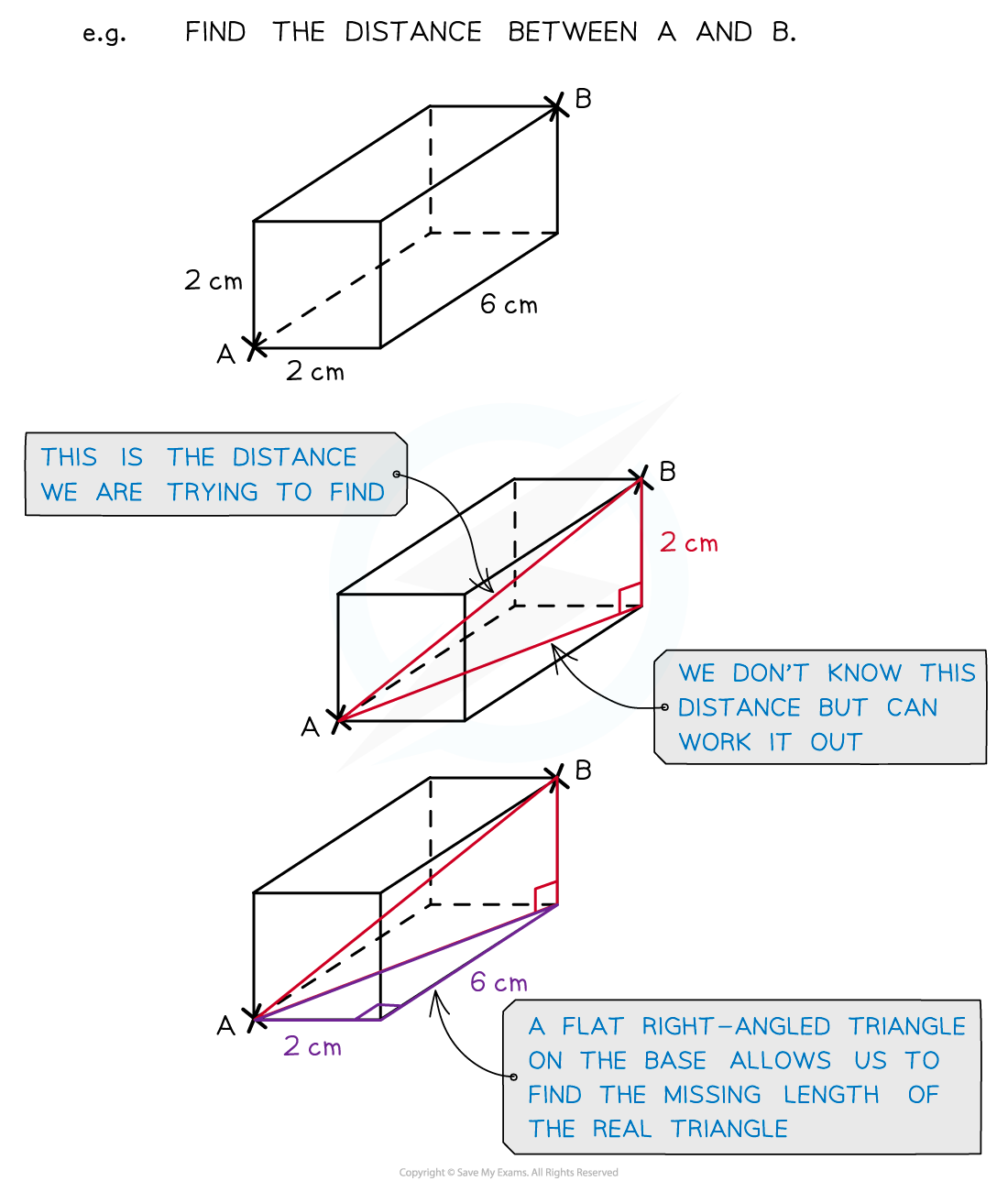
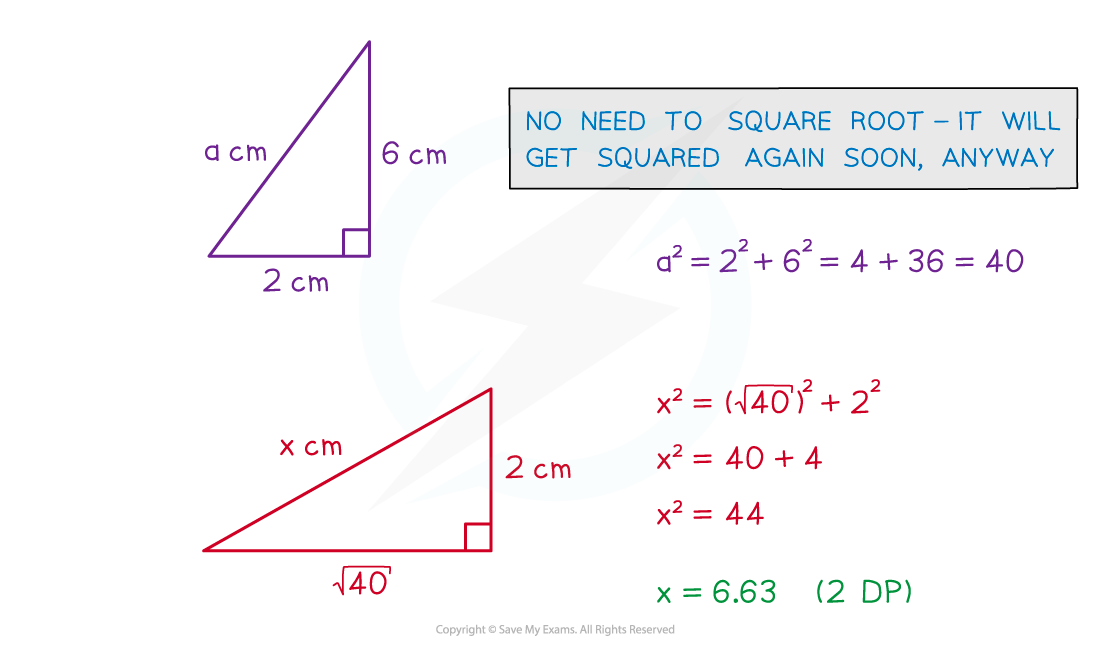
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are not given the 3D Pythagoras formula in the exam.
However it is essentially the same as the formula for finding the magnitude of a 3D vector
And you can always split 3D problems into two 2D problems (which don't need this formula)
How do I apply 3D Pythagoras to more complicated problems?
Always split up a complicated problem into 2D right-angled triangles
Some questions may require more than one 2D right-angled triangle
Some 2D triangles on the diagram are still drawn in 3D
It helps to redraw these 2D triangles flat on the page (not at angles)
You can then spot any uses of Pythagoras' theorem
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are stuck in the exam with a complicated 3D diagram, it is always better to just start finding any lengths in the shape, as
these may end up being useful
you may score more marks than if you had left the question blank
Worked Example
A cuboid shaped box has dimensions 3 cm by 4 cm by 6 cm.
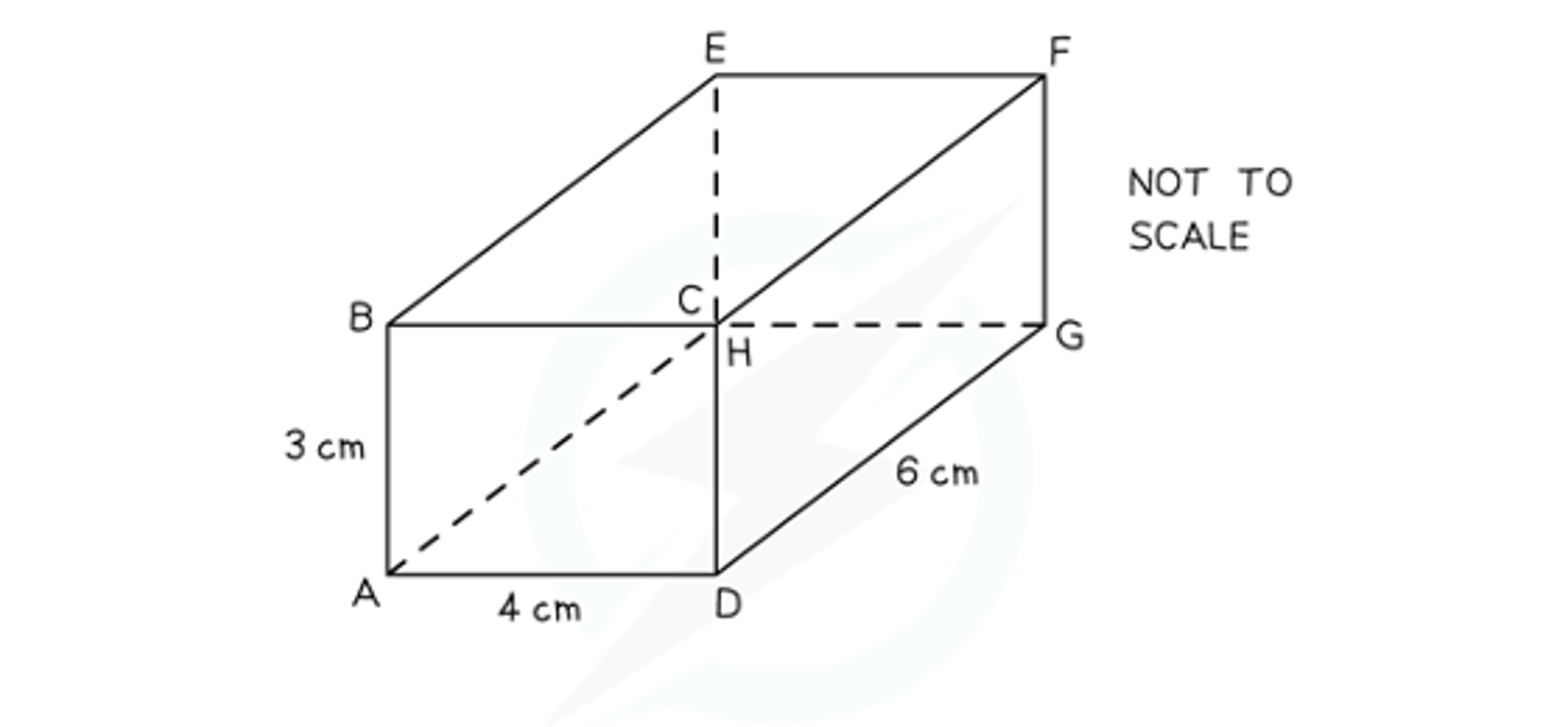
Calculate the length of the space diagonal AF.
Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures.
Answer:
Method 1
AF is the hypotenuse of triangle ABF
You know AB, but you don't know the length of BF
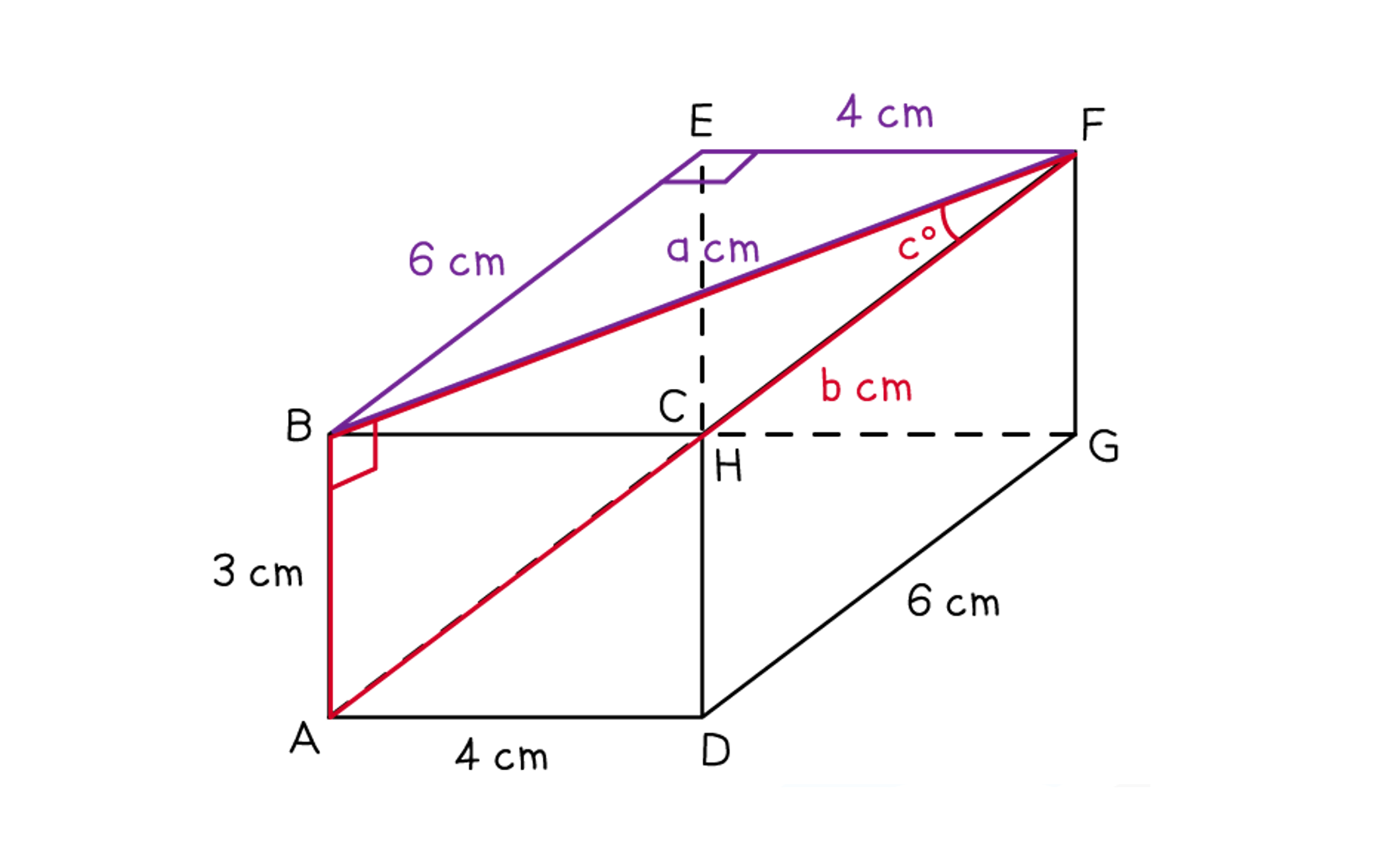
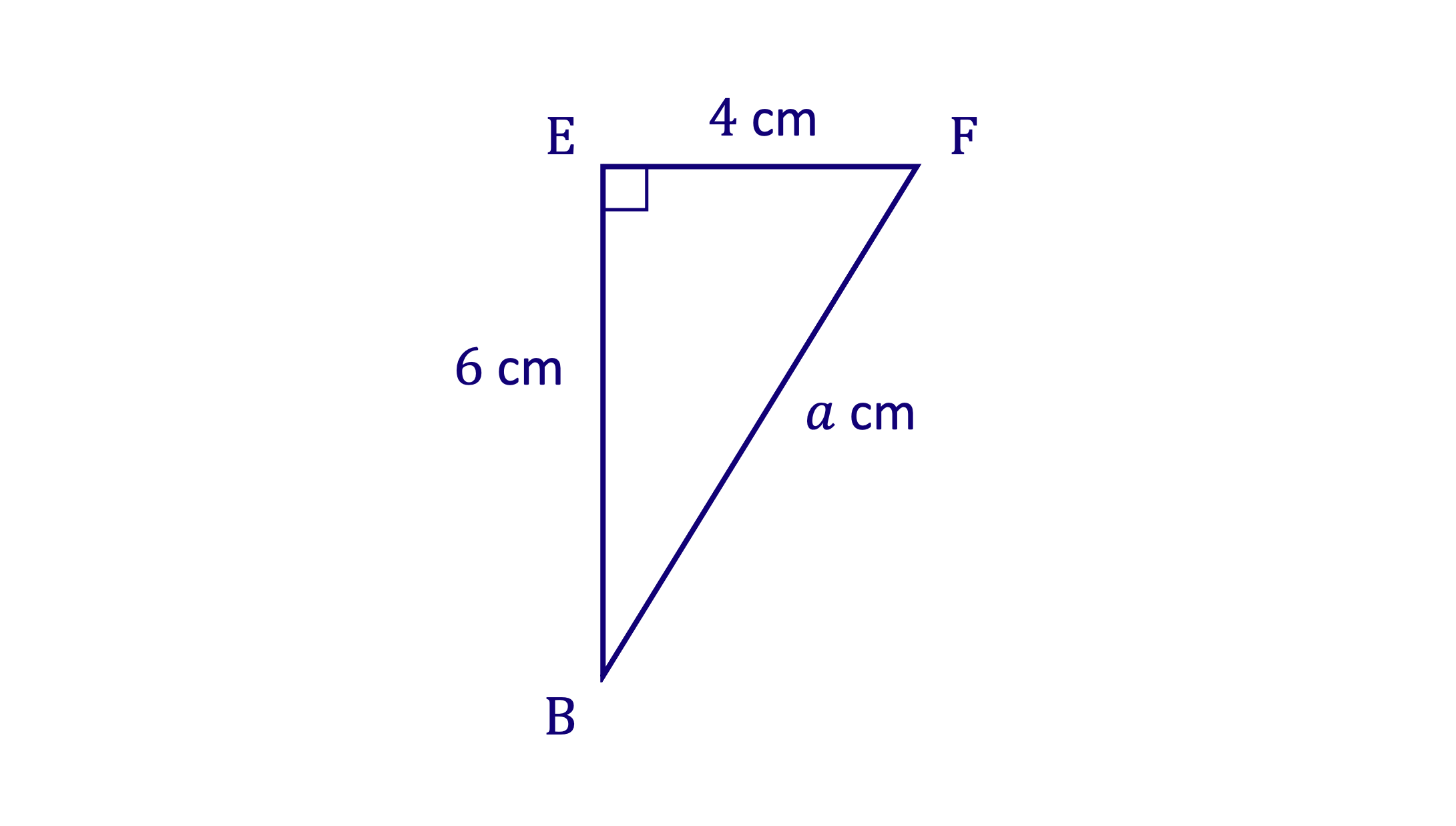
Draw triangle BEF flat and use Pythagoras' theorem to find BF
Draw triangle ABF flat and use Pythagoras' theorem to calculate AF
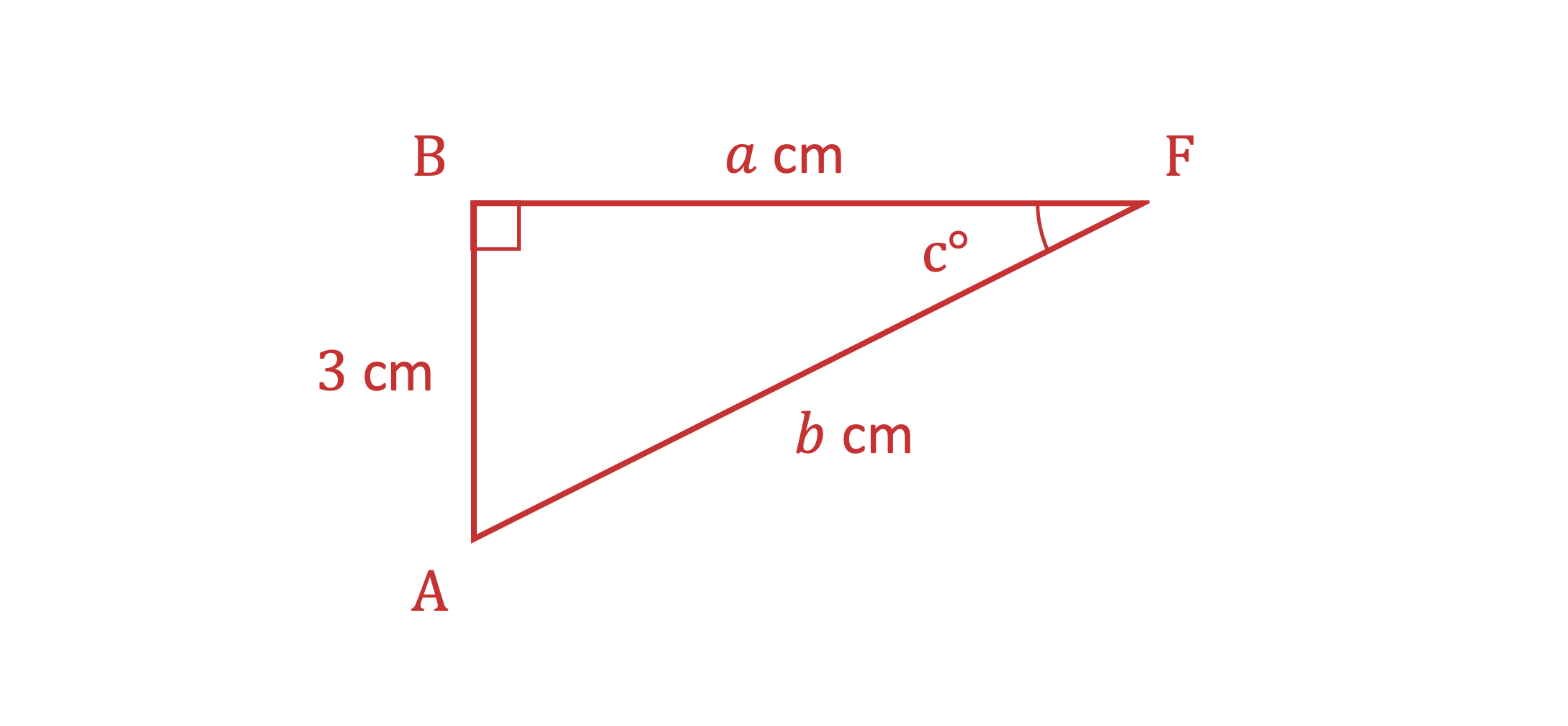
Round to 3 significant figures, as required
7.81 cm (3 s.f.)
Method 2
Apply the 3D version of Pythagoras’ theorem:
The distance in the x direction is 4 cm
The distance in the y direction is 6 cm
The distance in the z direction is 3 cm
Round to 3 significant figures, as required
7.81 cm (3 s.f.)

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?