Similar Areas & Volumes (SQA National 5 Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: X847 75
Similar areas & volumes
What are similar shapes?
Two shapes are mathematically similar if they have the same shape and their corresponding sides are in proportion
One shape is an enlargement of the other
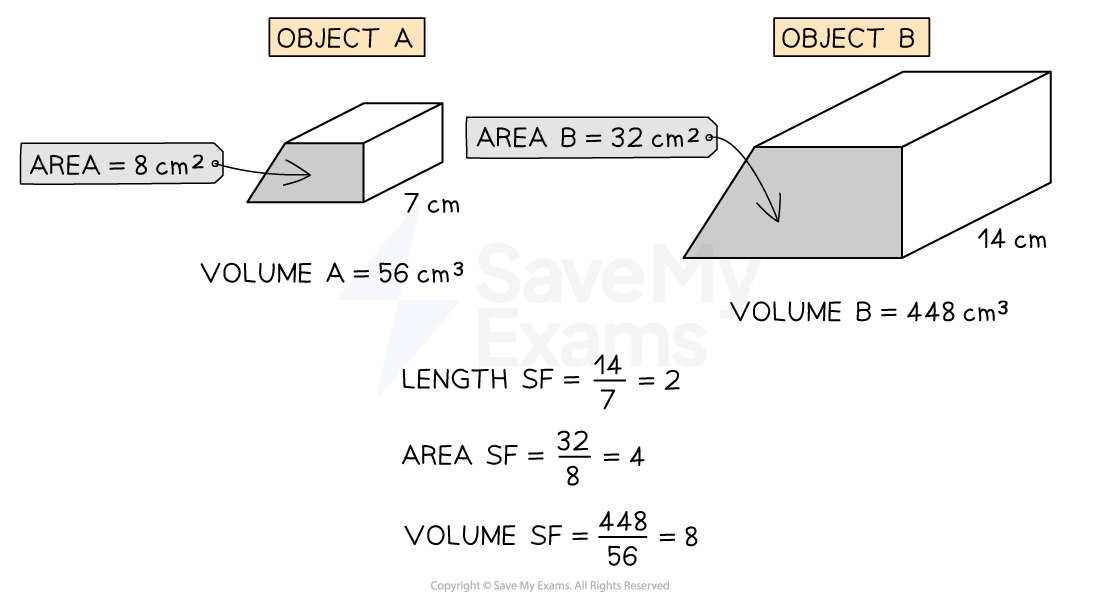
How do I find the length, area or volume scale factors of similar shapes?
The scale factor (SF) for a given quantity (length, area or volume), can be found by dividing the quantity on one shape by the quantity on the other shape
An object could be made either bigger or smaller by a scale factor
When k > 1, the object is getting bigger
This is also true for k2 > 1 and k3 > 1
When 0 < k < 1, the object is getting smaller
This is also true for 0< k2 < 1 and 0 < k3 < 1
What is the connection between the scale factors for lengths, areas and volumes of similar shapes?
In mathematically similar shapes
the length, area and volume scale factors can be written as powers with the same base number
If the length scale factor is k then
The area scale factor is k2
The volume scale factor is k3
If you know one scale factor, you can find the other scale factors
If you have the length scale factor
If you have the area scale factor
If you have the volume scale factor
How do I find missing lengths, areas and volumes for similar shapes?
STEP 1
Identify the equivalent known quantitiesRecognise if the quantities are lengths, areas or volumes
STEP 2
Find the scale factor from two known lengths, areas or volumesSTEP 3
Use the scale factor you have found to find other required scale factor(s)STEP 4
Multiply or divide by relevant scale factor to find the missing quantityThink about whether the quantity should be bigger or smaller than the given quantity
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Take extra care not to mix up which shape is which when you have started carrying out the calculations.
It can help to label the shapes and write an equation
Worked Example
Solid A and solid B are mathematically similar.
The height of solid A is 10 cm.
The height of solid B is 15 cm.
The surface area of solid A is 80 cm2.
The volume of solid A is 32 cm3.
(a) Find the surface area of solid B.
(b) Find the volume of solid B.
Answer:
Part (a)
Divide the height of B by the height of A to find the length scale factor k
Square that to find the area scale factor, k2
B has a larger height than A, so it will also have a larger surface area
Multiply the surface area of A by k2 to find the surface area of B
Don't forget to include units in your final answer
180 cm2
Part (b)
You already know the length scale factor, k, from part (a)
Cube that to find the volume scale factor, k3
B has a larger height than A, so it will also have a larger volume
Multiply the volume of A by k3 to find the volume of B
Don't forget to include units in your final answer
108 cm3
Using scale factors to test similarity
How do I use scale factors to show that two shapes are not similar?
If two shapes are mathematically similar then the following relationships must be true
If you know one of the scale factors, then the other two are determined automatically
If those relationships are not true then the shapes are not similar
You can use this in the exam to show that two shapes are not similar
E.g. if the length scale factor for two shapes is 4 and the area scale factor is 15
, which is not equal to
The length factor squared is not equal to the area scale factor
So the two shapes are not mathematically similar
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Note that you cannot use this test to prove that two shapes definitely are similar. You can only use it to show that two shapes are not similar.
Worked Example
A sports stadium sells soft drinks in two different sized cups.
The small cup has a height of 12 centimetres and a volume of 330 cubic centimetres.
The large cup has a height of 13.5 centimetres and a volume of 440 cubic centimetres.
Show that the two cups are not mathematically similar.
Answer:
Divide the height of the large cup by the height of the small cup to find the length scale factor
Cube that to find what the volume scale factor would be, if the cups were mathematically similar
Divide the volume of the large cup by the volume of the small cup to find the actual length scale factor
Those are not equal, so the cups are not mathematically similar
Be sure to give your reason
The volume scale factor is not equal to the length scale factor cubed, so the cups are not mathematically similar

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?