Magnitude of a Vector (SQA National 5 Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: X847 75
Calculating the magnitude of a vector
What is the magnitude of a vector?
The magnitude of a vector is its length
It is also called the modulus
This is always a positive value
The direction of the vector is irrelevant
The magnitude of vector
is written
The magnitude of vector a is written |a|
In real world contexts, the magnitude of a vector can represent different quantities
For a velocity vector, its magnitude would be speed
For a force vector, its magnitude would be the strength of the force (in newtons)
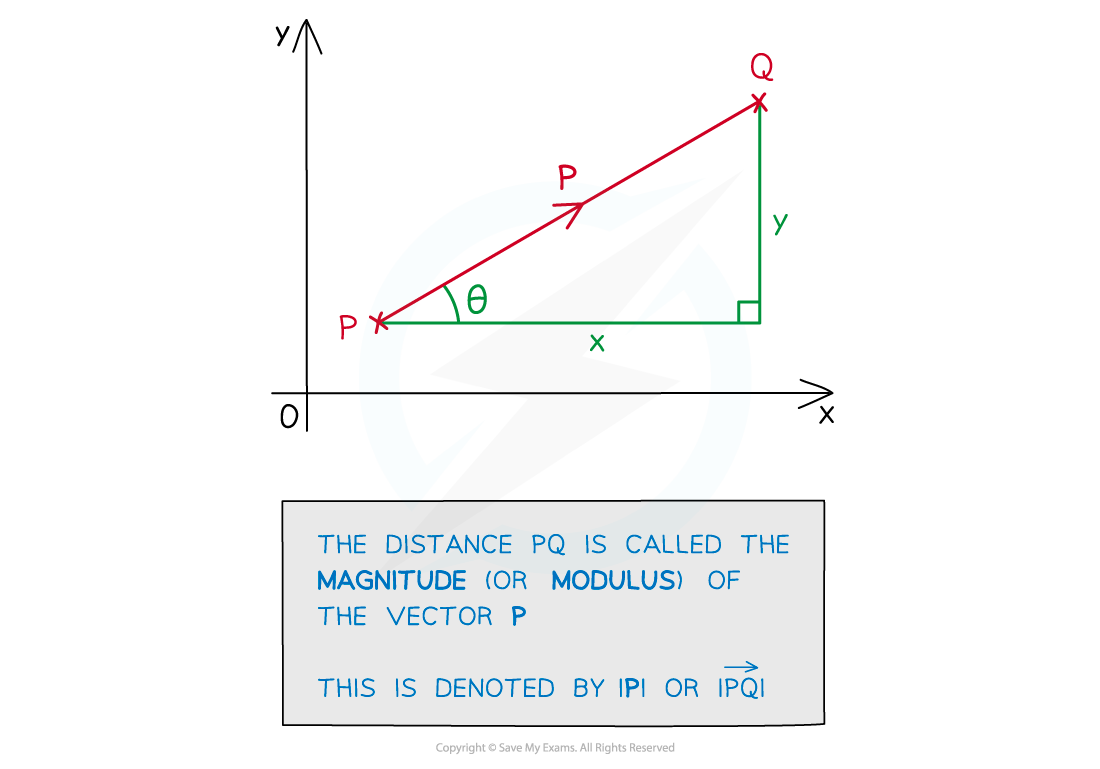
How do I find the magnitude of a two-dimensional vector?
For a 2D vector in component form, the magnitude is the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle
Use Pythagoras' theorem to find the magnitude
The magnitude of
is
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If there is no diagram, sketch one!
You can sketch a vector and use it to form a right-angled triangle
How do I find the magnitude of a three-dimensional vector?
For a 3D vector in component form, the magnitude can be found using the following formula
The magnitude of
is
This is formula is related to Pythagoras' Theorem in 3D
Worked Example
Consider two points and
.
(a) Write down the vector in component form.
(b) Find the modulus of vector .
Answer:
Part (a)
Find the horizontal and vertical distances between the two points
You can do this by subtracting the x and y components of A from B
Part (b)
Sketching a diagram of the vector can help
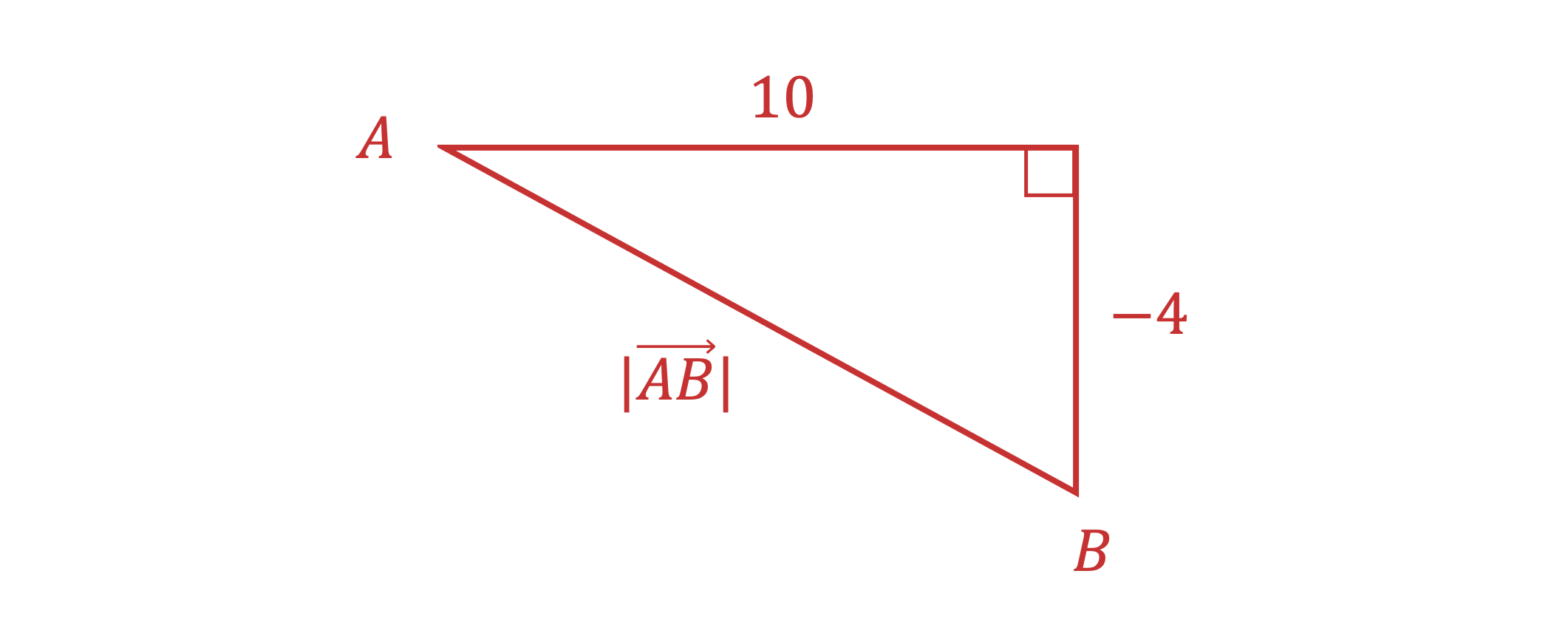
Apply Pythagoras' theorem to the x and y components of
Worked Example
Find , the magnitude of vector
.
Answer:
Use the formula , where
Use your calculator to work that out

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?