Vector Pathways (SQA National 5 Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: X847 75
Vector pathway basics
How do I find the vector between two points?
A vector pathway is a path of vectors taking you from a start point to an end point
The following grid is made up entirely of parallelograms
The vectors a and b are defined as marked in the diagram:
Any vector that goes horizontally to the right along a side of a parallelogram will be equal to a
Any vector that goes up diagonally to the right along a side of a parallelogram will be equal to b
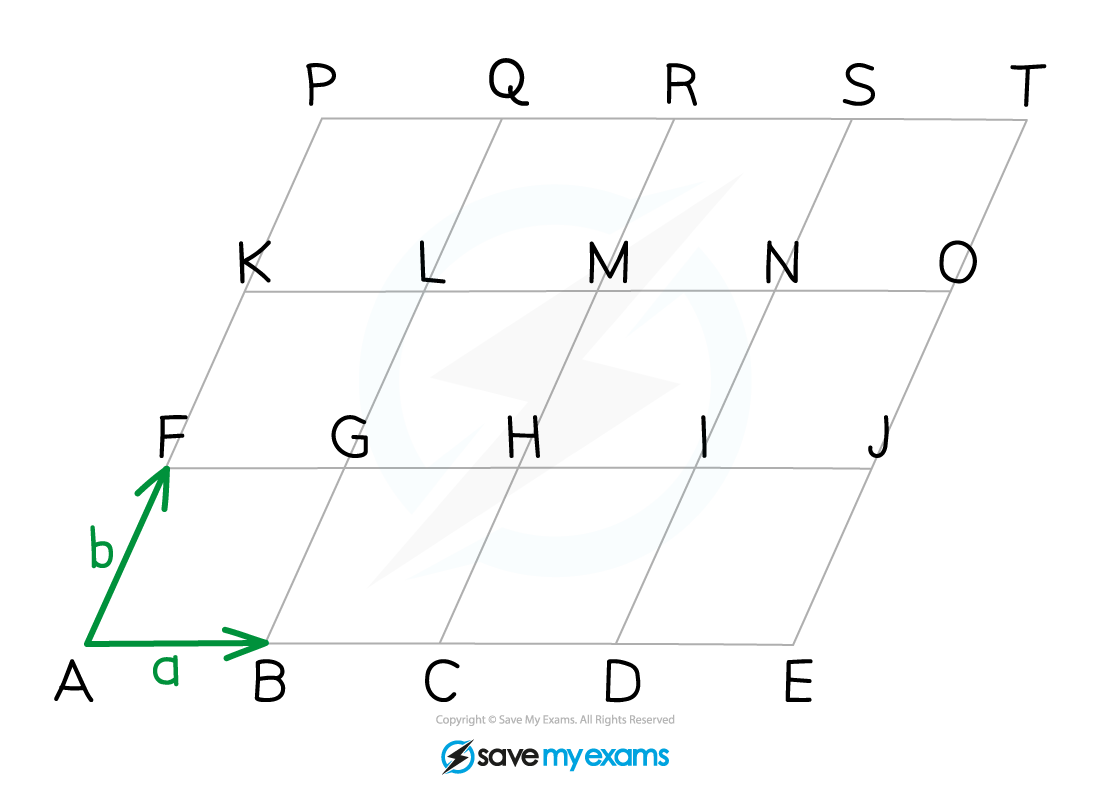
To find the vector between two points
Count how many times you need to go horizontally to the right
This will tell you how many a's are in your answer
Count how many times you need to go up diagonally to the right
This will tell you how many b's are in your answer
Add the a's and b's together
E.g.
You will have to put a negative in front of the vector if it goes in the opposite direction
-a is one length horizontally to the left
-b is one length down diagonally to the left
E.g.
or
Likewise,

It is possible to describe any vector that goes from one point to another in the above diagram in terms of a and b
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the exam, different correct pathways will earn full marks, as long as the final answer is fully simplified.
Check for symmetries in the diagram to see if the vectors given can be used anywhere else.
Worked Example
The following diagram consists of a grid of identical parallelograms.
Vectors a and b are defined by and
.

Write the following vectors in terms of a and b.
a)
b)
c)
Answer:
Part (a)
To get from A to E you need to follow vector four times to the right
Part (b)
There are many ways to get from G to T
One option is to go from G to Q ( twice), and then from Q to T (
three times)
Part (c)
There are many ways to get from E to K
One option is to go from E to O ( twice), and then from O to K (
four times)
Finding more challenging vector pathways
How can vector pathway questions be made more challenging?
You may need to find expressions for vectors in places where you cannot simply count spaces on a grid
You should be familiar with the properties of different types of triangle and quadrilateral
You may need to use these properties to answer a vector pathway question
Look out for places where two vectors in a diagram are equal or where one is a multiple of the other
How do I use multiples in vector pathways?
When multiplying a vector by a scalar number, you can use the normal rules of algebra
E.g. expanding brackets, collecting like terms

In the example shown, if
and you know that
then
Questions may specify that a point is the midpoint of a line segment
E.g. point
may be the midpoint of line segment
This means that
and
Note that if one vector is a multiple of another, this means that the vectors are parallel
E.g.
is parallel to
It is twice as long and points in the same direction
is also parallel to
It is three times as long and points in the opposite direction (because of the minus sign)
If two vectors are parallel, have the same length and point in the same direction
then they are equal
Worked Example
The diagram shows a parallelogram with a diagonal
drawn.
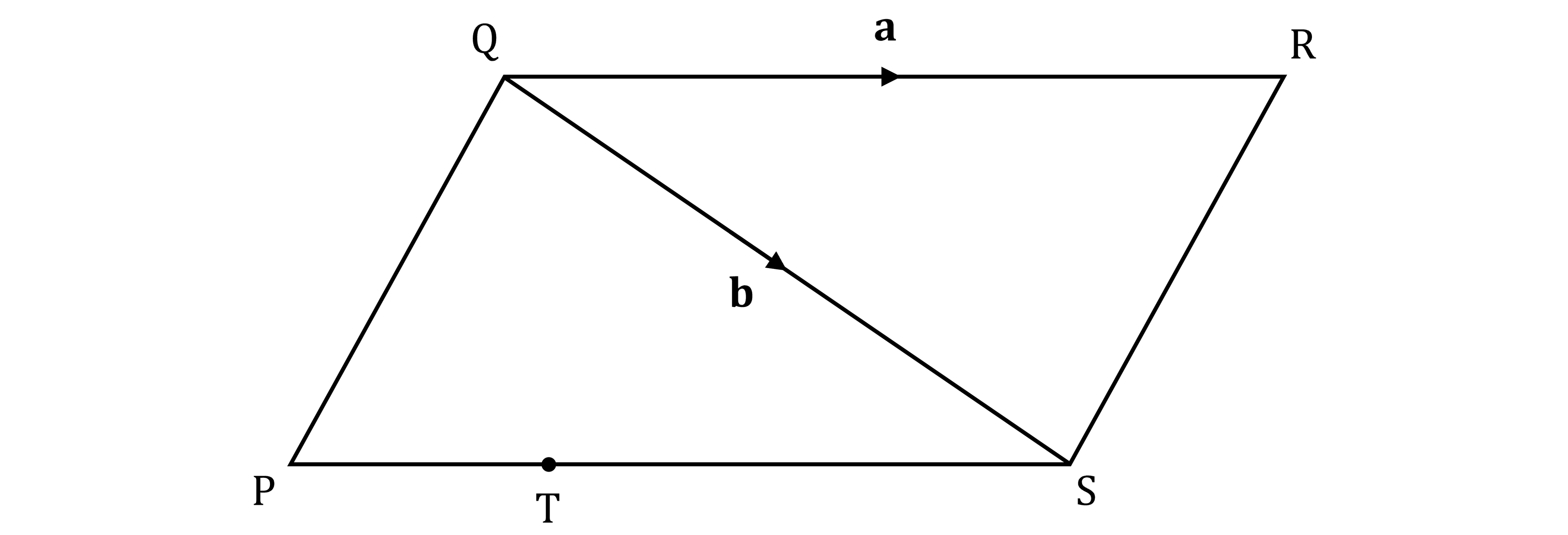
represents vector
and
represents vector
.
a) Express in terms of
and
.
is the point such that
.
b) Express in terms of
and
. Give your answer in simplest form.
Answer:
Part (a)
To get from R to S you can go
the 'wrong way' down vector
to Q
then the 'right way' down vector
to S
Part (b)
Write as a vector pathway; one possibility is
Use what you know about those vectors
Because PQRS is a parallelogram, sides QP and RS are parallel and the same length
Therefore
(using the answer from part (a) )
Also because PQRS is a parallelogram, sides PS and QR are parallel and the same length
And
So
Collect like terms and simplify
Worked Example
In triangle ,
and
.
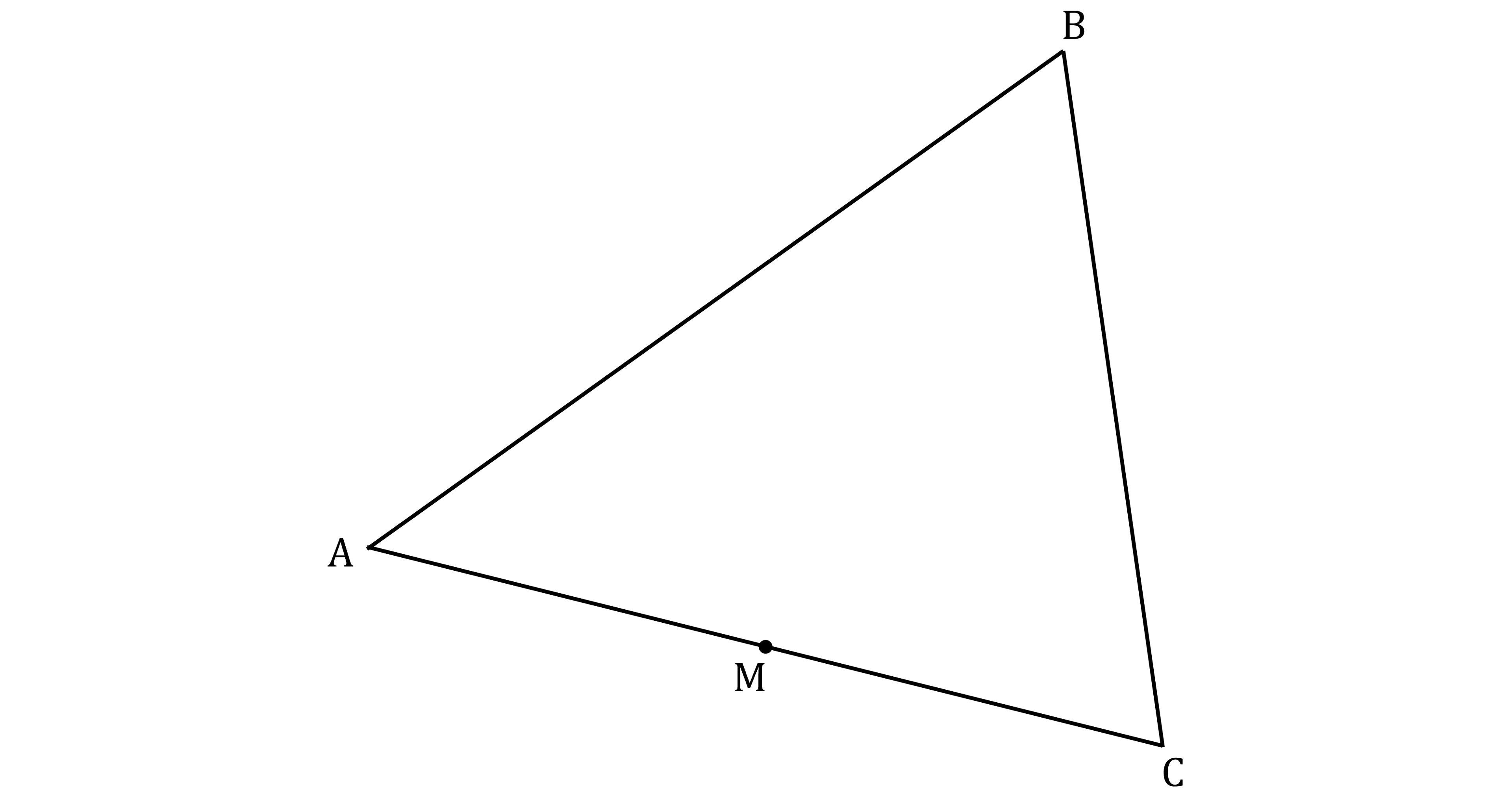
a) Express in component form.
is the midpoint of
.
b) Express in component form.
Answer:
Part (a)
Find a path from A to B using vectors whose components you know
You can get from A to B by going from A to C, then from C to B
Substitute in the components from the question
Add the components
Part (b)
Write as a vector pathway; one possibility is
is the midpoint of
That means that
Substitute in the components from the question
Multiply the components of by
Add the components

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
