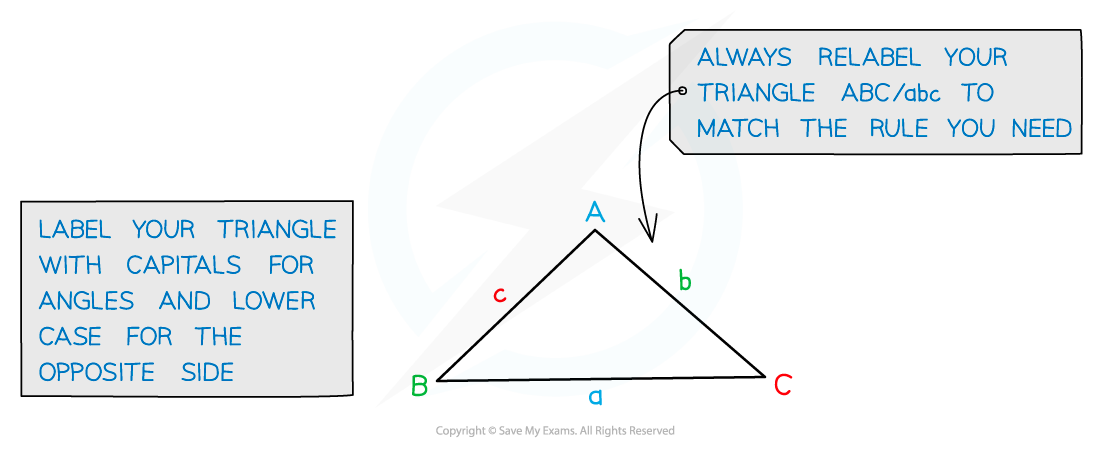
Area of a Triangle (SQA National 5 Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: X847 75
Calculating the area of a triangle
How do I find the area of a non-right-angled triangle?
The area of any triangle can be found using the formula
C is the angle between sides
and
If angle C is 90°, you get a right-angled triangle
sin 90° = 1 so the formula becomes the familiar "Area = ½ × base × height"!
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Swapping the letters around allows the triangle area formula to be written in these forms as well:
Just make sure the angle used in the formula is in between the two sides used.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The area of a triangle formula appears on the Formulae List in the exam paper in the form
Remember that the there is for 'Area'. It is not referring to an angle labelled
!
Worked Example
Triangle is shown in the diagram.
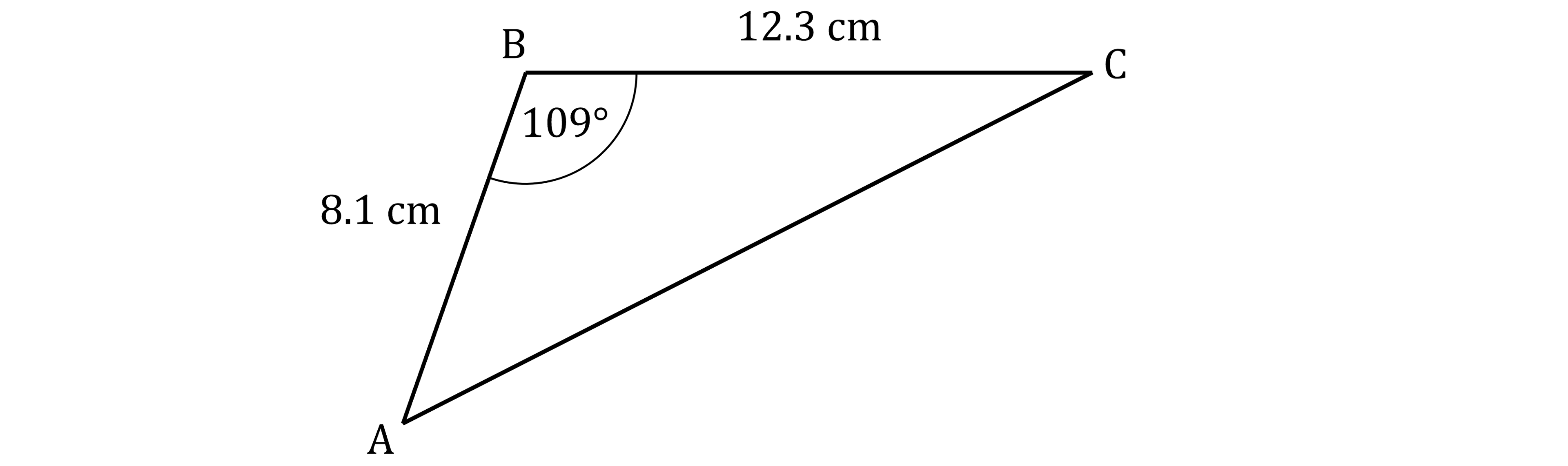
Angle ABC = 109°
AB = 8.1 cm
BC = 12.3 cm
Calculate the area of the triangle.
Answer:
Label the sides of the triangle
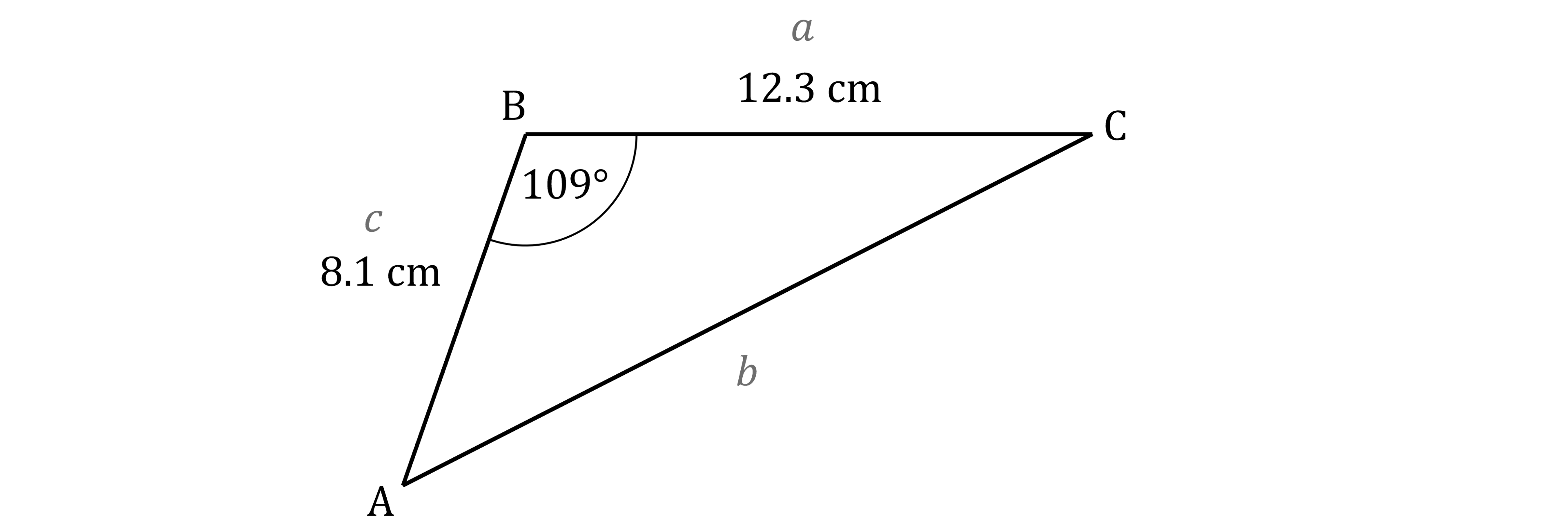
You want to find the area and are given the size of angle B
So swap the letters around in the Formulae List form of the triangle area formula to get
Substitute the known values into that equation
Round to a sensible degree of accuracy
Unless a question tells you otherwise, 3 significant figures is usually a good choice
47.1 cm2 (3 s.f.)
Using the area of a triangle to find a length or angle
How do I find a length or angle when I know the area of a non-right-angled triangle?
You may be given the area of a non-right-angled triangle
and asked to find a side length or an angle
To do this
Substitute the information you do know into the triangle area formula
Then rearrange the formula to make the thing you are looking for the subject
For example, to find the length of side
the formula rearranges to
Or to find the angle C
the formula rearranges to
Then use the cos-1 feature on your calculator to find C
Worked Example
In the diagram
Angle BAC = 26°
AC = 30 cm
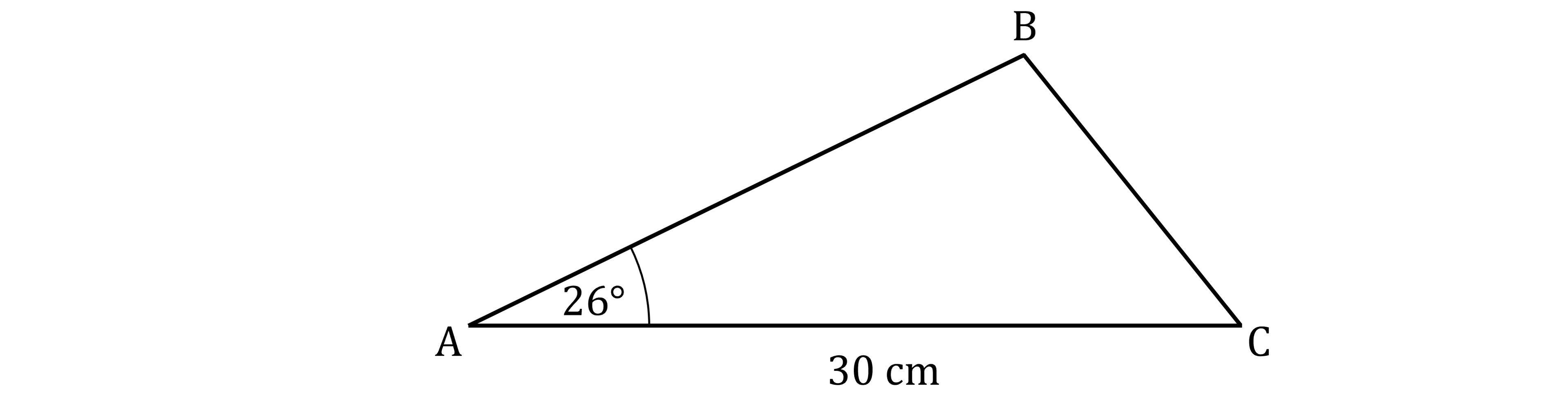
The area of triangle ABC is 160 square centimetres.
Calculate the length of AB.
Answer:
Label the sides of the triangle
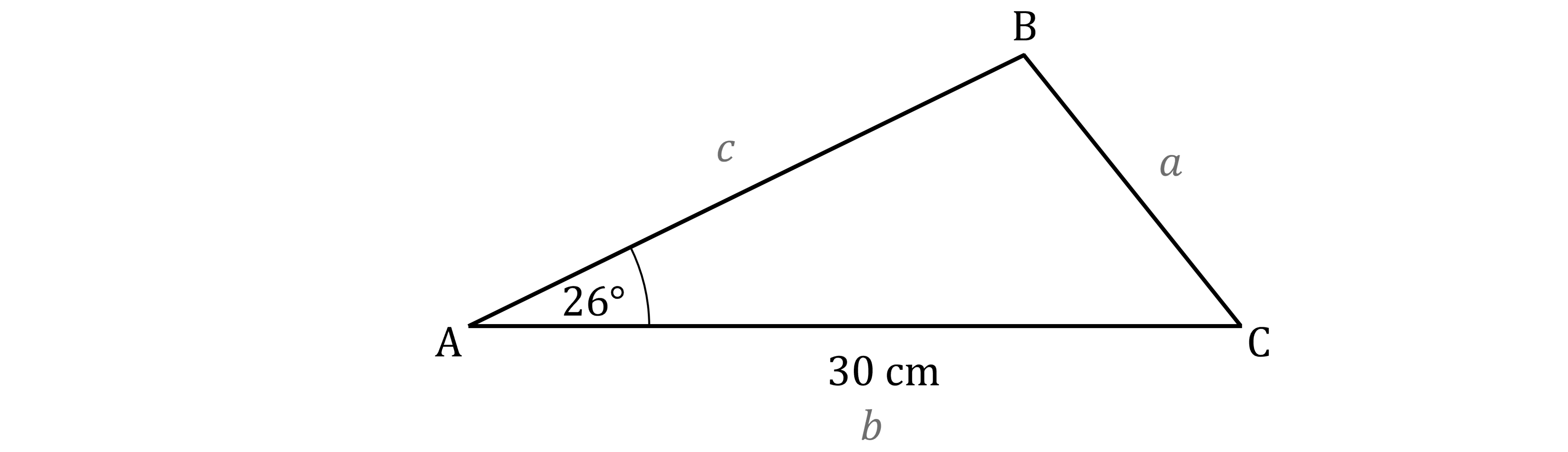
You want to find the length of c, and you know the area, the length of b and the angle at A
So swap the letters around in the Formulae List form of the triangle area formula to get
Substitute the known values into that equation
Rearrange to make c the subject
Round to a sensible degree of accuracy
Unless a question tells you otherwise, 3 significant figures is usually a good choice
24.3 cm (3 s.f.)

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
